KerasTunerを使ってHyperBandのハイパーパラメータチューニングをしたので、その記録です。概要レベルでしか調査・理解していません。以前使ったHyperasとAPIの呼び方自体はあまり変わりませんが、探索アルゴリズムが違いますし、Kerasに対してはとても使いやすいです。
※Hyperasに関しては記事「Hyperasを使ったKerasハイパーパラメータチューニング」に書いています。
今回は、言語処理100本ノック 2020 (Rev2)の「第9章: RNN, CNN」の88本目「パラメータチューニング」を解くために調べました。実際に使った内容は以下の記事にあります。
参考リンク
当記事には全然書きませんが、リンクは載せておきます。
| リンク | 備考 |
|---|---|
| 機械学習におけるハイパーパラメータ最適化の理論と実践 | ハイパーパラメータ最適化の非常に素晴らしい記事 |
| Hyperband(Banditを基礎とした効率的なRandom Search)のアルゴリズム | HyperBand解説 |
| Successive Halvingの性能解析 | HyperBandのベースのアルゴリズム解説 |
| HyperBand and BOHB: Understanding State of the Art Hyperparameter Optimization Algorithms | 解説の図がわかりやすい |
| 【公式ガイド】Getting started with KerasTuner | |
| 【公式ガイド】Visualize the hyperparameter tuning process | |
| 【公式 API】Hyperband Tuner | |
| 【公式チュートリアル】Keras Tuner の基礎 |
環境
Google Colaboratory使っています。KerasTunerは、Google Colaboratoryにプリインストールされておらず、Google内部での立ち位置悪い?
| 種類 | バージョン | 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| Python | 3.7.12 | Google Colaboratoryのバージョン |
| tensorflow | 2.7.0 | ディープラーニング |
| keras-tuner | 1.1.0 | 今回のメイン |
| numpy | 1.19.5 | 行列処理 |
ハイパーパラメータ最適化とHyperBand
記事「機械学習におけるハイパーパラメータ最適化の理論と実践」が最初に読むといいです。
ハイパーパラメータ最適化を分類すると下図のとおりです(引用元: Automated Machine Learning: State-of-The-Art and Open Challenges)。
※ "Successive Having" ではなく"Successive Halving"が正解
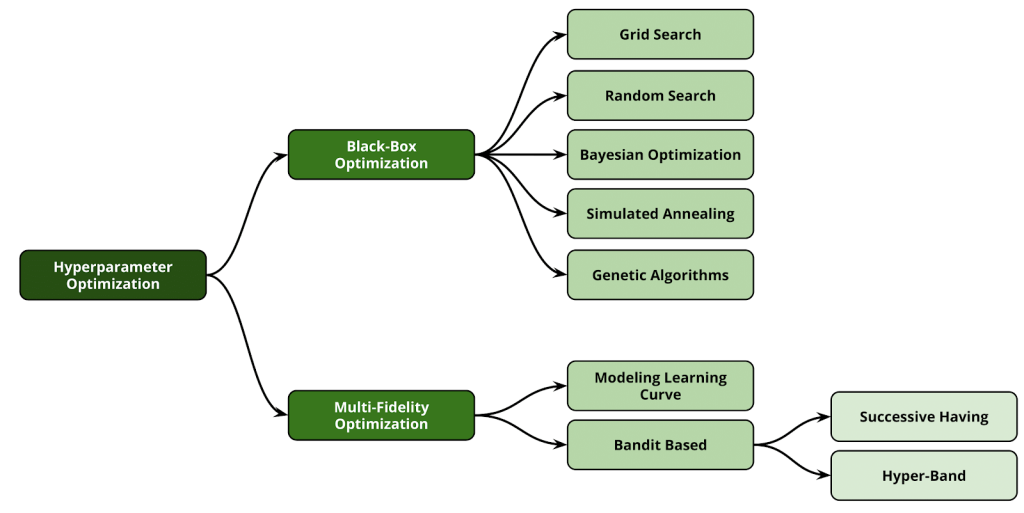
