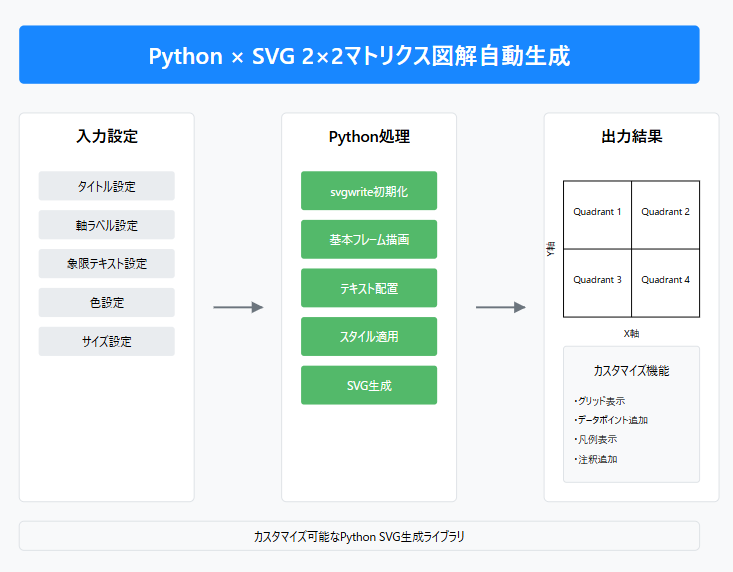
はじめに
ビジネス戦略の議論で頻繁に使用される2×2マトリクスを、Pythonを使って自動生成する方法をご紹介します。
必要なライブラリのインストール
pip install svgwrite
基本的な実装
import svgwrite
def create_2x2_matrix(filename, title, x_label, y_label, quadrant_labels):
# SVGの作成
dwg = svgwrite.Drawing(filename, size=('800px', '600px'))
# 背景色の設定
dwg.add(dwg.rect((0, 0), ('800px', '600px'), fill='white'))
# マトリクスの基本設定
margin = 50
width = 700
height = 500
# マトリクスの外枠を描画
dwg.add(dwg.rect((margin, margin), (width, height),
fill='none', stroke='black', stroke_width=2))
# 中央の十字線を描画
mid_x = margin + width/2
mid_y = margin + height/2
dwg.add(dwg.line((mid_x, margin), (mid_x, margin + height),
stroke='black', stroke_width=1))
dwg.add(dwg.line((margin, mid_y), (margin + width, mid_y),
stroke='black', stroke_width=1))
# タイトルを追加
dwg.add(dwg.text(title,
insert=(400, 30),
text_anchor="middle",
style="font-size:20px; font-weight:bold"))
# 軸ラベルを追加
dwg.add(dwg.text(x_label,
insert=(400, 580),
text_anchor="middle",
style="font-size:14px"))
# Y軸ラベル(回転)
y_label_group = dwg.g(transform="rotate(-90 20 300)")
y_label_group.add(dwg.text(y_label,
insert=(20, 300),
text_anchor="middle",
style="font-size:14px"))
dwg.add(y_label_group)
# 象限のラベルを追加
for position, label in quadrant_labels.items():
x = margin + (width * 0.25 if 'left' in position else width * 0.75)
y = margin + (height * 0.25 if 'bottom' in position else height * 0.75)
dwg.add(dwg.text(label,
insert=(x, y),
text_anchor="middle",
style="font-size:16px"))
# SVGを保存
dwg.save()
# BCGマトリクスの生成
def create_bcg_matrix():
quadrant_labels = {
'top_right': '花形\n(Star)',
'top_left': '問題児\n(Question Mark)',
'bottom_right': '金のなる木\n(Cash Cow)',
'bottom_left': '負け犬\n(Dog)'
}
create_2x2_matrix(
'bcg_matrix.svg',
'BCGマトリクス',
'相対的市場シェア →',
'市場成長率 →',
quadrant_labels
)
# SWOT分析の生成
def create_swot_matrix():
quadrant_labels = {
'top_right': 'Strengths\n(強み)',
'top_left': 'Opportunities\n(機会)',
'bottom_right': 'Weaknesses\n(弱み)',
'bottom_left': 'Threats\n(脅威)'
}
create_2x2_matrix(
'swot_matrix.svg',
'SWOT分析',
'内部要因 ← → 外部要因',
'プラス要因 ← → マイナス要因',
quadrant_labels
)
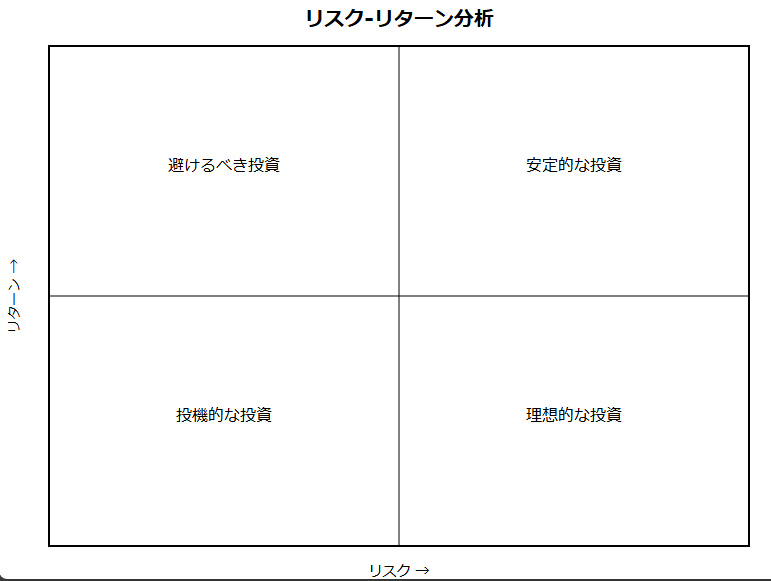
# リスク-リターン分析の生成
def create_risk_return_matrix():
quadrant_labels = {
'top_right': '理想的な投資',
'top_left': '投機的な投資',
'bottom_right': '安定的な投資',
'bottom_left': '避けるべき投資'
}
create_2x2_matrix(
'risk_return_matrix.svg',
'リスク-リターン分析',
'リスク →',
'リターン →',
quadrant_labels
)
# 使用例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 各マトリクスを生成
create_bcg_matrix()
create_swot_matrix()
create_risk_return_matrix()
実行結果の例
応用:カスタマイズ可能なバージョン
def create_custom_matrix(filename, config):
"""
カスタマイズ可能な2×2マトリクス生成関数
