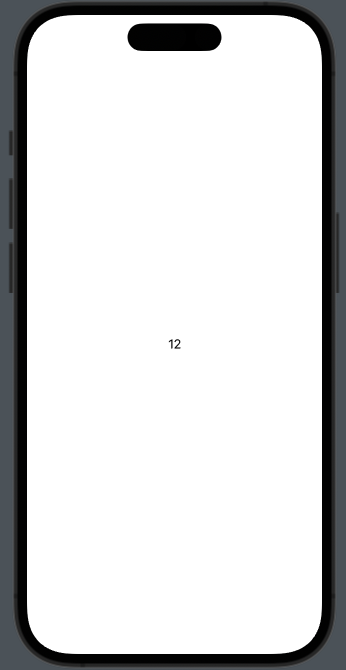
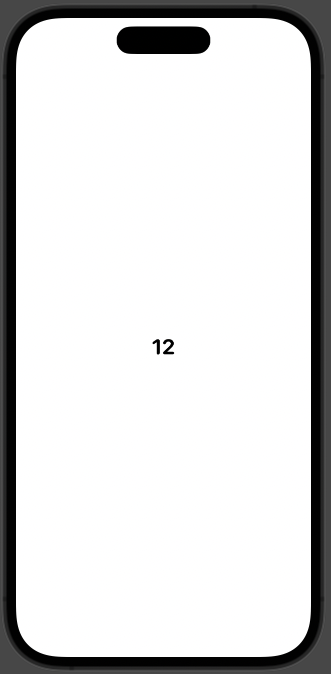
Layoutプロトコルに準拠した構造体を独自に定義すれば、
Viewのコレクションの配置をカスタムすることができる。
これを使って、Viewを円形に配置し、時計の文字盤を作ってみる。
placeSubviewsの挙動を理解する
まずはLayoutに準拠した、RadialLayoutを定義して、
ただのテキストを囲ってみる
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
}
}
boundsはRadialLayoutが占有する画面の領域。この場合だと画面全体。
subviewsはRadialLayoutに渡されたViewの配列。この場合だとText("12")が入った配列。
placeメソッドで座標を指定すれば、その要素は指定した座標に描画される。
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
subviews[0].place(at: CGPoint(x: 50, y: 50), proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
画面の中心を取得するには、以下のようにする。
(わかりやすいように、文字も大きく太くした)
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
subviews[0].place(at: CGPoint(x: bounds.midX, y: bounds.midY), proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
画面の中心は取得できたが、これでは要素の左上が画面の中心に配置されただけ。
要素の中心を画面の中心に配置するには、anchorを指定する。
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
subviews[0].place(at: CGPoint(x: bounds.midX, y: bounds.midY), anchor: .center, proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
CGPointのapplyingメソッドを使えば、軸を回転させることができる。
(0度)
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
let angle = Angle.degrees(0.0).radians
var point = CGPoint(x: 0, y: -100)
.applying(CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: angle))
point.x += bounds.midX
point.y += bounds.midY
subviews[0].place(at: point, anchor: .center, proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
(90度)
struct Clock: View {
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
Text("12")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
let angle = Angle.degrees(90.0).radians
var point = CGPoint(x: 0, y: -100)
.applying(CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: angle))
point.x += bounds.midX
point.y += bounds.midY
subviews[0].place(at: point, anchor: .center, proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
あとはこれを動的にやればOK
動的に配置する
1~12のテキストをRadialLayoutに渡す
subviewをfor文で回して、indexによって角度を変える。
struct Clock: View {
let numbers = [12, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
var body: some View {
RadialLayout {
ForEach(numbers, id: \.self) { item in
Text("\(item)")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
for (index, subview) in subviews.enumerated() {
let radius = bounds.width / 3.0
let angle = Angle.degrees(360.0 / Double(subviews.count)).radians
var point = CGPoint(x: 0, y: -radius)
.applying(CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: angle * Double(index)))
point.x += bounds.midX
point.y += bounds.midY
subview.place(at: point, anchor: .center, proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
}
いろいろ付け加えていい感じにする
struct Clock: View {
let numbers = [12, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
var body: some View {
ZStack {
RadialLayout {
ForEach(numbers, id: \.self) { item in
Text("\(item)")
.font(.system(.title, design: .rounded)).bold()
}
}
.frame(width: 240)
RadialLayout {
ForEach(numbers, id: \.self) { item in
Text("\(item * 5)")
.font(.system(.caption, design: .rounded))
}
}
.frame(width: 360)
Circle()
.strokeBorder(style: StrokeStyle(lineWidth: 10, dash: [1, 10]))
.frame(width: 220)
}
}
}
struct RadialLayout: Layout {
func sizeThatFits(proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) -> CGSize {
proposal.replacingUnspecifiedDimensions()
}
func placeSubviews(in bounds: CGRect, proposal: ProposedViewSize, subviews: Subviews, cache: inout ()) {
for (index, subview) in subviews.enumerated() {
let radius = bounds.width / 3.0
let angle = Angle.degrees(360.0 / Double(subviews.count)).radians
var point = CGPoint(x: 0, y: -radius)
.applying(CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: angle * Double(index)))
point.x += bounds.midX
point.y += bounds.midY
subview.place(at: point, anchor: .center, proposal: .unspecified)
}
}
}