上の"Black-Box Optimazation"では、機械学習モデルの中身はわからなくても結果だけを見てハイパーパラメータ最適化をします。
下の"Multi-Fidelty Optimization"は、機械学習の訓練途中経過を見ながらハイパーパラメータ最適化をします。
使ってみた
プログラム
Jupyterのプログラム全体です。マジックコマンドも含んでいます。
!pip install keras-tuner
%load_ext tensorboard
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import keras_tuner as kt
import numpy as np
def build_model(hp):
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(units=32, activation=hp.Choice("activation", ["relu", "tanh"])))
model.add(layers.Dropout(rate=0.25))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
learning_rate = hp.Float("lr", min_value=1e-4, max_value=1e-3, sampling="log")
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
return model
tuner = kt.Hyperband(
hypermodel=build_model,
objective='val_loss',
max_epochs=10,
overwrite=True,
directory="./",
project_name="helloworld",
)
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
x_train = x[:-50000] #末尾50000件を除外して10000件
x_val = x[-1000:]
y_train = y[:-50000]
y_val = y[-1000:]
x_train = np.expand_dims(x_train, -1).astype("float32") / 255.0
x_val = np.expand_dims(x_val, -1).astype("float32") / 255.0
x_test = np.expand_dims(x_test, -1).astype("float32") / 255.0
num_classes = 10
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_val = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_val, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
