Swiftのソートアルゴリズムを読んでみた。だけ。
(2016年7月8日お昼頃までのコミットのソースを読んでます)
Swiftのソートというと sort とか sortInPlace である。では具体的に何ソートをしているかというと、イントロソートである。
イントロソートの具体的な実装については
https://github.com/apple/swift/blob/5d1af107a33cb2459258524bf8a858d30e2906d3/stdlib/public/core/Sort.swift.gyb
を読むと分かる。
↑で実装されたイントロソートは
https://github.com/apple/swift/blob/6ef62f3c7357caa288bc97ba320b9c1a5dec51d8/stdlib/public/core/CollectionAlgorithms.swift.gyb
で呼び出されているっぽい。
以下、Sort.swift.gybについて。
そもそも.swift.gybについて
Swiftの実装の一部はSwiftそのものだが、ほとんど同じ実装になるものについては.swift.gybファイル中でPythonまじりで書かれている。
def cmp(a, b, p)
%{
def cmp(a, b, p):
if p:
return "isOrderedBefore(" + a + ", " + b + ")"
else:
return "(" + a + " < " + b + ")"
}%
// Generate two versions of sorting functions: one with an explicitly passed
// predicate 'isOrderedBefore' and the other for Comparable types that don't
// need such a predicate.
定番のcompare。 isOrderedBefore は sort や sortInPlace の引数で渡されるもの↓
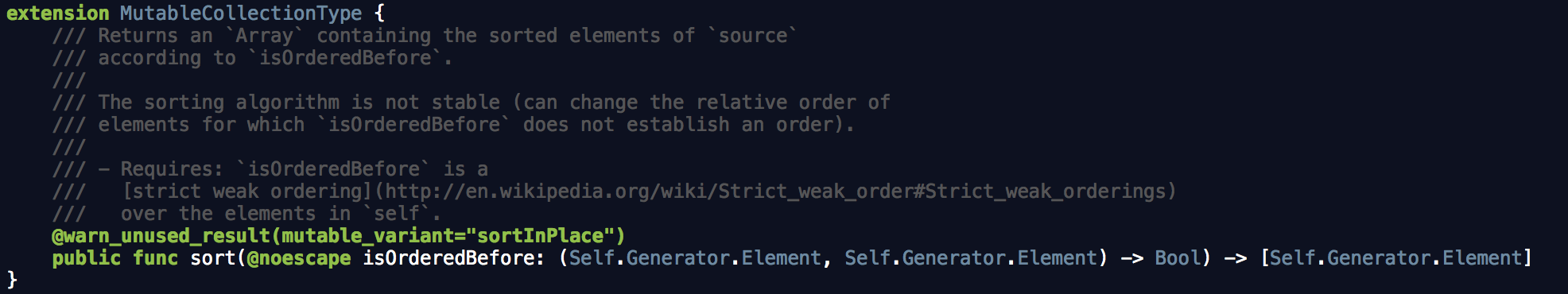
各種ソート
% preds = [True, False]
% for p in preds:
# 略
% end
により、 略 の位置にある
- 挿入ソート
func _insertionSort<C>
- クイックソート
func _partition<C>
- イントロソート
func _introSort<C>func _introSortImpl<C>
- ヒープソート
func _siftDown<C>func _heapify<C>func _heapSort<C>
のそれぞれについて True 版と False 版の2つを作る。正確に言うと、 isOrderedBefore 有り版と無し版を両方生成する。たぶん。
func _insertionSort<C>
挿入ソート。
func _insertionSort<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, BidirectionalCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
if !range.isEmpty {
let start = range.lowerBound
// Keep track of the end of the initial sequence of sorted
// elements.
var sortedEnd = start
// One element is trivially already-sorted, thus pre-increment
// Continue until the sorted elements cover the whole sequence
elements.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
while sortedEnd != range.upperBound {
// get the first unsorted element
let x: C.Iterator.Element = elements[sortedEnd]
// Look backwards for x's position in the sorted sequence,
// moving elements forward to make room.
var i = sortedEnd
repeat {
let predecessor: C.Iterator.Element = elements[elements.index(before: i)]
// if x doesn't belong before y, we've found its position
if !${cmp("x", "predecessor", p)} {
break
}
// Move y forward
elements[i] = predecessor
elements.formIndex(before: &i)
} while i != start
if i != sortedEnd {
// Plop x into position
elements[i] = x
}
elements.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
}
}
}
func _partition<C>
たぶんクイックソートのこと。
func _partition<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) -> C.Index
where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
var lo = range.lowerBound
var hi = range.upperBound
if lo == hi {
return lo
}
// The first element is the pivot.
