はじめに
音声特徴量抽出ソフトウェアとしてopenSMILEやPraatなどが有名だが,近年のDeepLearningの流行もあり,少々扱いにくい部分もある.
そこで,今回はPython上で特徴量抽出が完結するSurfboardを紹介する.
※Pythonの音声分析ライブラリとしてlibrosaやpysptkなどが有名だが,本ライブラリはそれらには含まれていない特徴量もあるので参考にしてもらえればよいと思う.
Surfboardとは?
Novoic社が発表した音声特徴量抽出ライブラリ.
主に医療領域の研究を行っている会社らしい.
Paper: Surfboard: Audio Feature Extraction for Modern Machine Learning
GitHub: https://github.com/novoic/surfboard
以下論文よりアブストを引用.
We introduce Surfboard, an open-source Python library forextracting audio features with application to the medical do-main. Surfboard is written with the aim of addressing painpoints of existing libraries and facilitating joint use with mod-ern machine learning frameworks. The package can be accessedboth programmatically in Python and via its command line in-terface, allowing it to be easily integrated within machinelearn-ing workflows. It builds on state-of-the-art audio analysispack-ages and offers multiprocessing support for processing largeworkloads. We review similar frameworks and describe Surf-board’s architecture, including the clinical motivation for itsfeatures. Using the mPower dataset, we illustrate Surfboard’sapplication to a Parkinson’s disease classification task, high-lighting common pitfalls in existing research. The source codeis opened up to the research community to facilitate future audioresearch in the clinical domain.
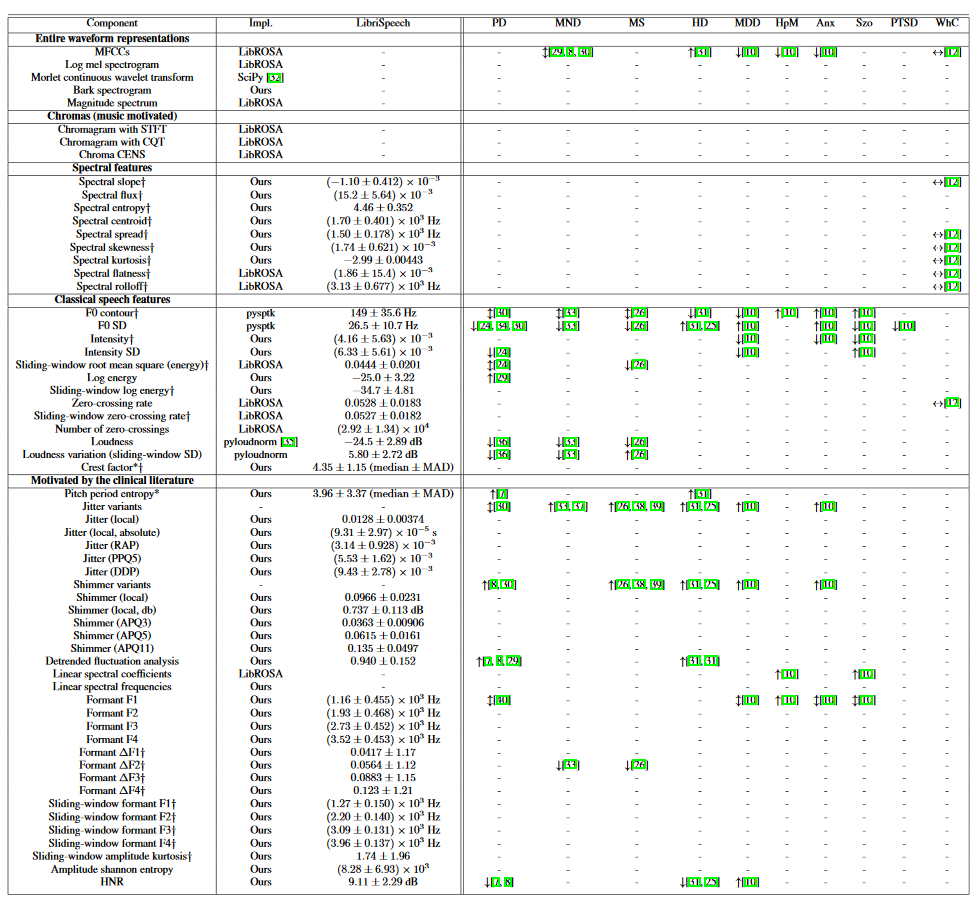
Surfboardで用意されている特徴量
論文より図を引用.
一番左側のComponentの列が特徴量,左から2番目のImpl.の列が実装元を示してある.
他の情報については論文を参照してほしい.
動作手順
では実際にどのように使用するのか,または使いやすいのかを以下で確認する.
※仮想環境推奨
e.g. Virtualenv, Docker, Singularity, etc...
実行環境
OS: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
CPU: i7-8700K CPU @ 3.70GHz
メモリ: 32GB
Python version: 3.6.9
Surfboard version: 0.2.0
1. 必要なパッケージ&ライブラリをインストール
sudo apt-get install libsndfile1-dev
pip3 install surfboard # latest version(2020/11/10現在は0.2.0)
pip3 install surfboard==0.2.0 # version指定用
2. 実行例
ここでは用意されているメソッドを適当にピックアップして実行する.
なお特徴量の詳細について,ここでは説明しない.