%tensorboard --logdir /tmp/tb_logs
tuner.search_space_summary()
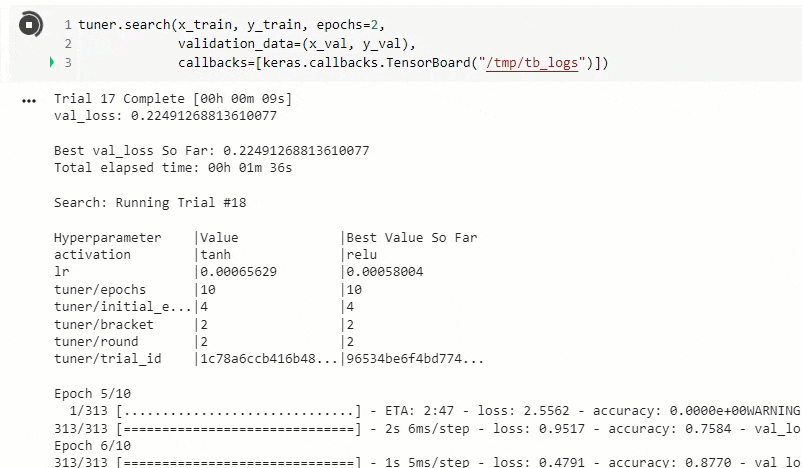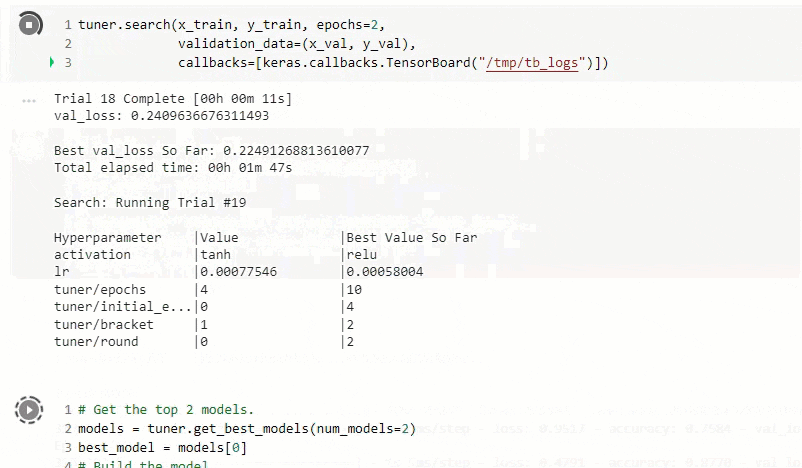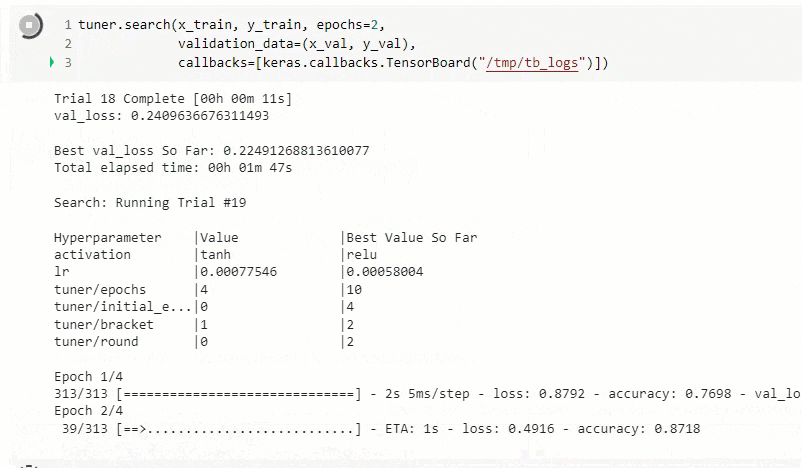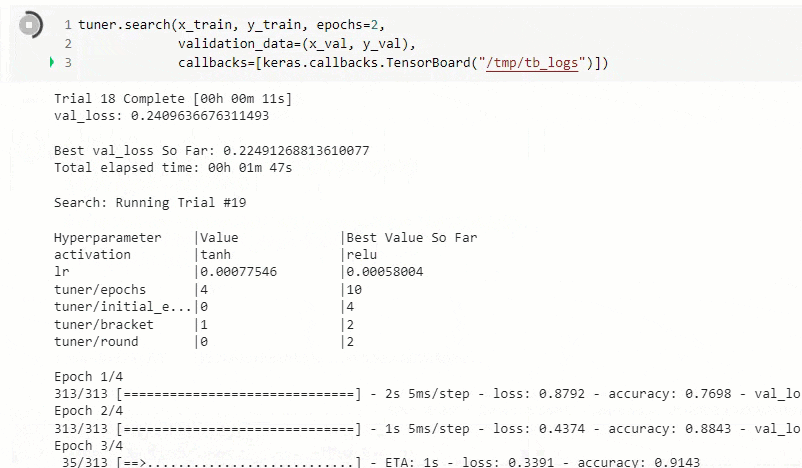
tuner.search(x_train, y_train,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
callbacks=[keras.callbacks.TensorBoard("/tmp/tb_logs")])
# Get the top 2 models.
models = tuner.get_best_models(num_models=2)
best_model = models[0]
# Build the model.
# Needed for `Sequential` without specified `input_shape`.
best_model.build(input_shape=(None, 28, 28))
best_model.summary()
tuner.results_summary()
モデル
ハイパーパラメータを受け取り、Kerasモデルを返す関数build_modelを定義します。
シンプルなモデル
今回使ったシンプルなモデルです。
def build_model(hp):
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(units=32, activation=hp.Choice("activation", ["relu", "tanh"])))
model.add(layers.Dropout(rate=0.25))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
learning_rate = hp.Float("lr", min_value=1e-4, max_value=1e-3, sampling="log")
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
return model
いろいろ使った場合
いろいろな種類使うと以下のように書きます。Int, Choice, Boolean, Floatで選択肢を定義できます(他にもいくつかありHyperParameters参照)。最初は単純にしたかったので、以下のコードは非採用。
def build_model(hp):
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten())
# Tune the number of layers.
for i in range(hp.Int("num_layers", 1, 2)):