Parameters:
-----------
filename : str
出力するSVGファイルの名前
config : dict
マトリクスの設定情報を含む辞書
{
'title': str,
'x_label': str,
'y_label': str,
'quadrants': dict,
'colors': dict (optional),
'size': tuple (optional)
}
"""
# デフォルト値の設定
default_config = {
'size': ('800px', '600px'),
'colors': {
'background': 'white',
'border': 'black',
'text': 'black'
}
}
# 設定をマージ
config = {**default_config, **config}
# SVGの作成
dwg = svgwrite.Drawing(filename, size=config['size'])
# 実装は基本バージョンと同様...(省略)
return dwg
# 使用例
custom_config = {
'title': 'カスタムマトリクス',
'x_label': 'X軸 →',
'y_label': 'Y軸 →',
'quadrants': {
'top_right': 'Quadrant 1',
'top_left': 'Quadrant 2',
'bottom_right': 'Quadrant 3',
'bottom_left': 'Quadrant 4'
},
'colors': {
'background': '#f0f0f0',
'border': '#333333',
'text': '#000000'
},
'size': ('1000px', '800px')
}
create_custom_matrix('custom_matrix.svg', custom_config)
実行結果の例
まとめ
このコードを使用することで、以下のようなことが可能です:
- 基本的な2×2マトリクスの自動生成
- タイトルや軸ラベルのカスタマイズ
- 象限内のテキスト配置
- サイズや色のカスタマイズ
発展的な使い方
- データの可視化との組み合わせ:
def add_data_points(dwg, points, margin, width, height):
"""
マトリクス内にデータポイントを追加
"""
for point in points:
x = margin + (width * point['x'])
y = margin + (height * (1 - point['y']))
# ポイントを描画
dwg.add(dwg.circle(center=(x, y), r=5,
fill=point.get('color', 'red')))
# ラベルを追加
if 'label' in point:
dwg.add(dwg.text(point['label'],
insert=(x + 10, y),
style="font-size:12px"))
- アニメーションの追加:
def add_animation(dwg):
"""
SVGにアニメーション効果を追加
"""
style = """
@keyframes fade {
from { opacity: 0; }
to { opacity: 1; }
}
.animated {
animation: fade 2s;
}
"""
dwg.defs.add(dwg.style(style))
注意点
-
フォントの互換性:
- SVG内で使用するフォントは、表示環境によって異なる場合があります
- 重要な場合は、Web-safeフォントを使用するか、フォントを埋め込む必要があります
-
ファイルサイズ:
- 大量のデータポイントや複雑な図形を追加すると、ファイルサイズが大きくなる場合があります
- 必要に応じて最適化を検討してください
例: カレーの評価や分類のための2×2マトリクス
import svgwrite
def create_curry_matrix(filename):
"""カレーを評価するための2×2マトリクスを生成(改善版)"""
# SVGの基本設定
dwg = svgwrite.Drawing(filename, size=('800px', '600px'))
dwg.add(dwg.rect((0, 0), ('800px', '600px'), fill='#FFF8E7'))
# マトリクスの基本設定
margin = 50
width = 700
height = 500
# メインタイトル
dwg.add(dwg.text('カレー分析マトリクス',
insert=(400, 40),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=24,
font_weight="bold",
fill='#8B4513'))
# サブタイトル
dwg.add(dwg.text('価格帯と味の特徴による分類',
insert=(400, 70),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=16,
fill='#A0522D'))
# マトリクスの外枠
dwg.add(dwg.rect((margin, margin + 50), (width, height),
fill='none',
stroke='#8B4513',
stroke_width=2))
# 中央の十字線
mid_x = margin + width/2
mid_y = margin + height/2 + 50
dwg.add(dwg.line((mid_x, margin + 50), (mid_x, margin + height + 50),
stroke='#8B4513',
