言語処理100本ノック 2015の77本目「正解率の計測」の記録です。
ノックの設問内容は訓練データに対する正解率の計測ですが、今回は前回と同じくあえてテストデータで実施しています。
今までは基本的に「素人の言語処理100本ノック」とほぼ同じ内容にしていたのでブロクに投稿していなかったのですが、「第8章: 機械学習」については、真剣に時間をかけて取り組んでいてある程度変えているので投稿します。scikit-learnをメインに使用します。
※次回の78本目「5分割交差検定」はやりません。既に訓練時にGridSearchCV関数を使って5分割交差検定をしているため、無駄だからです(正確には5分割交差検定で適合率などを求めていないでやっていないのですが、面倒なので割愛します)。
参考リンク
| リンク | 備考 |
|---|---|
| 077.正解率の計測.ipynb | 回答プログラムのGitHubリンク |
| 素人の言語処理100本ノック:77 | 言語処理100本ノックで常にお世話になっています |
| 言語処理100本ノックでPython入門 #77 - 機械学習、scikit-learnでの正解率の計測 | scikit-learn使ったノック結果 |
環境
| 種類 | バージョン | 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu18.04.01 LTS | 仮想で動かしています |
| pyenv | 1.2.15 | 複数Python環境を使うことがあるのでpyenv使っています |
| Python | 3.6.9 | pyenv上でpython3.6.9を使っています 3.7や3.8系を使っていないことに深い理由はありません パッケージはvenvを使って管理しています |
上記環境で、以下のPython追加パッケージを使っています。通常のpipでインストールするだけです。
| 種類 | バージョン |
|---|---|
| matplotlib | 3.1.1 |
| numpy | 1.17.4 |
| pandas | 0.25.3 |
| scikit-learn | 0.21.3 |
課題
第8章: 機械学習
本章では,Bo Pang氏とLillian Lee氏が公開しているMovie Review Dataのsentence polarity dataset v1.0を用い,文を肯定的(ポジティブ)もしくは否定的(ネガティブ)に分類するタスク(極性分析)に取り組む.
77. 正解率の計測
76の出力を受け取り,予測の正解率,正例に関する適合率,再現率,F1スコアを求めるプログラムを作成せよ.
今回は「76の出力を受け取り」という部分を無視し、テストデータに対して実施しています。前回同様に学習データよりテストデータの方が有用では、と考えたからです。
回答
回答プログラム 077.正解率の計測.ipynb
基本的に前回の「076.ラベル付け.ipynb」に正解率および関連指標出力ロジックを付加した程度です。
import csv
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
# 単語ベクトル化をGridSearchCVで使うのためのクラス
class myVectorizer(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
def __init__(self, method='tfidf', min_df=0.0005, max_df=0.10):
self.method = method
self.min_df = min_df
self.max_df = max_df
def fit(self, x, y=None):
if self.method == 'tfidf':
self.vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(min_df=self.min_df, max_df=self.max_df)
else:
self.vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=self.min_df, max_df=self.max_df)
self.vectorizer.fit(x)
return self
def transform(self, x, y=None):
return self.vectorizer.transform(x)
# GridSearchCV用パラメータ
PARAMETERS = [
{
'vectorizer__method':['tfidf', 'count'],
'vectorizer__min_df': [0.0003, 0.0004],
'vectorizer__max_df': [0.07, 0.10],
'classifier__C': [1, 3], #10も試したが遅いだけでSCORE低い
'classifier__solver': ['newton-cg', 'liblinear']},
]
# ファイル読込
def read_csv_column(col):
with open('./sentiment_stem.txt') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file, delimiter='\t')
header = next(reader)
return [row[col] for row in reader]
x_all = read_csv_column(1)
y_all = read_csv_column(0)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_all, y_all)
def train(x_train, y_train, file):
pipline = Pipeline([('vectorizer', myVectorizer()), ('classifier', LogisticRegression())])
# clf は classificationの略
clf = GridSearchCV(
pipline, #
PARAMETERS, # 最適化したいパラメータセット
cv = 5) # 交差検定の回数
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(clf.cv_results_).to_csv(file)
print('Grid Search Best parameters:', clf.best_params_)
print('Grid Search Best validation score:', clf.best_score_)
print('Grid Search Best training score:', clf.best_estimator_.score(x_train, y_train))
# 素性の重み出力
output_coef(clf.best_estimator_)
return clf.best_estimator_
# 素性の重み出力
def output_coef(estimator):
vec = estimator.named_steps['vectorizer']
clf = estimator.named_steps['classifier']
coef_df = pd.DataFrame([clf.coef_[0]]).T.rename(columns={0: 'Coefficients'})
coef_df.index = vec.vectorizer.get_feature_names()
coef_sort = coef_df.sort_values('Coefficients')
coef_sort[:10].plot.barh()
coef_sort.tail(10).plot.barh()
def validate(estimator, x_test, y_test):
for i, (x, y) in enumerate(zip(x_test, y_test)):
y_pred = estimator.predict_proba([x])
if y == np.argmax(y_pred).astype( str ):
if y == '1':
result = 'TP:正解がPositiveで予測もPositive'
else:
result = 'TN:正解がNegativeで予測もNegative'
else:
if y == '1':
result = 'FN:正解がPositiveで予測はNegative'
else:
result = 'FP:正解がNegativeで予測はPositive'
print(result, y_pred, x)
if i == 29:
break
# TSV一覧出力
y_pred = estimator.predict(x_test)
y_prob = estimator.predict_proba(x_test)
results = pd.DataFrame([y_test, y_pred, y_prob.T[1], x_test]).T.rename(columns={ 0: '正解', 1 : '予測', 2: '予測確率(ポジティブ)', 3 :'単語列'})
results.to_csv('./predict.txt' , sep='\t')
print('\n', classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
print('\n', confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
estimator = train(x_train, y_train, 'gs_result.csv')
validate(estimator, x_test, y_test)
回答解説
scikit-learnのclassification_reportを使っているだけで、特に大した処理は書いていないです。
前回の「ラベル付け」で使ったpredict関数の結果y_predを流用します。
y_pred = estimator.predict(x_test)
あとはclassification_report関数にもともとの正解ラベルy_testとともに渡してあげるだけです。
print('\n', classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
適合率・再現率・F1スコア・正答率などが出力されます。
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.75 0.73 0.74 1351
1 0.73 0.75 0.74 1315
accuracy 0.74 2666
macro avg 0.74 0.74 0.74 2666
weighted avg 0.74 0.74 0.74 2666
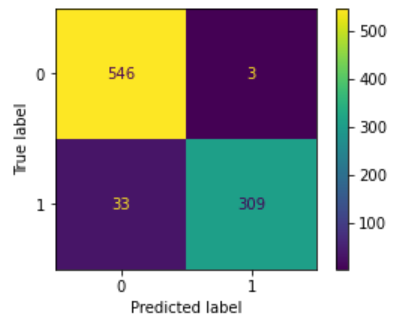
渡すパラメータが同じなので、ついでにconfusion_matrix関数で混合行列(Confusion matrix)も出力します。
print('\n', confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
素朴な形で混合行列が出ます。混合行列の詳細は、別記事「【入門者向け】機械学習の分類問題評価指標解説(正解率・適合率・再現率など)」を参照ください。
[[992 359]
[329 986]]
※2021/3/17追記 scikit-learn 0.22から関数plot_confusion_matrixが使えます。数値は上記と違いますが、こんなグラフが出力されます。