はじめに
DatabricksのML Quickstartやっていきます
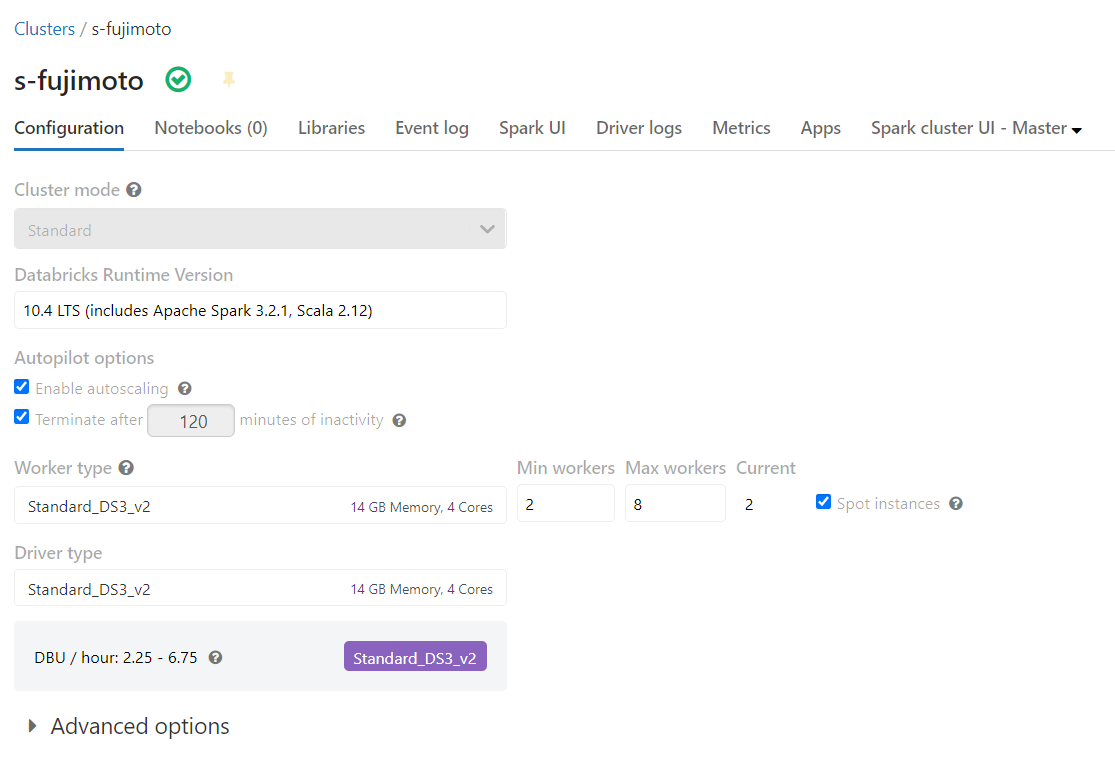
開発環境
10.4 LTS ML, Standard_NC6s_v3(※クォータ制限の緩和申請が必要です)
実装
1.Azure Databricksで新しいノートブックを作成する
2.ライブラリのインストール
%pip install mlflow
%pip install numpy
%pip install pandas
%pip install scikit-learn
%pip install hyperopt
3.ライブラリのインポート
import mlflow
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.metrics
import sklearn.model_selection
import sklearn.ensemble
from hyperopt import fmin, tpe, hp, SparkTrials, Trials, STATUS_OK
from hyperopt.pyll import scope
4.ワインのクオリティデータセットをダウンロード
Wine Quality Dataset
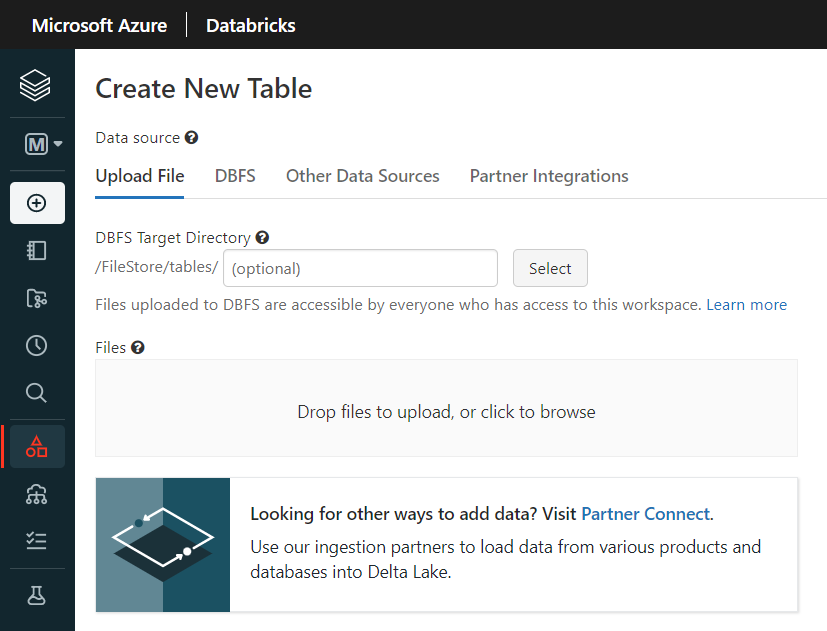
5.Create Tableから、winequality-white.csvとwinequality-red.csvをアップロード
6.データセットの読み込み
white_wine = pd.read_csv("/dbfs/FileStore/tables/winequality_white.csv", sep=';')
red_wine = pd.read_csv("/dbfs/FileStore/tables/winequality_red.csv", sep=';')
white_wine['is_red'] = 0.0
red_wine['is_red'] = 1.0
data_df = pd.concat([white_wine, red_wine], axis=0)
# Define classification labels based on the wine quality
data_labels = data_df['quality'] >= 7
data_df = data_df.drop(['quality'], axis=1)
# Split 80/20 train-test
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(
data_df,
data_labels,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=1
)
7.autologgingの有効化
# Enable MLflow autologging for this notebook
mlflow.autolog()
JavaPackageがないと怒られました(10.4 LTS MLで実行した場合、怒られませんでした)
2022/04/12 15:46:01 INFO mlflow.tracking.fluent: Autologging successfully enabled for sklearn.
2022/04/12 15:46:01 WARNING mlflow.utils.autologging_utils: Encountered unexpected error during spark autologging: Exception while attempting to initialize JVM-side state for Spark datasource autologging. Please create a new Spark session and ensure you have the mlflow-spark JAR attached to your Spark session as described in http://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html#automatic-logging-from-spark-experimental. Exception:
'JavaPackage' object is not callable
2022/04/12 15:46:01 WARNING mlflow.tracking.fluent: Exception raised while enabling autologging for pyspark: Exception while attempting to initialize JVM-side state for Spark datasource autologging. Please create a new Spark session and ensure you have the mlflow-spark JAR attached to your Spark session as described in http://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html#automatic-logging-from-spark-experimental. Exception:
'JavaPackage' object is not callable
2022/04/12 15:46:01 WARNING mlflow.utils.autologging_utils: Encountered unexpected error during spark autologging: Exception while attempting to initialize JVM-side state for Spark datasource autologging. Please create a new Spark session and ensure you have the mlflow-spark JAR attached to your Spark session as described in http://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html#automatic-logging-from-spark-experimental. Exception:
'JavaPackage' object is not callable
2022/04/12 15:46:01 INFO mlflow.tracking.fluent: Autologging successfully enabled for pyspark.ml.
