TakeAway
背景・理由
立派なプログラマーになるためにThink Javaを学びます。
#リソース
Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist
Allen B. Downey https://www.amazon.co.jp/dp/1492072508/ref=cm_sw_r_tw_dp_THGFFJFBXVVCYQ54R9ES
但し書き エクササイズ主にThink Javaの前のバージョンを使います。
https://books.trinket.io/thinkjava/
注
2eのテキストを使ったもの。
chap 4
chap 5
chap1
語彙
problem solving:
hardware:
processor:
memory:
statement:
print statement:
method:
class:
comment:
high-level language:
low-level language:
portable:
compile:
source code:
object code:
executable:
virtual machine:
byte code:
string:
newline:
escape sequence:
algorithm:
computer science:
bug:
debugging:
プログラムソース
一瞥して良しとした。
https://github.com/ChrisMayfield/ThinkJavaCode2/tree/master/ch01
ex 1_2
エクササイズ
ex 1_1
1
a statement → 実行する
comment → 実行しない。
2
portable
The ability of a program to run on more than one kind of computer
3
〈文書・抜粋資料などを〉1冊にまとめる,編集する
4
Another name for object code that is ready to run on specific hardware.
Because of name is name.
package thinkJava2;
public class ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// this is my first Program
System.out.println("Hello World");
System.out.println("Again");
}
}
chap2
語彙
variable:
value:
type:
declaration:
assignment:
initialize:
state:
memory diagram:
operator:
operand:
expression:
floating-point:
rounding error:
order of operations:
compile-time error:
parse:
logic error:
プログラムソース
public class FloatingPoint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double pi;
pi = 3.14159;
double minute3 = 59.0;
System.out.print("Fraction of the hour that has passed: ");
System.out.println(minute3 / 60.0);
double y = 1.0 / 3.0; // correct
System.out.println(0.1 * 10);
System.out.println(0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1
+ 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1);
double balance = 123.45; // potential rounding error
int balance2 = 12345; // total number of cents
}
}
public class StringConcat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1 + 2 + "Hello");
// the output is 3Hello
System.out.println("Hello" + 1 + 2);
// the output is Hello12
}
}
ソリューション
//
// Date.java
// ThinkJava-Chapter2
//
// Created by Apollo Zhu on 7/20/16.
// Copyright © 2015-2016 WWITDC. All rights reserved.
//
public class Date{
public static void main(String args[]){
String day = "Wednesday", month = "July";
int date = 20, year = 2016;
System.out.println("American format:");
System.out.println(day + ", " + month + " " + date + ", " + year);
System.out.println("European format:");
System.out.println(day + " " + date + " " + month + " " + year);
}
}
//
// Time.java
// ThinkJava-Chapter2
//
// Created by Apollo Zhu on 7/20/16.
// Copyright © 2015-2016 WWITDC WWITDC. All rights reserved.
