Introduction
Unity provides brilliant framework to apply RL to the game object.
In this article, I would like Unity-chan to learn walking to the target object using Tensorflow.
Procedure
- Finish the basic "Get started project" of 3DBall
- Finish this tutorial about how to create your own game from scratch
- Get Unity-chan
- Place Unity-chan onto the plane.
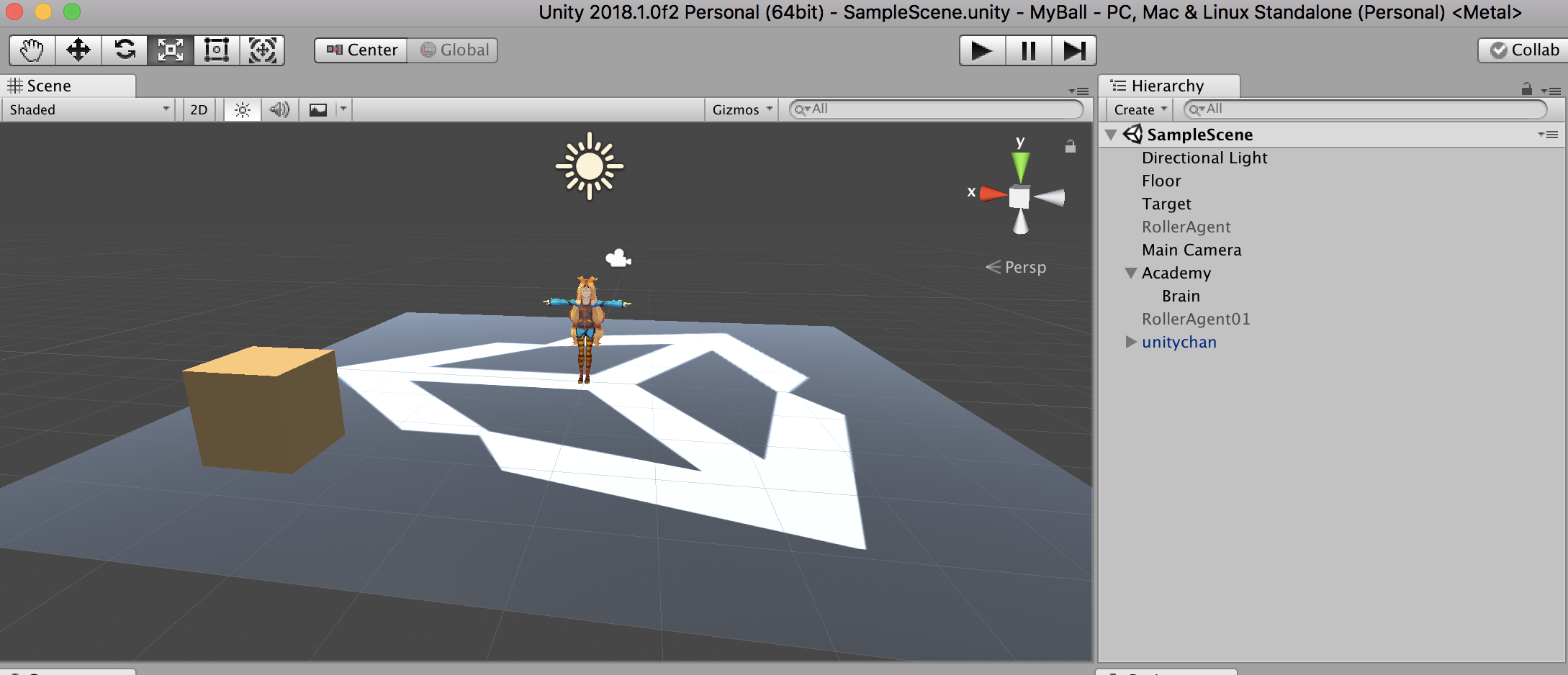
- Create animator controller.
