最近流行りの機械学習なんかをやりたいとき、Pythonで環境構築って大変ですよね。
ローカルの環境も汚れますし...。
コードを動かしながら機械学習を学べる教材などではAnacondaやMinicondaを使っているものをよく見ます。
そしてこれらの環境を作るとき、ROSユーザーは割と困ることが多いんですが、意外と記事が少なかったりするのでここに残すことにしました。環境は以下のとおりです。
- Ubuntu18.04
- Python3.6
- Miniconda
Minicondaのインストール
ここからPython3.7の64bit版をダウンロード
$ cd ~/Downloads
$ bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
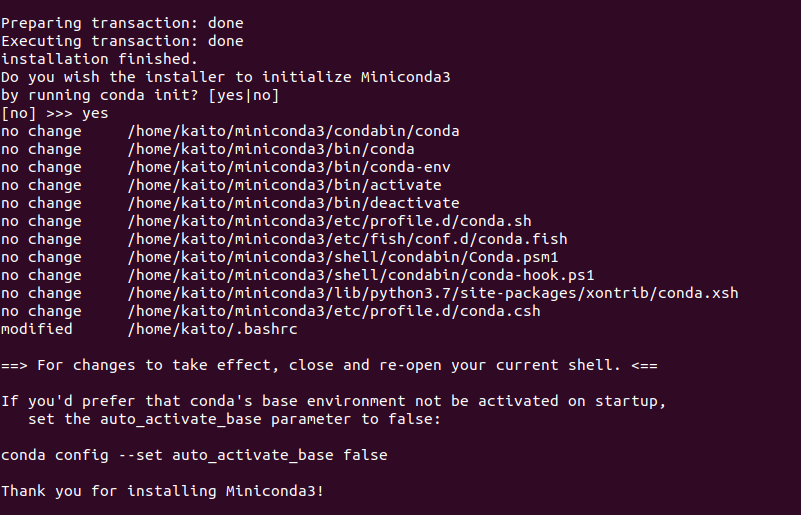
上のコマンドを実行し、端末の指示にしたがってインストールを進めます。
最後に conda initを実行するか聞かれるので、yesと答えれば環境構築は終了となります。
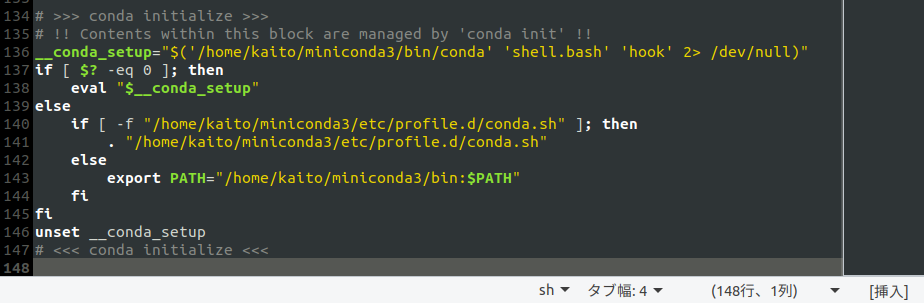
正常にインストールできた場合、conda initの実行で何が起きるのかは以下をご覧ください。
.bashrcが編集されるようなので、中身を一応確認してきましょう。
追記されたのは以下の部分です。
ここで注意!
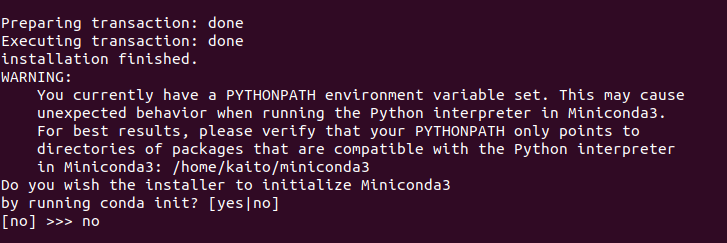
.bashrcでROSの読み込みを行っている場合、conda initのときに以下のようなワーニングが出ます。
ROSの環境を読み込んでいると、PYTHONPATHが/opt/ros/melodic/lib/python2.7/dist-packagesを指すようになっているからですね。
なので、インストール前にはROSの読み込みを無効にしておきましょう。
condaを用いてROSの環境構築
以下のコマンドを打つだけ
$ conda create --name ros --channel conda-forge ros-core ros-actionlib ros-dynamic-reconfigure python=2.7
$ conda activate ros
これだけで、condaの仮想環境上にROSの環境ができるのって便利ですね。
roscoreやrosrun、roslaunchなどの基本コマンドは使えます。
自作パッケージ
condaを使った仮想環境上でROSを動かす上で気になるのは自作パッケージです。
今回はROS1を使っているのでC++でパッケージなどを作成すると、catkin_makeが必要になります。
https://github.com/nakano16180/roscpp_practice
上記リンクのパッケージを今回使用しました。
はまった点
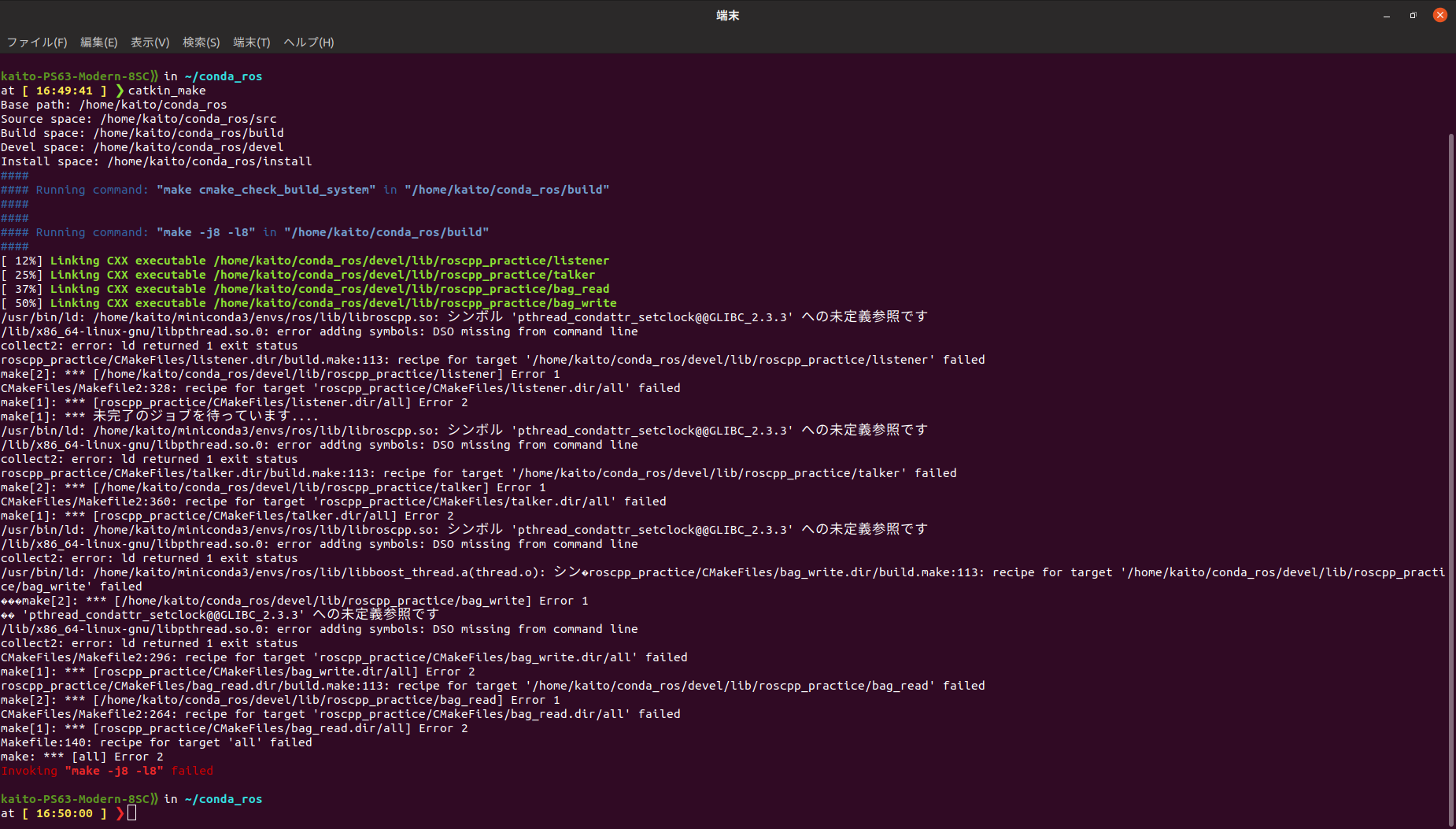
本来ならば、githubのパッケージをcloneしてcatkin_makeすればrosrunで起動することができます。
しかし今回はまったのはこちら。pthreadへのパスが通っていない模様?
これを解決するために、CMakeLists.txtを以下のように編集しました。
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
project(roscpp_practice)
## Compile as C++11, supported in ROS Kinetic and newer
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
## Find catkin macros and libraries
## if COMPONENTS list like find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS xyz)
## is used, also find other catkin packages
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
std_msgs
rosbag
)
## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)
find_package(Threads REQUIRED) # ここ追記
## Uncomment this if the package has a setup.py. This macro ensures
## modules and global scripts declared therein get installed
## See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/user_guide/setup_dot_py.html
# catkin_python_setup()
###########
## Build ##
###########