let pivot = elements[range.lowerBound]
// Loop invariants:
// * lo < hi
// * elements[i] < pivot, for i in range.lowerBound+1..lo
// * pivot <= elements[i] for i in hi..range.upperBound
Loop: while true {
FindLo: repeat {
elements.formIndex(after: &lo)
while lo != hi {
if !${cmp("elements[lo]", "pivot", p)} { break FindLo }
elements.formIndex(after: &lo)
}
break Loop
} while false
FindHi: repeat {
elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
while hi != lo {
if ${cmp("elements[hi]", "pivot", p)} { break FindHi }
elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
}
break Loop
} while false
swap(&elements[lo], &elements[hi])
}
elements.formIndex(before: &lo)
if lo != range.lowerBound {
// swap the pivot into place
swap(&elements[lo], &elements[range.lowerBound])
}
return lo
}
introSort
イントロソート。再帰のレベルによって使用するソートを切り替える。そのため、イントロソートの実装は func _introSort<C> と func _introSortImpl<C> の2つで行っている。
コメント中にあるpsファイルは考案者であるDavid R Musserさんの論文。
func _introSort<C>
public // @testable
func _introSort<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
% if p:
var isOrderedBeforeVar = isOrderedBefore
% end
let count =
elements.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound).toIntMax()
if count < 2 {
return
}
// Set max recursion depth to 2*floor(log(N)), as suggested in the introsort
// paper: http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~musser/gp/introsort.ps
let depthLimit = 2 * _floorLog2(Int64(count))
_introSortImpl(
&elements,
subRange: range,
${"isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBeforeVar," if p else ""}
depthLimit: depthLimit)
}
func _introSortImpl<C>
- 基本はクイックソート。
- 20未満の距離の範囲では挿入ソートを行う。
- クイックソートをした分だけ再帰レベルの値が減っていく。レベル0になったらヒープソートで済ます。
func _introSortImpl<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""},
depthLimit: Int
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
// Insertion sort is better at handling smaller regions.
if elements.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound) < 20 {
_insertionSort(
&elements,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
return
}
if depthLimit == 0 {
_heapSort(
&elements,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
return
}
// Partition and sort.
// We don't check the depthLimit variable for underflow because this variable
// is always greater than zero (see check above).
let partIdx: C.Index = _partition(
&elements,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
_introSortImpl(
&elements,
subRange: range.lowerBound..<partIdx,
${"isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore, " if p else ""}
depthLimit: depthLimit &- 1)
_introSortImpl(
&elements,
subRange: (elements.index(after: partIdx))..<range.upperBound,
${"isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore, " if p else ""}
depthLimit: depthLimit &- 1)
}
heapSort
ヒープソート。ヒープソートなので、_siftDownと_heapifyがある。
func _siftDown<C>
siftDownとは、ヒープ構造からルートを削除する操作である。ってwikipedia先生が言ってた。 left と right を比較したのち、ルートである index と差し替えているのがわかる。
func _siftDown<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
index: C.Index,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
let countToIndex = elements.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: index)
let countFromIndex = elements.distance(from: index, to: range.upperBound)
// Check if left child is within bounds. If not, return, because there are
// no children of the given node in the heap.
if countToIndex + 1 >= countFromIndex {
return
}
let left = elements.index(index, offsetBy: countToIndex + 1)
var largest = index
if ${cmp("elements[largest]", "elements[left]", p)} {
largest = left
}
// Check if right child is also within bounds before trying to examine it.
if countToIndex + 2 < countFromIndex {
let right = elements.index(after: left)
if ${cmp("elements[largest]", "elements[right]", p)} {
largest = right
}
}
// If a child is bigger than the current node, swap them and continue sifting
// down.
if largest != index {
swap(&elements[index], &elements[largest])
_siftDown(
&elements,
index: largest,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
}
}
func _heapify<C>
ヒープ構造を作る。コメントにある通り、2分木において、親ノードの値が子ノードの値より大きいようなやつ。
func _heapify<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
// Here we build a heap starting from the lowest nodes and moving to the root.
// On every step we sift down the current node to obey the max-heap property:
// parent >= max(leftChild, rightChild)
//
// We skip the rightmost half of the array, because these nodes don't have
// any children.
let root = range.lowerBound
var node = elements.index(
root,
offsetBy: elements.distance(
from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound) / 2)
while node != root {
elements.formIndex(before: &node)
_siftDown(
&elements,
index: node,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
}
}
func _heapSort<C>
_heapifyでヒープを作った後、_siftDownとswapを繰り返す。ヒープ構造が空になったら終わり。
func _heapSort<C>(
_ elements: inout C,
subRange range: Range<C.Index>
${", isOrderedBefore: inout (C.Iterator.Element, C.Iterator.Element) -> Bool" if p else ""}
) where
C : protocol<MutableCollection, RandomAccessCollection>
${"" if p else ", C.Iterator.Element : Comparable"} {
var hi = range.upperBound
let lo = range.lowerBound
_heapify(
&elements,
subRange: range
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
while hi != lo {
swap(&elements[lo], &elements[hi])
_siftDown(
&elements,
index: lo,
subRange: lo..<hi
${", isOrderedBefore: &isOrderedBefore" if p else ""})
elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
}
}
func swap<T>
定番のswap。
対象の a と b は互いに同じところを参照していないとか、 retain / release がないよう最適化しているとか。
/// Exchange the values of `a` and `b`.
///
/// - Precondition: `a` and `b` do not alias each other.
public func swap<T>(_ a: inout T, _ b: inout T) {
// Semantically equivalent to (a, b) = (b, a).
// Microoptimized to avoid retain/release traffic.
let p1 = Builtin.addressof(&a)
let p2 = Builtin.addressof(&b)
_debugPrecondition(
p1 != p2,
"swapping a location with itself is not supported")
// Take from P1.
let tmp: T = Builtin.take(p1)
// Transfer P2 into P1.
Builtin.initialize(Builtin.take(p2) as T, p1)
// Initialize P2.
Builtin.initialize(tmp, p2)
}
まとめ
3種のソートでイントロソートでした。