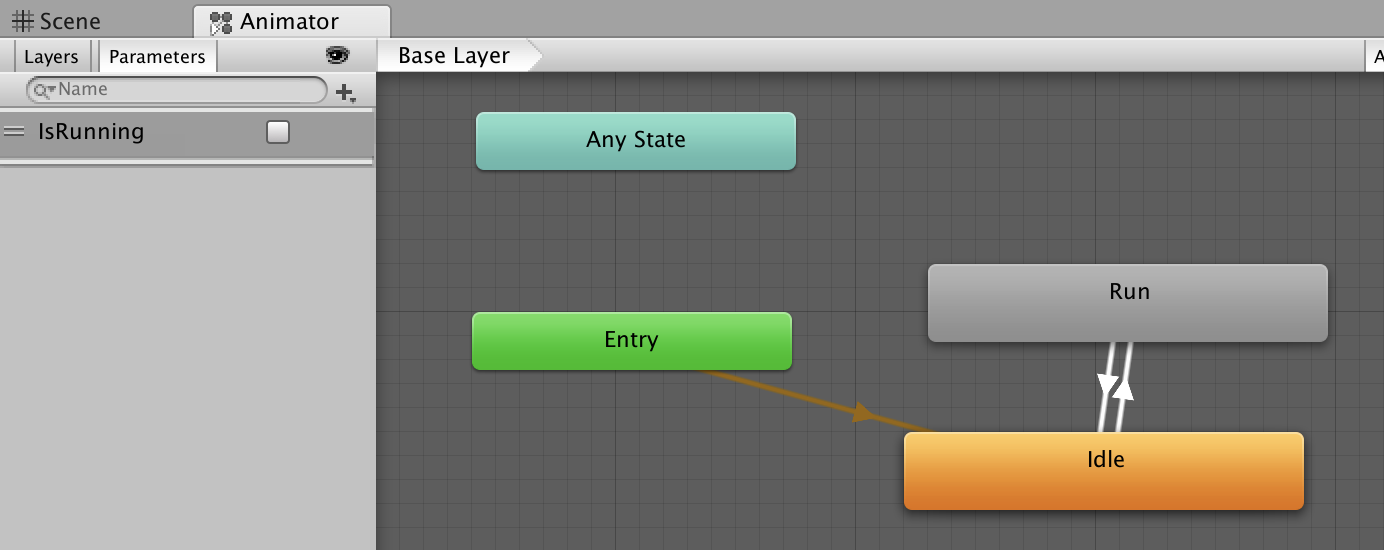
- Set the parameter "IsRunning" true to the transition from "idle" to "run".
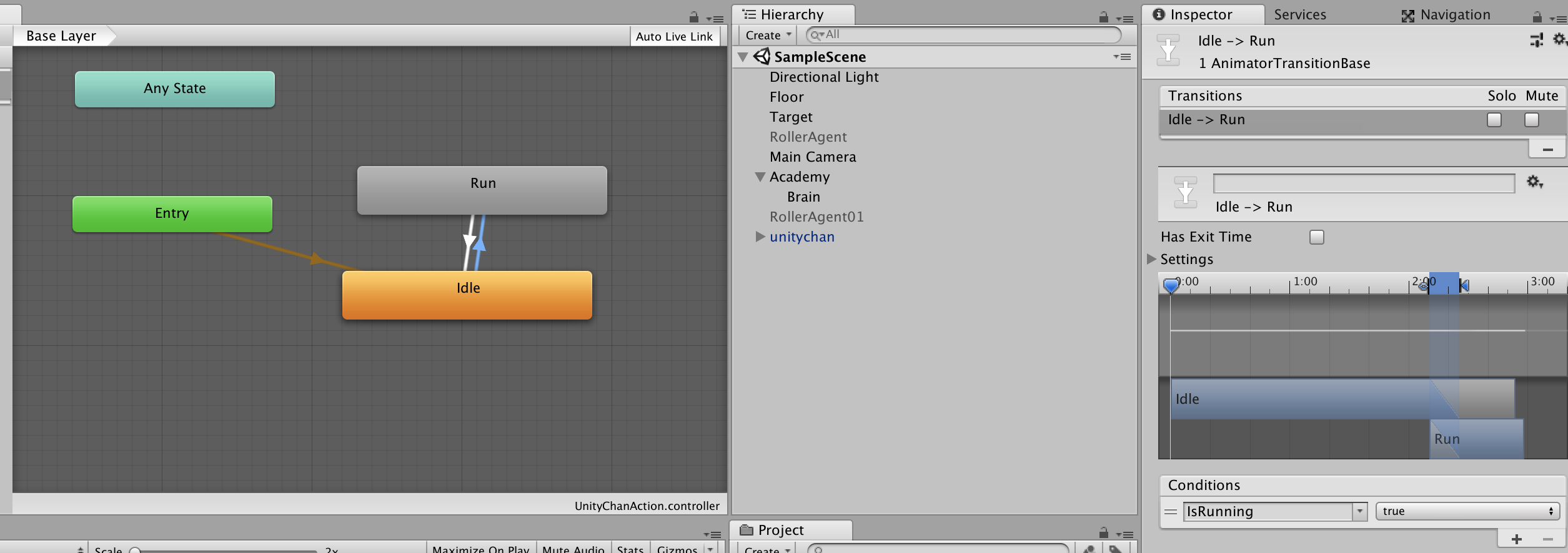 7. Set the parameter "IsRunning" false to the transition from "idle" to "run".