model.add(
layers.Dense(
# Tune number of units separately.
units=hp.Int(f"units_{i}", min_value=32, max_value=64, step=32),
activation=hp.Choice("activation", ["relu", "tanh"]),
)
)
if hp.Boolean("dropout"):
model.add(layers.Dropout(rate=0.25))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
learning_rate = hp.Float("lr", min_value=1e-4, max_value=1e-3, sampling="log")
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
return model
依存関係あり
チューニング対象のハイパーパラメータ間に依存関係がある場合です。parent_nameとparent_valuesを使います。試していないのですが、親→子→孫の3階層以上の依存関係も定義できるのでないでしょうか。
def build_model(hp):
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(units=32, activation='relu'))
if hp.Boolean("dropout"):
dropout_rate = hp.Float("dropout_rate",
min_value=0.1,
max_value=0.4,
sampling="linear",
parent_name="dropout", parent_values=True)
model.add(layers.Dropout(rate=dropout_rate))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
return model
依存関係ありの別解として以下のような書き方もできます。conditional_scope関数を使ってスコープをきります。こっちの方がスッキリする場合も多いかと思います。
def build_model(hp):
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(units=32, activation='relu'))
if hp.Boolean("dropout"):
with hp.conditional_scope("dropout", True):
dropout_rate = hp.Float("dropout_rate",
min_value=0.1,
max_value=0.4,
sampling="linear")
model.add(layers.Dropout(rate=dropout_rate))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
return model
ハイパーパラメータ探索tuner定義
ハイパーパラメータを探索するtuner定義します。
tuner = kt.Hyperband(
hypermodel=build_model,
objective='val_loss',
max_epochs=10,
directory="./",
project_name="helloworld",
)
