はじめに
本記事では多層パーセプトロンをFlux.jlで定義し,そのモデルでMNISTを学習する.
パラメータを学習したモデルを保存し,FluxJS.jlで使うことを目的とした記事です.
ニューラルネットの知識は最低限で大丈夫です.
MNISTのデータを読み込んで多層パーセプトロンで学習する.
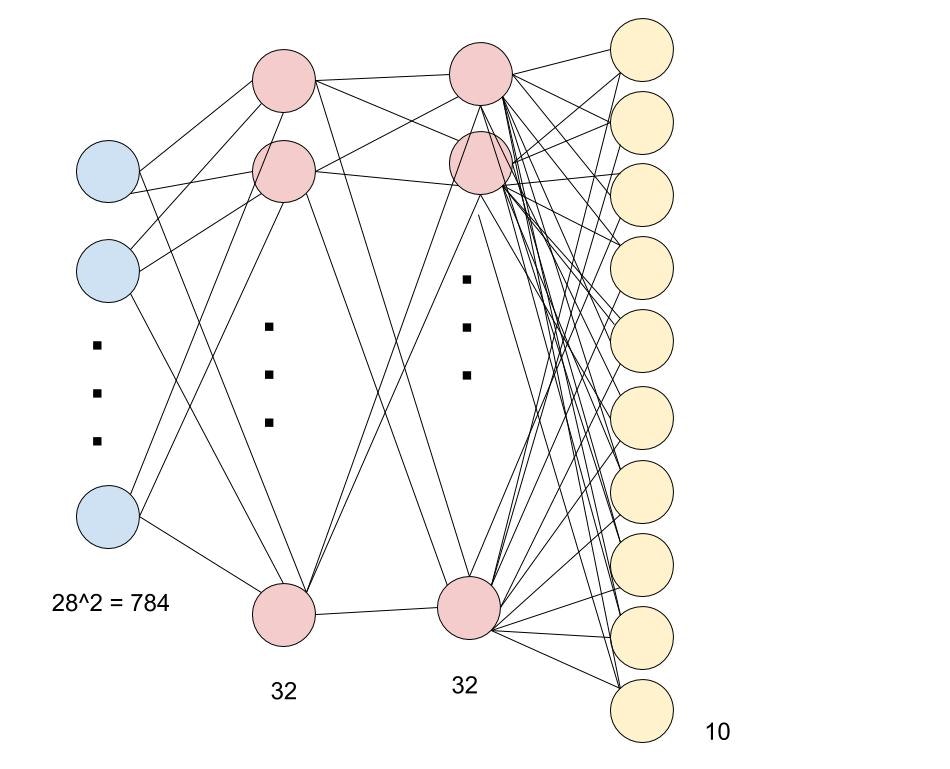
MLPのモデルは以下になります.
モデルの説明としてはMNISTは数字の画像集合である.
一つの画像のサイズは28×28つまり28^2=784これが入力層になるわけである.
そして隠れ層は32層が2つ,出力層は10個のニューロンをもつ.冗長だが説明すると数字は0~9で10種類.
なので10個の出力層をもつわけである.
using Flux, Flux.Data.MNIST, Statistics
using Flux: @epochs, mse, onehotbatch, onecold
using Random
using Base.Iterators: partition
using BSON: @load, @save
imgs = MNIST.images(:train)
train_X = hcat(float.(vec.(imgs))...)
labels = MNIST.labels(:train)
train_Y = onehotbatch(labels,0:9)
batchsize = 64
train_dataset = ([(train_X[:,batch] ,train_Y[:,batch]) for batch in partition(1:size(train_Y)[2],batchsize)])
# 全結合
# つまりニューロンが下のニューロンと全射になっていることである.
model = Chain(
Dense(28^2, 32, relu),
Dense(32, 32, relu),
Dense(32, 10),
softmax)
loss(x, y) = mse(model(x), y)
opt = ADAM(params(model))
@epochs 100 Flux.train!(loss, train_dataset, opt)
# モデルの保存
pretrained = model |> cpu
weights = Tracker.data.(params(pretrained))
@save "pretrained.bson" pretrained
@save "weights.bson" weights
println("Finished to train")
予測
function prepare_dataset(;train=true)
train_or_test = ifelse(train,:train,:test)
imgs = MNIST.images(train_or_test)
X = hcat(float.(vec.(imgs))...)
labels = MNIST.labels(train_or_test)
Y = onehotbatch(labels,0:9)
return X, Y
end
function split_dataset_random(X, Y)
divide_ratio=0.9
shuffled_indices = shuffle(1:size(Y)[2])
divide_idx = round(Int,0.9*length(shuffled_indices))
train_indices = shuffled_indices[1:divide_idx]
val_indices = shuffled_indices[divide_idx:end]
train_X = X[:,train_indices]
train_Y = Y[:,train_indices]
val_X = X[:,val_indices]
val_Y = Y[:,val_indices]
return train_X, train_Y, val_X, val_Y
end
function predict()
println("Start to evaluate testset")
println("loading pretrained model")
@load "pretrained.bson" pretrained
model = pretrained |> cpu
accuracy(x, y) = mean(onecold(model(x)) .== onecold(y))
println("prepare dataset")
X, Y = prepare_dataset(train=false)
X = X |> cpu
Y = Y |> cpu
@show accuracy(X, Y)
println("Done")
end
predict()
出力
Start to evaluate testset
loading pretrained model
prepare dataset
accuracy(X, Y) = 0.9691
Done
FluxJS.jl
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs@0.9.0"></script>
<script src="bson.js"></script>
<script src="flux.js"></script> <!-- Or embed the script directly -->
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
let model = (function () {
let math = tf;
function model(kinkajou) {
return kinkajou;
};
model.weights = [];
return model;
})();
flux.fetchWeights("pretrained.bson").then((function (ws) {
return model.weights = ws;
}));
</script>
</body>
</html>
ミソはFlux.jlで作ったモデルをtensorflow.jsで使えるということです.
参考
@SatoshiTerasaki さん 「Julia 1.0 + FluxでMNIST学習」
https://qiita.com/SatoshiTerasaki/items/0f772caba3a1bc6ceae4
ソースコード
全体のソースコードはこちらにあります.
https://github.com/Ooshita/mlp_flux
最後に
MNISTのデータの読み込みが凄いめんどくさい.なんとかならないのでしょうかね.
でも,慣れれば自由度は高いライブラリなので,PyTorch以上に,楽しいツールではあると思います.