//
public class Time{
public static void main(String args[]){
int timeOfDayInSeconds = 24 * 60 * 60;
int hour = 18, minute = 58, second = 10;
int timeSinceMidnightInSeconds = hour * 3600 + minute * 60 + second;
int timeLeftInSeconds = timeOfDayInSeconds - timeSinceMidnightInSeconds;
int startHour = 18, startMinute = 45, startSecond = 36;
int startTimeSinceMidnightInSeconds = startHour * 3600 + startMinute * 60 + startSecond; //in seconds
int timeInterval = timeSinceMidnightInSeconds - startTimeSinceMidnightInSeconds;
System.out.println("Time since midnight: " + timeSinceMidnightInSeconds + " seconds");
System.out.println("Time remaining today: " + timeLeftInSeconds + " seconds");
System.out.println("Percentage of day passed: " + (double)timeSinceMidnightInSeconds / (double)(24 * 60 *60) +"%");
System.out.println("Elapsed time: " + timeInterval + " seconds");
}
}
chap3
問題全部できて良かったと思う。テストプログラムを取り入れたせいもあるかも。
語彙
package:
address:
library:
import statement:
token:
literal:
prompt:
magic number:
constant:
format specifier:
stack trace:
type cast:
modulo:
modulus:
##ソリューション
ex3_1
下記のような現象が起こります。
Exception in thread "main" java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException: f != java.lang.Integer
10.0 = Exception in thread "main" java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException: d != java.lang.Double
java: シンボルを見つけられません
ex3_2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ex3_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please write temperature (Celsius?)");
double clss = in.nextDouble();
double fhrnht = convertsTemperatureFromCelsius(clss);
System.out.printf("%.1f C = %.1f F\n", clss, fhrnht);
}
public static double convertsTemperatureFromCelsius(double clss) {
double fhrnht = clss * 9/5 + 32;
return fhrnht;
}
}
ex3_3
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ex3_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int h = 0;
int minutes = 0;
int second = 0;
int[] array = {h, minutes, second};
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please write second");
int bSeconds= in.nextInt();
array = convertsTotalNumberOfSecondsToHoursMinutesSeconds(bSeconds);
//"5000 seconds = 1 hours, 23 minutes, and 20 seconds".
System.out.printf("%d seconds = %d hours, %d minutes, and %d seconds\n", bSeconds, array[0], array[1], array[2]);
}
public static int[] convertsTotalNumberOfSecondsToHoursMinutesSeconds(int bSecond) {
int h = 0;
int m = 0;
int s = 0;
int[] array = {h, m, s};
h = bSecond / 60 / 60;
s = bSecond % 60;
m = (bSecond - h * 60 * 60 - s) / 60;
array[0] = h;
array[1] = m;
array[2] = s;
return array;
}
}
ex3_4
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ex3_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("I'm thinking of a number between 1 and 100");
System.out.println("(including both). Can you guess what it is?");
System.out.println("Type a number:");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = in.nextInt();
int guessMyNumber = guessMyNumber();
int off = 0;
System.out.printf("Your guess is:%d\n", number);
System.out.printf("I was thinking of is:%d\n", guessMyNumber);
if (number > guessMyNumber){
off = number - guessMyNumber;
}
if (number < guessMyNumber){
off = guessMyNumber - number;
}
if (guessMyNumber == number){
off = 0;
}
System.out.printf("You were off by:%d\n", off);
}
public static int guessMyNumber() {
// pick a random number
Random random = new Random();
int number = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
return number;
}
}
chap4
命名規則
ローワーキャメルケース → メソッド名に使用
アッパーキャメルケース クラス名に使用
語彙
void:
invoke:
flow of execution:
argument:
parameter:
parameter passing:
local variable:
stack diagram:
frame:
scope:
composition:
return type:
return value:
stub:
##ソリューション
ex4_1
package ex4;
public class ex4_1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
printAmerican("Wednesday", "July", 20, 2016);
printEuropean("Wednesday", "July", 20, 2016);
}
private static void printAmerican(String day, String month, int date, int year) {
System.out.println("American format:");
System.out.println(day + ", " + month + " " + date + ", " + year);
}
private static void printEuropean(String day, String month, int date, int year) {
System.out.println("European format:");
System.out.println(day + " " + date + " " + month + " " + year);
}
}
ex4_2
1.
ans → 5行目
2.
ans → 15行目
3.
ans → rattle
4.
ex4_3
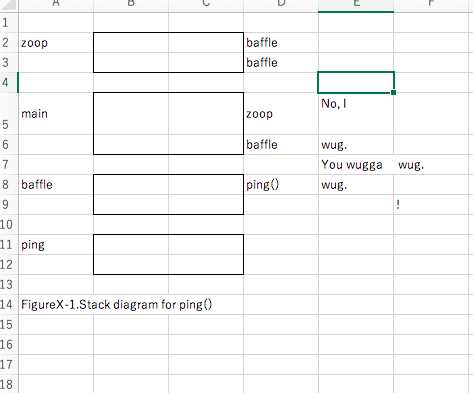
ex4_4
1.