8.
7. Set the parameter "IsRunning" false to the transition from "idle" to "run".
8.  9. Set this animator controller to Unity-chan.
10. Create Script name "Controller" in C#.
9. Set this animator controller to Unity-chan.
10. Create Script name "Controller" in C#.
Controller.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using MLAgents;
public class Controller : Agent {
Rigidbody rb;
public float speed = 2f;
public float thrust = 100;
private Animator animator;
bool ground;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
rb = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
animator = GetComponent<Animator>();
}
public void goRight(){
rb.velocity = new Vector3(speed, 0, 0);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 90, 0);
animator.SetBool("IsRunning", true);
}
public void goLeft()
{
rb.velocity = new Vector3(-speed, 0, 0);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 270, 0);
animator.SetBool("IsRunning", true);
}
public void goUp()
{
rb.velocity = new Vector3(0, 0, speed);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 0);
animator.SetBool("IsRunning", true);
}
public void goDown()
{
rb.velocity = new Vector3(0, 0, -speed);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 180, 0);
animator.SetBool("IsRunning", true);
}
private void OnCollisionStay(Collision collision)
{
ground = true;
}
public void DecisionMaker(int data){
Debug.Log(data);
if(data == 1){
goRight();
} else if(data == 2){
goLeft();
} else if(data == 3){
goUp();
} else {
goDown();
}
}
public Transform Target;
public override void AgentReset()
{
if (this.transform.position.y < -1.0)
{
this.transform.position = Vector3.zero;
this.rb.angularVelocity = Vector3.zero;
this.rb.velocity = Vector3.zero;
}
else
{
Target.position = new Vector3(Random.value * 8 - 4,
0.5f,
Random.value * 8 - 4);
}
}
public override void CollectObservations()
{
Vector3 relativePosition = Target.position - this.transform.position;
AddVectorObs(relativePosition.x / 5);
AddVectorObs(relativePosition.z / 5);
AddVectorObs((this.transform.position.x + 5) / 5);
AddVectorObs((this.transform.position.x - 5) / 5);
AddVectorObs((this.transform.position.z + 5) / 5);
AddVectorObs((this.transform.position.z - 5) / 5);
AddVectorObs(rb.velocity.x / 5);
AddVectorObs(rb.velocity.z / 5);
}
private float previousDistance = float.MaxValue;
public override void AgentAction(float[] vectorAction, string textAction)
{
float distanceToTarget = Vector3.Distance(this.transform.position, Target.position);
if (distanceToTarget < 1.42f)
{
AddReward(1.0f);
Done();
}
if (distanceToTarget < previousDistance)
{
AddReward(0.1f);
}
AddReward(-0.05f);
if (this.transform.position.y < -1.0)
{
AddReward(-1.0f);
Done();
}
previousDistance = distanceToTarget;
// vectorAction contains a discrete value.
DecisionMaker(System.Convert.ToInt32(vectorAction.GetValue(0)));
}
}
- Then follow the same direction as we did in the tutorial
Command
python3 learn.py --run-id=<run-identifier> --train
Demo
License
© UTJ/UCL