以下がパラメータです。
- hypermodel: 先程定義したモデルを返す関数を渡します
- objective: 最適化のための指標
- max_epochs: 最大のエポック数。収束するエポックより多いエポック数の指定と、EalyStopping使用が推奨。公式APIの記載 → It is recommended to set this to a value slightly higher than the expected epochs to convergence for your largest Model, and to use early stopping during training (for example, via tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping).
- directory: 途中経過やログを保存するディレクトリ
- project_name: ディレクトリ内に保存されるサブディレクトリ名
今回はパラメータ指定していませんが、factorの数を大きくするほど、枝刈り回数が増えます。具体例およびHyperband Algorithmを見て、以下のコードをサンプルで動かしながら理解しました。コード中のmax_iterがパラメータのmax_epochsを意味し、etaがfactorを意味します。
import math
max_iter = 81 # maximum iterations/epochs per configuration
eta = 3 # defines downsampling rate (default=3)
logeta = lambda x: math.log(x)/math.log(eta)
s_max = int(logeta(max_iter)) # number of unique executions of Successive Halving (minus one)
B = (s_max+1)*max_iter # total number of iterations (without reuse) per execution of Succesive Halving (n,r)
print(f'{s_max}, {B}')
#### Begin Finite Horizon Hyperband outlerloop. Repeat indefinetely.
for s in reversed(range(s_max+1)):
print(f's: {s}')
n = int(math.ceil(int(B/max_iter/(s+1))*eta**s)) # initial number of configurations
r = max_iter*eta**(-s) # initial number of iterations to run configurations for
print(f'n: {n}, r: {r}')
#### Begin Finite Horizon Successive Halving with (n,r)
# T = [ get_random_hyperparameter_configuration() for i in range(n) ]
# for i in range(s+1):
# # Run each of the n_i configs for r_i iterations and keep best n_i/eta
# n_i = n*eta**(-i)
# r_i = r*eta**(i)