コンパイルできません。
以下のようなエラーメッセージが出ます。
java: シンボルを見つけられません
2.
コンパイルできません。
以下のようなエラーメッセージが出ます。
java: 文ではありません
ex4_4

chap5
語彙
boolean:
relational operator:
conditional statement:
block:
branch:
chaining:
nesting:
logical operator:
short circuit:
De Morgan’s laws:
flag:
validate:
hacker:
NaN:
ex5_1
省略
ex5_2省略
ublic class ex5_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("I'm thinking of a number between 1 and 100");
System.out.println("(including both). Can you guess what it is?");
System.out.println("Type a number:");
int time = 0;
int off = 0;
getOff(off, time);
}
public static void getOff(int off, int time) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int guessMyNumber = guessMyNumber();
int number = in.nextInt();
System.out.printf("Your guess is:%d\n", number);
System.out.printf("I was thinking of is:%d\n", guessMyNumber);
if (number > guessMyNumber && time < 3) {
off = number - guessMyNumber;
System.out.printf("the guess is too high %d\n", off);
off = 0;
time += 1;
if (time < 3) {
getOff(off, time);
}
}
if (number < guessMyNumber) {
off = guessMyNumber - number;
System.out.printf("the guess is too low %d\n", off);
off = 0;
time += 1;
if (time < 3) {
getOff(off, time);
}
}
if (guessMyNumber == number) {
System.out.println("the guess is correct");
}
}
public static int guessMyNumber() {
// pick a random number
Random random = new Random();
int number = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
return number;
}
}
public class ex5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(1,1,1,3);
}
public static void method(int a, int b, int c, int n) {
if (!(n <= 2))
{
boolean b1;
if ((int) Math.pow(a, n) + (int) Math.pow(b, n) == (int) Math.pow(c, n)) b1 = true;
else b1 = false;
if (b1){
System.out.println("Holy smokes, Fermat was wrong!");
}else{
System.out.println("No, that doesn’t work.");
}
}
}
}
ex5_4
表現 結果
yes == no || grade > amount true
amount == 40.0 || 50.0 error
hiVal != loVal || loVal < 0 true
True || hello.length() > 0 true
hello.isEmpty() && yes false
grade <= 100 && !false true
!yes || no false
grade > 75 > amount error
amount <= hiVal && amount >= loVal true
no && !no || yes && !yes false
ex5_5
true
true
ping!
pong
ex5_6
package ex5;
public class ex5_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
int c = 1;
double[] root = method(a, b, c);
if (root.equals(null)) {
System.out.println("Test");
}
}
public static double[] method(int a, int b, int c) {
double root1 = 0.0;
double root2 = 0.0;
int determinant = b * b - 4 * a * c;
if (2 * a != 0) {
if (determinant > 0) {
root1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(determinant)) / 2 * a;
root2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(determinant)) / 2 * a;
System.out.printf("root1 = %.2f and root2 = %.2f\n", root1, root2);
} else if (determinant == 0) {
root1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(determinant)) / 2 * a;
root2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(determinant)) / 2 * a;
System.out.printf("root1 = root2 = %.2f\n", root1);
} else {
System.out.printf("invalid input. %d,%d,%d\n", a, b, c);
double[] root = {999.0};
return root;
}
} else {
System.out.printf("invalid input. %d,%d,%d\n", a, b, c);
double[] root = {999.0};
return root;
}
double root[] = {root1, root2};
return root;
}
}
package ex5;
public class ex5_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Test");
//Display an error if any of the lengths are negative or zero.