8.MLFlowを開始
with mlflow.start_run(run_name='gradient_boost') as run:
model = sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
# Models, parameters, and training metrics are tracked automatically
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
predicted_probs = model.predict_proba(X_test)
roc_auc = sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, predicted_probs[:,1])
# The AUC score on test data is not automatically logged, so log it manually
mlflow.log_metric("test_auc", roc_auc)
print("Test AUC of: {}".format(roc_auc))
Test AUC of: 0.8834365701533531
9.n_estimatorsを追加して再度MLFlowを実行
# Start a new run and assign a run_name for future reference
with mlflow.start_run(run_name='gradient_boost') as run:
model_2 = sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(
random_state=0,
# Try a new parameter setting for n_estimators
n_estimators=200,
)
model_2.fit(X_train, y_train)
predicted_probs = model_2.predict_proba(X_test)
roc_auc = sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, predicted_probs[:,1])
mlflow.log_metric("test_auc", roc_auc)
print("Test AUC of: {}".format(roc_auc))
Test AUC of: 0.8914761673151751
10.別のノートブックやジョブから利用できる
# After a model has been logged, you can load it in different notebooks or jobs
# mlflow.pyfunc.load_model makes model prediction available under a common API
model_loaded = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(
'runs:/{run_id}/model'.format(
run_id=run.info.run_id
)
)
predictions_loaded = model_loaded.predict(X_test)
predictions_original = model_2.predict(X_test)
# The loaded model should match the original
assert(np.array_equal(predictions_loaded, predictions_original))
11.ハイパーパラメータチューニング
# Define the search space to explore
search_space = {
'n_estimators': scope.int(hp.quniform('n_estimators', 20, 1000, 1)),
'learning_rate': hp.loguniform('learning_rate', -3, 0),
'max_depth': scope.int(hp.quniform('max_depth', 2, 5, 1)),
}
def train_model(params):
# Enable autologging on each worker
mlflow.autolog()
with mlflow.start_run(nested=True):
model_hp = sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(
random_state=0,
**params
)
model_hp.fit(X_train, y_train)
predicted_probs = model_hp.predict_proba(X_test)
# Tune based on the test AUC
# In production settings, you could use a separate validation set instead
roc_auc = sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, predicted_probs[:,1])
mlflow.log_metric('test_auc', roc_auc)
# Set the loss to -1*auc_score so fmin maximizes the auc_score
return {'status': STATUS_OK, 'loss': -1*roc_auc}
# SparkTrials distributes the tuning using Spark workers
# Greater parallelism speeds processing, but each hyperparameter trial has less information from other trials
# On smaller clusters or Databricks Community Edition try setting parallelism=2
spark_trials = SparkTrials(
parallelism=8
)
with mlflow.start_run(run_name='gb_hyperopt') as run:
# Use hyperopt to find the parameters yielding the highest AUC
best_params = fmin(
fn=train_model,
space=search_space,
algo=tpe.suggest,
max_evals=32,
trials=spark_trials)
12.ベストスコアのモデルで実行
# Sort runs by their test auc; in case of ties, use the most recent run
best_run = mlflow.search_runs(
order_by=['metrics.test_auc DESC', 'start_time DESC'],
max_results=10,
).iloc[0]
print('Best Run')
print('AUC: {}'.format(best_run["metrics.test_auc"]))
print('Num Estimators: {}'.format(best_run["params.n_estimators"]))
print('Max Depth: {}'.format(best_run["params.max_depth"]))
print('Learning Rate: {}'.format(best_run["params.learning_rate"]))
best_model_pyfunc = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(
'runs:/{run_id}/model'.format(
run_id=best_run.run_id
)
)
best_model_predictions = best_model_pyfunc.predict(X_test[:5])
print("Test Predictions: {}".format(best_model_predictions))
Best Run
AUC: 0.9142824444953079
Num Estimators: 782
Max Depth: 5
Learning Rate: 0.08908078790759665
Test Predictions: [False False False True False]
お疲れ様でした。
参考文献
10 分間のチュートリアル:Azure Databricks での機械学習の概要
Azure Databricks での機械学習の概要
ノートブック(Databricks ML Quickstart: Model Training)