# val_losses = [ run_then_return_val_loss(num_iters=r_i,hyperparameters=t) for t in T ]
# T = [ T[i] for i in argsort(val_losses)[0:int( n_i/eta )] ]
#### End Finite Horizon Successive Halving with (n,r)
実行するとディレクトリ内に以下のように途中経過やログが保存。
探索空間
search_space_summaryで探索空間を見ることができます。
> tuner.search_space_summary()
Search space summary
Default search space size: 2
activation (Choice)
{'default': 'relu', 'conditions': [], 'values': ['relu', 'tanh'], 'ordered': False}
lr (Float)
{'default': 0.0001, 'conditions': [], 'min_value': 0.0001, 'max_value': 0.001, 'step': None, 'sampling': 'log'}
TensorBoard
TensorBoardを実行中に見るために探索開始前に起動しておきます。Visualize the hyperparameter tuning processを参考にしました。
%load_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir /tmp/tb_logs
SCALARS
KerasTunerと直接関係ないですが、Epochごとに各ハイパーパラメータ選択時の指標がわかります。途中で打ち切られた組み合わせもわかります。
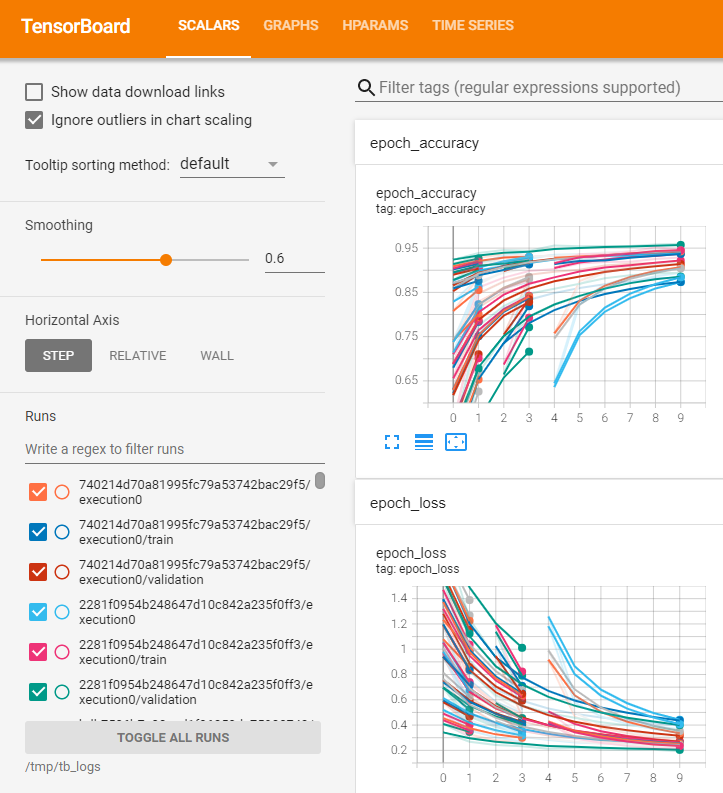
HPARAMS
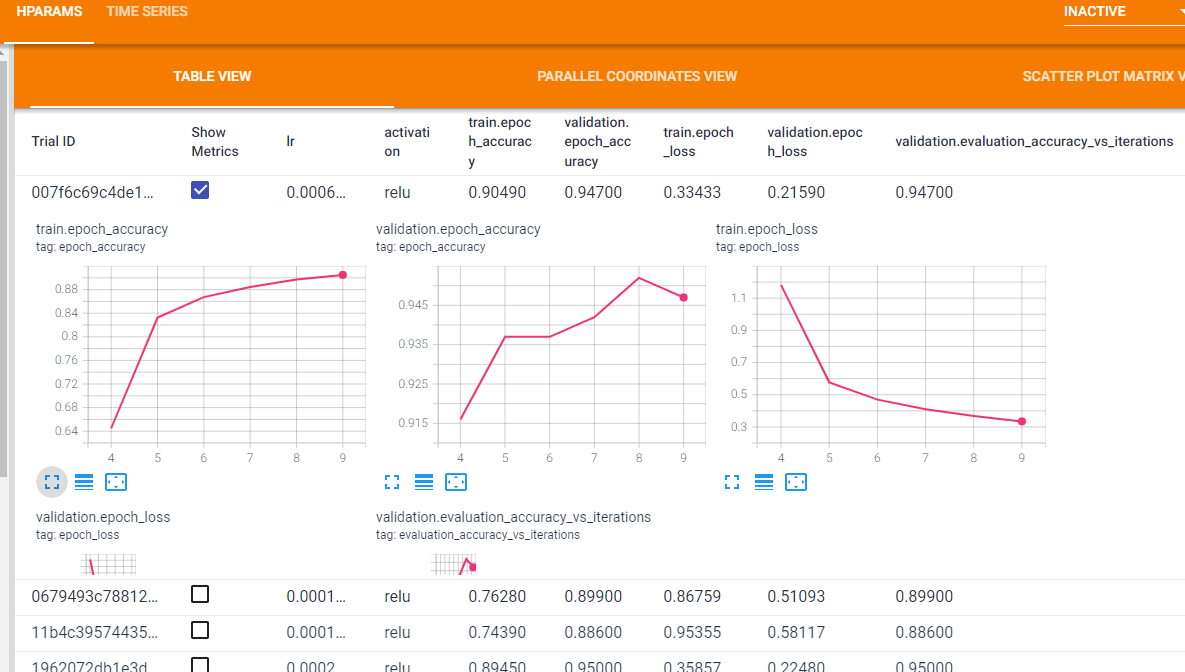
メニューHPARAMSは共通して左側でハイパーパラメータでフィルタできます。
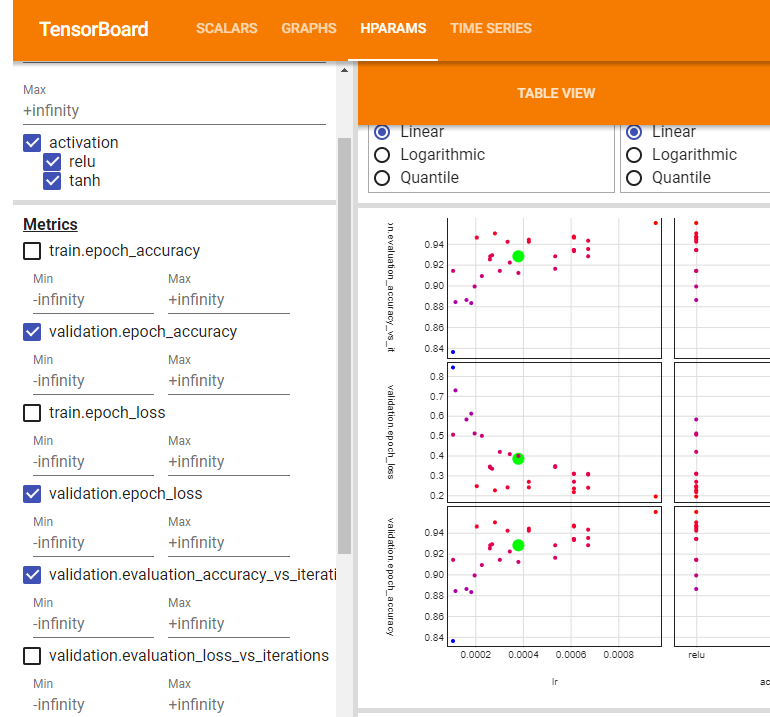
TABLE VIEW
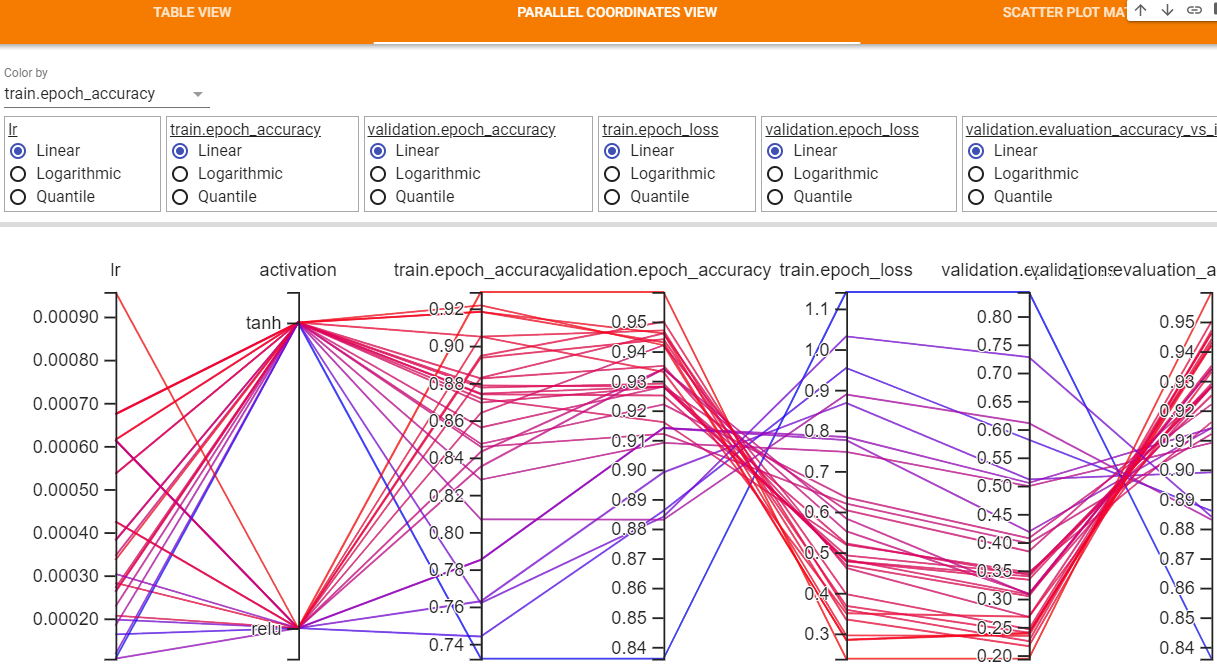
PARALLEL COORDINATES VIEW
ハイパーパラメータの選択肢と評価指標をグラフで見られるView
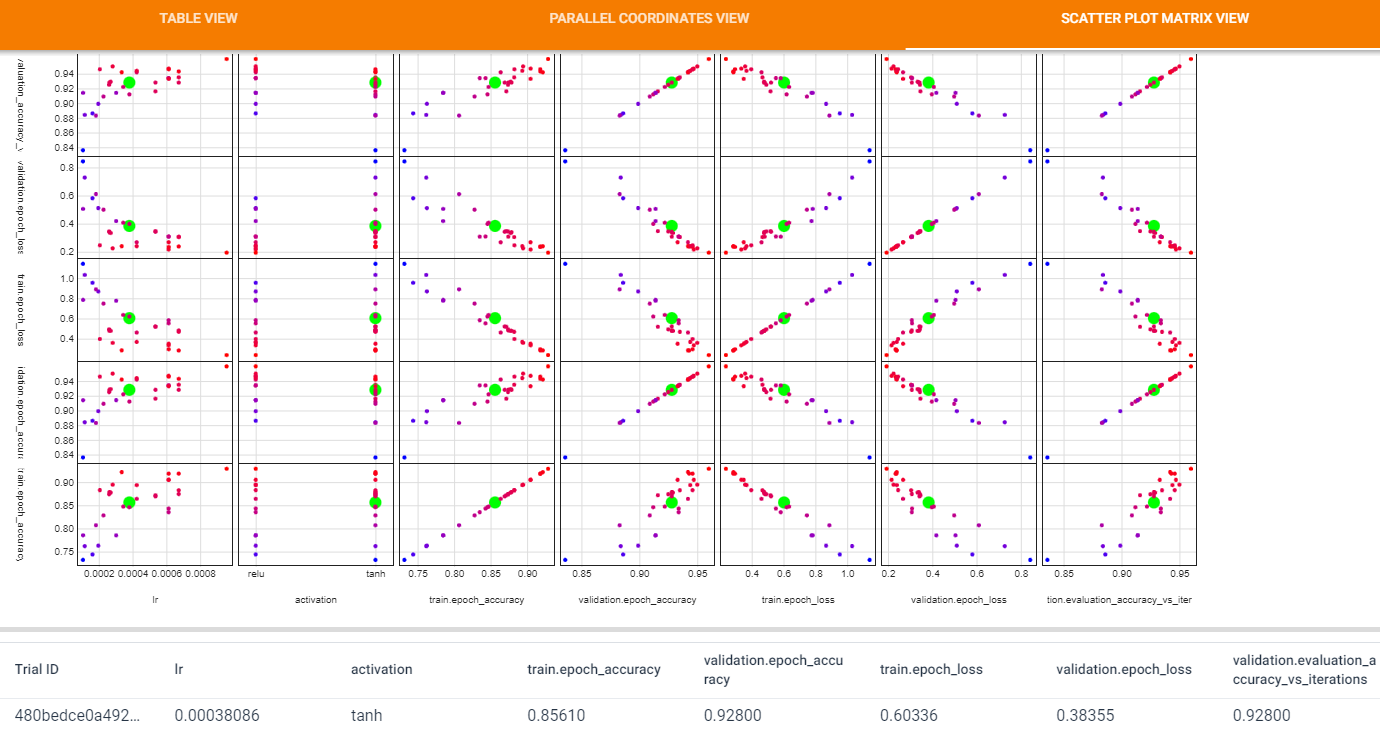
SCATTER PLOT MATRIX VIEW
散布図表示。散布図上の点を選択すると、下側に具体的な値をグラフを表示してくれる(グラフはこの図では省略)。
探索開始
fit関数と同じパラメータで探索開始します。ここでEarlyStoppingも本当はCallback関数に追加しておくべきなのでしょう。
tuner.search(x_train, y_train,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
callbacks=[keras.callbacks.TensorBoard("/tmp/tb_logs")])
実行後に以下の情報を出力。
Trial 30 Complete [00h 00m 21s]
val_loss: 0.3008600175380707
Best val_loss So Far: 0.18738491833209991