int a = 3;
int b = 4;
int c = 5;
String answer = method(a, b, c);
}
public static String method(int a, int b, int c) {
if (!(a < 0 || b < 0 || c < 0) || (!(a == 0 || b == 0 || c == 0))) {
if ((a + b) < c) {
return "NG";
} else if ((b + c) < a) {
return "NG";
} else if ((c + a) < b) {
return "NG";
} else {
return "OK";
}
} else {
return "NG";
}
}
}
package ex5;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ex5_7Test {
@Test
void method() {
assertAll(
() -> assertEquals("OK", (ex5_7.method(3, 4, 5))),
() -> assertEquals("NG", (ex5_7.method(-3, 4, 5))),
() -> assertEquals("NG", (ex5_7.method(3, 0, 5))),
() -> assertEquals("OK", (ex5_7.method(1, 1, 1)))
);
}
}
chap6
語彙
loop:
loop body:
infinite loop:
increment:
decrement:
iteration:
loop variable:
index:
Unicode:
empty string:
overloaded:
##エクササイズ
ex6_3
package ex6;
public class ex6_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 9;
squareRoot(a);
}
public static double squareRoot(double a) {
double oldValue = a / 2;
double newValue = a / 2;
double interval = 0;
do {
oldValue = newValue;
newValue = (oldValue + a / oldValue) / 2;
interval = Math.abs(newValue - oldValue);
System.out.println(interval);
} while (interval > 0.001);
return newValue;
}
}
public class ex6_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(gauss(1, 2));
}
public static double gauss(double x, int n) {
double result = 1;
int q = 1;
double p = 1;
int pre = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
result += (pre *= -1) * (p *= x * x) / (q *= i);
}
return result;
}
}
package ex6;
public class ex6_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static Boolean isAbecedarian(String s) {
if (s.length() != 6) {
return false;
} else {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
String temp = new String(chars);
if (temp.equals(s)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
package ex6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
public class ex6_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(doubloon("teet"));
}
public static boolean doubloon(String s) {
boolean flag = true;
int len = s.length();
int count;
if (len % 2 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < (len); i++) {
count = 2;
for (int j = 0; j < (len); j++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
count--;
}
}
if (count != 0) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
} else {
flag = false;
}
return flag;
}
}
public class ex6_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static int[] letterHist(String str) {
char[] characters = str.toUpperCase().toCharArray();
int[] result = new int[27];
for (char letter : characters) {
if (letter >= 65 && letter <= 90) {
result[letter - 65] += 1;
} else if (letter != 32) {
result[27] += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
public static boolean canSpell(String word, String libchar) {
int[] wordRequirment = letterHist(word);
int[] libCapacity = letterHist(libchar);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (wordRequirment[i] > libCapacity[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
chap7
語彙
array:
element:
allocate:
reference:
index:
alias:
traversal:
search:
reduce:
accumulator:
deterministic:
nondeterministic:
pseudorandom:
histogram:
##プログラムソース
https://github.com/ChrisMayfield/ThinkJavaCode2/blob/master/ch07/ArrayExamples.java
##ソリューション
ex8_1
public static double[]powArray(double[] array, double power){
double[] accumelator = new double[array.length];
for (int i=0; i<array.length;i++) {
accumelator[i] = Math.pow(array[i], power);
}
return accumelator;
}
public static int[] histogram(int[] array, int count) {
int[] counter = new int[count];
for (int element:array) {
counter[element]++;
}
return counter;
}
package thinkJava;
public class chap8_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] bob = make(5);
dub(bob);
System.out.println(mus(bob));
}
public static int[] make(int n) {
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = i + 1;
}
return a;
}
public static void dub(int[] jub) {
for (int i = 0; i < jub.length; i++) {
jub[i] *= 2;
}
}
/**
* Calculates the summary of adding all elements in `zoo` reduce(0) {$0 + $1}
*/
public static int mus(int[] zoo) {
int fus = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < zoo.length; i++) {
fus += zoo[i];
}
return fus;
}
}
package thinkJava;
public class chap8_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean a[] = sieve(100);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static boolean[] sieve(int n) {
boolean[] result = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
result[i] = true;
for (int number = 2; number <= (int) Math.sqrt(n); number++) {
if (result[number] == true) {
for (int indexInSeries = number * number; indexInSeries < n; indexInSeries += number) {
result[indexInSeries] = false;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
package thinkJava;
public class chap8_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
boolean b = arePrimeFactors(10,arr);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static boolean isPrime(int n){
if (n < 2){
return false;
}
else if (n > 2){
if (n % 2 == 0){
return false;
}
for (int i = 3;i<=(int)Math.sqrt(n);i+=2){
if (n % i !=0){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean arePrimeFactors(int n, int[] arr){
int result = 1;
for (int element:arr){
if (isPrime(element)){
result *= element;
}
else {
System.out.println(result);
return false;
}
}
if (result == n){
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println(result);
return false;
}
}
}
chap 8
前提 エクササイズは2eでやります。
語彙
iterative:
A method or algorithm that repeats steps by using one or more loops.
