はじめに
Python の NetworkX ライブラリを使い、Google Colab で試せるハンズオン形式のチュートリアルです。
必要なライブラリのインストール
以下を Google Colab 上で実行してください。
!pip install networkx
次に、必要なライブラリをインポートします。
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
Python のリスト・タプルからグラフを作る
エッジリストの例
# エッジリストの例(タプルのリスト)
edge_list = [
('A', 'B'),
('B', 'C'),
('C', 'D'),
('A', 'D')
]
# 無向グラフを作成
G1 = nx.Graph()
G1.add_edges_from(edge_list)
# グラフの可視化
nx.draw(G1, with_labels=True)
plt.show()
Pandas・CSV を用いたグラフ生成
CSV ファイルの例
以下は CSV ファイルを作成してエッジ情報を定義する例です。
import pandas as pd
# Google Colab 上での一時 CSV 作成例
csv_text = """source,target
A,B
B,C
C,D
D,A
A,E
"""
with open("edges.csv", "w") as f:
f.write(csv_text)
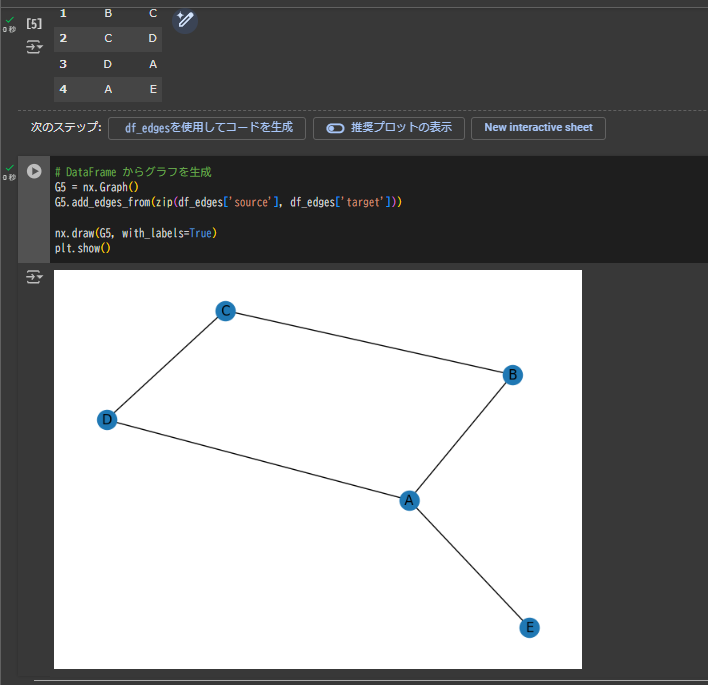
df_edges = pd.read_csv("edges.csv")
df_edges
CSV からグラフ生成
# DataFrame からグラフを生成
G5 = nx.Graph()
G5.add_edges_from(zip(df_edges['source'], df_edges['target']))
nx.draw(G5, with_labels=True)
plt.show()
まとめ
- NetworkX を使って、Python の基本データ構造や CSV ファイルからグラフを生成する方法を解説しました。
- Google Colab を使うことで簡単に可視化が可能です。
- ぜひ自身のデータを用いて試してみてください!
実装例: ノートブック
{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# \u3055\u307e\u3056\u307e\u306a\u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u751f\u6210\u65b9\u6cd5\uff1a\u30c7\u30fc\u30bf\u69cb\u9020\u3068 NetworkX \u306e\u9023\u643a\n",
"\n",
"Python \u306e NetworkX \u30e9\u30a4\u30d6\u30e9\u30ea\u3092\u4f7f\u3044\u3001Google Colab \u3067\u8a66\u305b\u308b\u30cf\u30f3\u30ba\u30aa\u30f3\u5f62\u5f0f\u306e\u30c1\u30e5\u30fc\u30c8\u30ea\u30a2\u30eb\u3067\u3059\u3002"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# \u5fc5\u8981\u306a\u30e9\u30a4\u30d6\u30e9\u30ea\u306e\u30a4\u30f3\u30b9\u30c8\u30fc\u30eb\n",
"!pip install networkx"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# \u5fc5\u8981\u306a\u30e9\u30a4\u30d6\u30e9\u30ea\u306e\u30a4\u30f3\u30dd\u30fc\u30c8\n",
"import networkx as nx\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"%matplotlib inline"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Python \u306e\u30ea\u30b9\u30c8\u30fb\u30bf\u30d7\u30eb\u304b\u3089\u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u3092\u4f5c\u308b"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# \u30a8\u30c3\u30b8\u30ea\u30b9\u30c8\u306e\u4f8b(\u30bf\u30d7\u30eb\u306e\u30ea\u30b9\u30c8)\n",
"edge_list = [\n",
" ('A', 'B'),\n",
" ('B', 'C'),\n",
" ('C', 'D'),\n",
" ('A', 'D')\n",
"]\n",
"\n",
"# \u7121\u5411\u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u3092\u4f5c\u6210\n",
"G1 = nx.Graph()\n",
"G1.add_edges_from(edge_list)\n",
"\n",
"# \u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u306e\u53ef\u8996\u5316\n",
"nx.draw(G1, with_labels=True)\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Pandas\u30fbCSV \u3092\u7528\u3044\u305f\u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u751f\u6210"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import pandas as pd\n",
"\n",
"# Google Colab \u4e0a\u3067\u306e\u4e00\u6642 CSV \u4f5c\u6210\u4f8b\n",
"csv_text = \"\"\"source,target\n",
"A,B\n",
"B,C\n",
"C,D\n",
"D,A\n",
"A,E\n",
"\"\"\"\n",
"\n",
"with open(\"edges.csv\", \"w\") as f:\n",
" f.write(csv_text)\n",
"\n",
"df_edges = pd.read_csv(\"edges.csv\")\n",
"df_edges"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# DataFrame \u304b\u3089\u30b0\u30e9\u30d5\u3092\u751f\u6210\n",
"G5 = nx.Graph()\n",
"G5.add_edges_from(zip(df_edges['source'], df_edges['target']))\n",
"\n",
"nx.draw(G5, with_labels=True)\n",
"plt.show()"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.8.16"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}