(ググったらいっぱい出てくるので,今更感が...ただ実行例の後半については説明を加えるかも)
音声の読み込み
surfboard.sound.Waveform(path=None, signal=None, sample_rate=44100)
>>> from surfboard.sound import Waveform
>>> sound = Waveform(path="input.wav", sample_rate=44100)
>>> sound
<surfboard.sound.Waveform object at 0x7f5d5a496630>
MFCC
mfcc(n_mfcc=13, n_fft_seconds=0.04, hop_length_seconds=0.01)
>>> mfccs = sound.mfcc()
>>> mfccs
array([[-5.9755945e+02, -5.9204047e+02, -5.9595471e+02, ...,
-5.9232190e+02, -6.0794177e+02, -6.8430023e+02],
[ 1.0296422e+02, 1.0394064e+02, 9.9498421e+01, ...,
1.0660390e+02, 1.1549076e+02, 8.2798584e+01],
[ 3.3768288e+01, 3.1600494e+01, 3.0664955e+01, ...,
1.9380785e+01, 1.6547699e+01, 2.9088814e+01],
...,
[-1.5465357e+00, -6.0288420e+00, -7.3418264e+00, ...,
-1.1875109e+01, -4.9084020e+00, -1.7681698e+00],
[-2.0479255e+00, -6.1789474e+00, -4.2426043e+00, ...,
-5.0735850e+00, -4.5268564e+00, -1.3781363e-01],
[-9.6166210e+00, -1.5932017e+01, -8.2316790e+00, ...,
-2.9154425e+00, 2.3177078e-01, -2.3197366e-02]], dtype=float32)
>>> mfccs.shape
(13, 251)
Log mel spectrogram
log_melspec(n_mels=128, n_fft_seconds=0.04, hop_length_seconds=0.01)
>>> log_mel_spec = sound.log_melspec()
>>> log_mel_spec
array([[-44.61756 , -49.462692, -51.023216, ..., -53.39418 , -51.823517,
-59.717033],
[-47.49347 , -49.678703, -48.11801 , ..., -52.568924, -51.97367 ,
-60.11091 ],
[-62.110283, -49.851852, -46.291267, ..., -51.796555, -52.07287 ,
-60.496307],
...,
[-72.22576 , -74.225525, -75.74116 , ..., -80. , -80. ,
-80. ],
[-75.85294 , -77.76551 , -75.66461 , ..., -80. , -80. ,
-80. ],
[-77.79902 , -76.97334 , -76.3596 , ..., -80. , -80. ,
-80. ]], dtype=float32)
>>> log_mel_spec.shape
(128, 251)
Magnitude spectrum
magnitude_spectrum(n_fft_seconds=0.04, hop_length_seconds=0.01)
>>> mag_spec = sound.magnitude_spectrum()
>>> mag_spec
array([[1.84691831e-01, 1.19033001e-01, 2.84719190e-05, ...,
8.66711214e-02, 6.99108988e-02, 2.52321120e-02],
[1.42162636e-01, 8.13821033e-02, 6.79990128e-02, ...,
5.17552570e-02, 6.20137081e-02, 2.49926206e-02],
[1.88411046e-02, 7.72730559e-02, 1.16427965e-01, ...,
6.17721789e-02, 5.98379932e-02, 2.26884745e-02],
...,
[1.00823166e-03, 9.13982571e-04, 9.08253191e-04, ...,
1.17852981e-03, 7.16711569e-04, 2.36942826e-04],
[2.61519599e-04, 9.38822108e-04, 3.16031976e-04, ...,
4.44596924e-04, 6.49552734e-04, 2.54548184e-04],
[7.14944093e-04, 8.84590496e-04, 1.49172614e-03, ...,
9.47592314e-04, 8.35590414e-04, 7.54383451e-04]], dtype=float32)
>>> mag_spec.shape
(257, 251)
Shimmer
shimmers(max_a_factor=1.6, p_floor=0.0001, p_ceil=0.02, max_p_factor=1.3)
>>> shimmers = sound.shimmers()
>>> shimmers
{'localShimmer': 0.12885916134577777, 'localdbShimmer': 0.7139508204315516, 'apq3Shimmer': 0.06556241042381906, 'apq5Shimmer': 0.23042452340218883, 'apq11Shimmer': 0.7440287411060755}
Jitter
jitters(p_floor=0.0001, p_ceil=0.02, max_p_factor=1.3)
>>> jitters = sound.jitters()
>>> jitters
{'localJitter': 0.019661538782247998, 'localabsoluteJitter': 9.918096659472624e-05, 'rapJitter': 0.004236280859121549, 'ppq5Jitter': 0.007349282515463625, 'ddpJitter': 0.012708842577364697}
Formant
formants()
>>> formants = sound.formants()
>>> formants
{'f1': 1598.7638894106142, 'f2': 2671.048125793429, 'f3': 3869.8610696529854, 'f4': 4427.027666549306}
Harmonics-to-Noise Ratio
hnr()
>>> hnrs = sound.hnr()
>>> hnrs
3.412263760552974
Zero-crossing rate
zerocrossing()
>>> zcrs = sound.zerocrossing()
>>> zcrs
{'num_zerocrossings': 3520, 'zerocrossing_rate': 0.10989010989010989}
より詳しく知りたい人は以下のページを参照してみると良い.
https://surfboard.readthedocs.io/en/latest/waveform.html
まとめ
- Surfboardという音声特徴量抽出ライブラリを紹介し,簡単な使い方をまとめた.
- JitterやShimmerはopenSMILEでもあったが,Pythonライブラリとして簡単に抽出できるのは良いと思った.
- ただ,n_fftとhop_lengthの引数については秒単位なのでそこは注意が必要(librosaなどはsample数)
- 他にも多くのメソッドが用意されているので興味があれば手を動かしてみよう.
参考サイト&論文
Praat: doing phonetics by computer
praat : jitter
openSMILE
機械学習のための音声の特徴量ざっくりメモ (Librosa ,numpy)
Speech Emotion Recognition with deep learning
Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Network and ExtremeLearning Machine