recursive:
A method or algorithm that invokes itself one or more times with different arguments.
base case:
A condition that causes a recursive method not to make another recursive call.
factorial:
The product of all the integers up to and including a given integer.
leap of faith:
A way to read recursive programs by assuming that the recursive call works, rather than following the flow of execution.
binary:
A system that uses only zeros and ones to represent numbers. Also known as “base 2”.
プログラムソース
省略
エクササイズ
ex8_1
package thinkJava;
public class ThinkJava8_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int bottles = 99;
ex8_2(bottles);
}
public static int ex8_2(int bottles) {
if (bottles == 0) {
System.out.println("No bottles of beer on the wall,");
System.out.println("no bottles of beer,");
System.out.println("ya’ can’t take one down, ya’ can’t pass it around,");
System.out.println("’cause there are no more bottles of beer on the wall!");
return 0;
}
System.out.println(bottles + " bottles of beer on the wall");
System.out.println(bottles + " bottles of beer,");
System.out.println("ya’ take one down, ya’ pass it around,");
bottles = bottles - 1;
System.out.println(bottles + " bottles of beer on the wall.");
return ex8_2(bottles);
}
}
ex8_3
package thinkJava;
public class ThinkJava2_8_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(prod(1, 5));
}
public static int prod(int m, int n) {
if (m == n) {
return n;
} else {
int recurse = prod(m, n - 1);
int result = n * recurse;
return result;
}
}
}
package thinkJava;
public class ThinkJava2_8_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(prod(1, 4));
}
public static int prod(int m, int n) {
return (m == n ? n : n * prod(m, n - 1));
}
}
階乗をしています。
ex8_5
public class ThinkJava2_8_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(power(2.0, 1));
}
static int power (double num, int pow){
if (pow == 0)
return 1;
else
return (int) (num * power(num, pow - 1));
}
}
ex8_7
public class Recurse{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(isPalindrome("otto"));
}
public static void printString(String str){
if (length(str) != 0){
System.out.println(first(str));
printString(rest(str));
}
}
public static void printBackward(String str){
if (length(str) != 0){
printBackward(rest(str));
System.out.println(first(str));
}
}
public static String reverseString(String str){
if (length(str) != 0){
return reverseString(rest(str)) + first(str);
}
return "";
}
public static boolean isPalindrome(String str){
int length = length(str);
if (length == 1){
return true;
}
else if (length == 2){
return first(str) == first(rest(str));
}
else {
return first(str) == first(reverseString(rest(str))) && isPalindrome(middle(str));
}
}
// MARK: Supporting
/**
* Returns the first character of the given String.
*/
public static char first(String s){
return s.charAt(0);
}
/**
* Returns all but the first letter of the given String.
*/
public static String rest(String s) {
return s.substring(1);
}
/**
* Returns all but the first and last letter of the String.
*/
public static String middle(String s) {
return s.substring(1, s.length() - 1);
}
/**
* Returns the length of the given String.
*/
public static int length(String s) {
return s.length();
}
}