## Specify additional locations of header files
## Your package locations should be listed before other locations
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
## Declare a C++ library
# add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
# src/${PROJECT_NAME}/roscpp_practice.cpp
# )
## Add cmake target dependencies of the library
## as an example, code may need to be generated before libraries
## either from message generation or dynamic reconfigure
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Declare a C++ executable
## With catkin_make all packages are built within a single CMake context
## The recommended prefix ensures that target names across packages don't collide
# add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}_node src/roscpp_practice_node.cpp)
add_executable(talker src/talker.cpp)
add_executable(listener src/listener.cpp)
add_executable(bag_write src/bag_write.cpp)
add_executable(bag_read src/bag_read.cpp)
## Rename C++ executable without prefix
## The above recommended prefix causes long target names, the following renames the
## target back to the shorter version for ease of user use
## e.g. "rosrun someones_pkg node" instead of "rosrun someones_pkg someones_pkg_node"
# set_target_properties(${PROJECT_NAME}_node PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME node PREFIX "")
## Add cmake target dependencies of the executable
## same as for the library above
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME}_node ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Specify libraries to link a library or executable target against
# target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}_node
# ${catkin_LIBRARIES}
# )
target_link_libraries(talker
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
Threads::Threads ##追記
)
target_link_libraries(listener
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
Threads::Threads ##追記
)
target_link_libraries(bag_write
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
Threads::Threads ##追記
)
target_link_libraries(bag_read
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
Threads::Threads ##追記
)
以上のように編集してやることで無事、buildして実行することができました。
最後に
ここまで書いといてなんですが、Python3系が使えるROS2に早く移行しましょう!