stroke_width=1))
dwg.add(dwg.line((margin, mid_y), (margin + width, mid_y),
stroke='#8B4513',
stroke_width=1))
# 象限の特徴を定義
quadrants = {
'top_right': {
'title': '贅沢スパイシー',
'items': [
'ハイエンドインド料理',
'高級スパイス使用',
'専門店の本格カレー',
'¥1,500〜'
]
},
'top_left': {
'title': '大衆派スパイシー',
'items': [
'大衆インド料理店',
'普通のスパイスカレー',
'エスニック系チェーン店',
'¥800〜1,500'
]
},
'bottom_right': {
'title': '贅沢まろやか',
'items': [
'高級欧風カレー',
'ホテルカレー',
'オリジナルブレンド',
'¥1,500〜'
]
},
'bottom_left': {
'title': '大衆派まろやか',
'items': [
'カレーチェーン店',
'ファミレスカレー',
'家庭的カレー',
'〜¥800'
]
}
}
def add_curry_icon(x, y, size=40):
"""改良版カレーアイコン"""
# アイコンの背景(円)
dwg.add(dwg.circle((x, y), size/2,
fill='#FFFFFF',
stroke='#8B4513',
stroke_width=1,
opacity=0.7))
# お皿(楕円)
dwg.add(dwg.ellipse((x, y), (size*0.8, size/3),
fill='#FFF',
stroke='#8B4513'))
# カレー(楕円)
dwg.add(dwg.ellipse((x, y-size/6), (size*0.7, size/4),
fill='#DAA520'))
# 軸ラベル(外側に配置)
dwg.add(dwg.text('価格帯 →',
insert=(400, margin + height + 90),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=16,
fill='#8B4513'))
# Y軸ラベル(回転、外側に配置)
y_label_group = dwg.g(transform=f"rotate(-90 25 {300})")
y_label_group.add(dwg.text('味の特徴(スパイシー度) →',
insert=(25, 300),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=16,
fill='#8B4513'))
dwg.add(y_label_group)
# 象限の描画(レイアウト改善)
positions = {
'top_right': (3/4, 1/4),
'top_left': (1/4, 1/4),
'bottom_right': (3/4, 3/4),
'bottom_left': (1/4, 3/4)
}
for position, content in quadrants.items():
x_ratio, y_ratio = positions[position]
x = margin + width * x_ratio
y = margin + height * y_ratio + 50
# アイコンを上部に配置
add_curry_icon(x, y - 60)
# タイトルをアイコンの下に配置
dwg.add(dwg.text(content['title'],
insert=(x, y - 20),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=16,
font_weight="bold",
fill='#8B4513'))
# 特徴リストをさらに下に配置
for i, item in enumerate(content['items']):
dwg.add(dwg.text(item,
insert=(x, y + 10 + i * 20),
text_anchor="middle",
font_size=12,
fill='#A0522D'))
# 凡例(下部に整理して配置)
legend_items = [
('価格帯', [
'〜¥800: リーズナブル',
'¥800〜1,500: スタンダード',
'¥1,500〜: プレミアム'
]),
('スパイシー度', [
'まろやか: 日本人向け味付け',
'スパイシー: 本格的スパイス使用'
])
]
legend_y = margin + height + 120
for i, (title, items) in enumerate(legend_items):
x = margin + i * 350
# 凡例タイトルの背景
dwg.add(dwg.rect((x-5, legend_y-15), (120, 20),
fill='#FFFFFF',
stroke='#8B4513',
stroke_width=1,
opacity=0.7))
# 凡例タイトル
dwg.add(dwg.text(title,
insert=(x, legend_y),
font_size=14,
font_weight="bold",
fill='#8B4513'))
# 凡例アイテム
for j, item in enumerate(items):
dwg.add(dwg.text(item,
insert=(x, legend_y + 20 + j * 20),
font_size=12,
fill='#A0522D'))
# SVGを保存
dwg.save()
# マトリクスを生成
create_curry_matrix('curry_matrix_improved.svg')