Total elapsed time: 00h 04m 29s
INFO:tensorflow:Oracle triggered exit
最適モデル使用
get_best_modelsで最適なモデルを取得できるようです。あまり調べていないです。
# Get the top 2 models.
models = tuner.get_best_models(num_models=2)
best_model = models[0]
# Build the model.
# Needed for `Sequential` without specified `input_shape`.
best_model.build(input_shape=(None, 28, 28))
best_model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
flatten (Flatten) (None, 784) 0
dense (Dense) (None, 32) 25120
dropout (Dropout) (None, 32) 0
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 330
=================================================================
Total params: 25,450
Trainable params: 25,450
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
結果出力
results_summary関数で上位10の結果出力。1つ1つの行を分けてほしい。
> tuner.results_summary()
Results summary
Results in ./helloworld
Showing 10 best trials
Objective(name='val_loss', direction='min')
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.0009570214467764447
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 0
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.19376720488071442
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.0006136739662904565
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 4
tuner/bracket: 2
tuner/round: 2
tuner/trial_id: b51f3f0bd0ace0b99f48ef03db9a93e6
Score: 0.21589896082878113
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.0002824952294528987
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 0
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.22479817271232605
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: tanh
lr: 0.0006141098124590815
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 4
tuner/bracket: 1
tuner/round: 1
tuner/trial_id: c70f7a6051127a4d37ca100acb443b27
Score: 0.23398013412952423
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: tanh
lr: 0.0006736282432334351
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 4
tuner/bracket: 2
tuner/round: 2
tuner/trial_id: 2ec22d95503871c8cad7111ee23a48c0
Score: 0.23797860741615295
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: tanh
lr: 0.00033550426727547506
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 0
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.23959438502788544
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.000424709121934671
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 4
tuner/bracket: 1
tuner/round: 1
tuner/trial_id: 82ea7550018d9b5f23dfe7a5ee369b10
Score: 0.2398107945919037
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.00020633386682052565
tuner/epochs: 10
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 0
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.24579833447933197
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: relu
lr: 0.000424709121934671
tuner/epochs: 4
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 1
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.26777052879333496
Trial summary
Hyperparameters:
activation: tanh
lr: 0.0006141098124590815
tuner/epochs: 4
tuner/initial_epoch: 0
tuner/bracket: 1
tuner/round: 0
Score: 0.26802679896354675