初めに
皆さん。こんにちは!
DreamHanksの254cmです。
今回はstaticについて説明していきます。
Java記事のまとめはこちらです。
前回の記事は【Java開発】第10回 ArrayListです。
static
staticとは?
staticはクラスの構成要素に付与できる修飾子として、メソッドとフィールドに付与することができます。
付与されたフィールドおよびメソッドはプログラムが実行される時、メモリの割り当てを受けて
プログラムが終了されるまで消えずに維持されます。そしてその値はすべてのインスタンスが共有します。
staticフィールド
一般的なフィールドはインスタンスが生成されるたびに新しく生成され、様々な値を持ちますが、
staticが付与されたフィールドはプログラムが実行される時に生成され、すべてのインスタンスが共有します。
サンプル
public class Student {
public static int studentNum = 20000;
public String studentName;
}
public class ExampleCalss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student harry = new Student();
Student tom = new Student();
Student mugi = new Student();
Student coco = new Student();
System.out.println(harry.studentNum);
System.out.println(tom.studentNum);
System.out.println(mugi.studentNum);
System.out.println(coco.studentNum);
}
}
実行結果
20000
20000
20000
20000
上記のサンプルではStudentクラスのインスタンスを生成して各インスタンスのstudentNumの値を出力しています。
各インスタンスのstudentNumに何も代入していませんが、二つ全部20000が出力されました。
つまりすべてのインスタンスはstaticフィールドの値を共有しています。
サンプル
public class ExampleCalss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student harry = new Student();
Student tom = new Student();
Student mugi = new Student();
Student coco = new Student();
System.out.println(harry.studentNum++);
System.out.println(tom.studentNum++);
System.out.println(mugi.studentNum++);
System.out.println(++coco.studentNum);
}
}
実行結果
20000
20001
20002
20004
すべてのインスタンスがstaticフィールドを共有しているので、すべてのインスタンスで
行った処理の結果も共有されます。
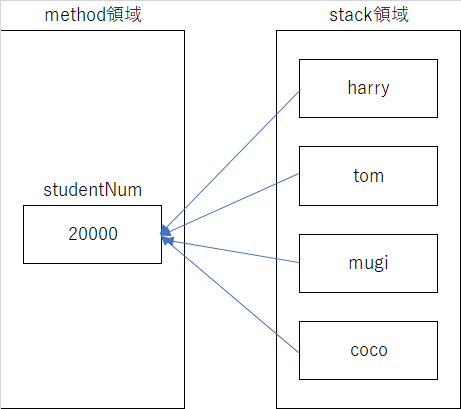
サンプルを実行結果をみるとStudentのすべてのインスタンスは同じstudentNumを指していることがわかります。
※static変数のメモリは他の変数と異なる領域に格納されます。その領域をmethod領域と呼びます。
staticフィールドはインスタンスと別の時点に生成されるので、インスタンスではなくクラスの名前で参照することができます。
サンプル
public class ExampleCalss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student harry = new Student();
Student tom = new Student();
Student mugi = new Student();
Student coco = new Student();
System.out.println(harry.studentNum++);
System.out.println(tom.studentNum++);
System.out.println(mugi.studentNum++);
System.out.println(++coco.studentNum);
System.out.println(Student.studentNum);
}
}
実行結果
20000
20001
20002
20004
20004
上記のようにインスタンスを使っても、使わなくてもstatic変数を呼び出すことができます。
staticメソッド
static修飾子はクラスの構成要素につけるので、メソッドにもstatic修飾子をつけることができます。
こんなメソッドをstaticメソッドと呼びます。staticメソッドにはstaticフィールドとローカル変数しか使えません。
サンプル
public class Student {
public static int studentNum = 20000;
public String studentName;
public static void displayStudentNum() {
System.out.println("今のStudentNumは" + studentNum + "です。");
}
}
public class ExampleCalss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student.displayStudentNum();
Student.studentNum++;
Student.displayStudentNum();
}
}
実行結果
今のStudentNumは20000です。
今のStudentNumは20001です。
上記のようにインスタンスを生成しなくても、クラスの名前を参照して呼び出すことができます。
staticメソッドで使える変数
public class Student {
public static int studentNum = 20000;
public String studentName;
public int grade;
public static void displayStudentNum() {
int localVariable = 100;
grade = 10;
System.out.println("今のStudentNumは" + studentNum + "です。");
}
}
staticは先ほどの説明した通り、ローカル変数とstaticフィールドしか使えません。
staticメソッドはインスタンスを生成しなくても使えるメソッドです。
なので、一般のフィールドはインスタンスが生成される時に生成されるので、
staticメソッドでは使えません。
・ローカル変数とは?
括弧「{}」の中で宣言され、宣言された括弧の中でのみ使える変数です。
ローカル変数は宣言された領域が終了されるとなくなる変数です。
終わりに
今回の記事は以上になります。
次回はJavaのfinalを学びましょう。
私たちの最新の記事はこちらで確認することができます。
ご覧いただきありがとうございます。