tl;dr
- GKE の Ingress (L7 Load Balancer) では、HTTP(S) の GET Request で、Health Check が行われる
- gRPC アプリで、gRPC の Health Check を用意する
- Envoy で Lua を使って、GET リクエストを Envoy の Health Check と繋げることで Health Check をクリアさせる
ソースコード
https://github.com/74th/try-envoy/tree/master/manifests/4_gke_ingress
問題点
GKE で、サービスを公開する手段として、L7 Load Balancer である Ingress を使うことが有効である。
しかし、GKE の標準の仕組みでは、カナリアリリースなどが行いにくいため、途中に gRPC のプロキシである Envoy を挟むことが有効である。
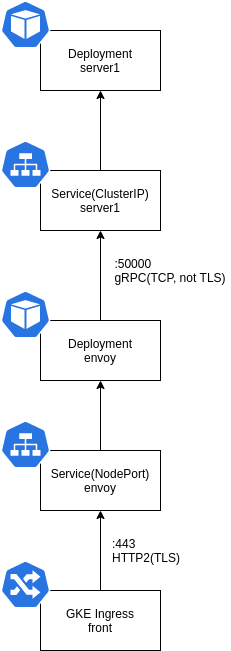
構成としては以下のようになる。
Ingress では、転送先のコンテナの Health Check が、HTTP(S)の GET リクエストで検証される。
ここでは、 Envoy のコンテナがチェックの対象になる。
しかし、gRPC のサービスとして Envoy を構築すると、HTTP(S)の GET リクエストに応答できないため、Ingress を使うことができない。
これを Envoy を使って回避する方法を解説する。
参考
以下の記事を参考にした。
- GKE gRPC Ingress LoadBalancing https://medium.com/google-cloud/gke-grpc-ingress-loadbalancing-4b9cdbc09758
gRPC アプリ (Go) で Health Check を実装する
gRPC には、gRPC の本家がて依拠する Health Check Protocol がある。
Go のこの Health Check Protocol の実装はパッケージ github.com/grpc/grpc-go/tree/master/health/grpc_health_v1 にある。
これを実装すると、以下のようになる。
import (
"google.golang.org/grpc/health/grpc_health_v1"
"google.golang.org/grpc/status"
)
type healthCheck struct {}
// Health Check の実装
func (hc *healthCheck) Check(ctx context.Context, in *grpc_health_v1.HealthCheckRequest) (*grpc_health_v1.HealthCheckResponse, error) {
// TODO: Health Check をここに実装する
// OK を返答する例
return &grpc_health_v1.HealthCheckResponse{
Status: grpc_health_v1.HealthCheckResponse_SERVING
}, nil
}
// 一旦 Watch は実装しない
func (hc *healthCheck) Watch(in *grpc_health_v1.HealthCheckRequest, srv grpc_health_v1.Health_WatchServer) error {
return status.Error(codes.Unimplemented, "Watch is not implemented")
}
この Health Check のサービスを、本来のアプリケーションのサービスと一緒に gRPC サーバに登録して、実行できるようにする。
package main
import (
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"github.com/74th/try-envoy/router"
)
func main() {
// gRPC サーバ
s := grpc.NewServer()
// 本来の gRPC アプリケーション の登録
sv := &server{baseWay: baseWay}
router.RegisterRouterServer(s, sv)
// Health Checkの登録
hc := &healthCheck{}
grpc_health_v1.RegisterHealthServer(s, sv)
// gRPC サーバの開始
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
err = s.Serve(lis)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
Envoy に gRPC アプリの Health Check を行わせる
Envoy にバックエンド(Clusters)の Health Check を行うように設定する。
Envoy の Health Check では、grpc_health_check に設定をすることで、その gRPC を使ってバックエンドの Health Check を行うようになる。
static_resources:
listeners: {} # 省略
clusters:
- name: service
# バックエンドサービスの設定
connect_timeout: 0.05s
type: STRICT_DNS
http2_protocol_options: {}
lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: 127.0.0.1
port_value: 50051
load_assignment:
cluster_name: server
endpoints:
- lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: server1
port_value: 50000
# Health Check の設定
common_lb_config:
healthy_panic_threshold:
value: 50.0
health_checks:
- timeout: 1s
interval: 5s
interval_jitter: 1s
no_traffic_interval: 5s
unhealthy_threshold: 1
healthy_threshold: 3
grpc_health_check:
service_name: "route.Router"
Envoy で、GET リクエストで Health Check にアクセスさせる
Envoy には、Envoy を操作したり状態を取得するための、Administration interface がある。
このバックエンドの状態を示す/clustersにアクセスすることで、バックエンドに行っている Health Check の結果を取得することができる。
正常な場合、以下のように、health_flagsの属性に、状態が入っている。
service::10.60.3.44:50000::health_flags::healthy
Envoy では Lua を使うことで、ちょっとした応答ができるようになっている。
ここで、パス / の GET リクエストを受けた時に/clustersにアクセスし、バックエンドの 1 つでも正常である場合、HTTP(S)の 200 応答を返すようにする。
package.path = "/etc/envoy/lua/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.1/nginx/?.lua;/etc/envoy/lua/" .. package.path
function envoy_on_request(request_handle)
if request_handle:headers():get(":path") == "/" then
local headers, body = request_handle:httpCall(
"local_admin",
{
[":method"] = "GET",
[":path"] = "/clusters",
[":authority"] = "local_admin"
},"", 50)
-- request_handle:logWarn(body)
str = "service::%d+.%d+.%d+.%d+:%d+::health_flags::healthy"
if string.match(body, str) then
request_handle:respond({[":status"] = "200"},"ok")
else
request_handle:respond({[":status"] = "503"},"unavailable")
end
end
end
この Lua を Envoy の Lister の設定取り込むと以下のようになる。
static_resources:
listeners:
- address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 443
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.http_connection_manager
config:
access_log:
- name: envoy.file_access_log
config:
path: "/dev/stdout"
codec_type: AUTO
stat_prefix: ingress_https
route_config:
name: local_route
virtual_hosts:
- name: http
domains: ["*"]
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/router.Router/"
route:
cluster: service
http_filters:
- name: envoy.lua
config:
inline_code: |
package.path = "/etc/envoy/lua/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.1/nginx/?.lua;/etc/envoy/lua/" .. package.path
function envoy_on_request(request_handle)
if request_handle:headers():get(":path") == "/" then
local headers, body = request_handle:httpCall(
"local_admin",
{
[":method"] = "GET",
[":path"] = "/clusters",
[":authority"] = "local_admin"
},"", 50)
request_handle:logWarn(body)
str = "service::%d+.%d+.%d+.%d+:%d+::health_flags::healthy"
if string.match(body, str) then
request_handle:respond({[":status"] = "200"},"ok")
else
request_handle:respond({[":status"] = "503"},"unavailable")
end
end
end
- name: envoy.router
config: {}
"/etc/ssl/envoy/key.pem
なお、ここでは、Envoy のサービスは自己証明書の TLS を使っている。
Ingress を Envoy につなぐ
最後に、この設定を有効にする Kubernetes のマニフェストを作成する。
アプリ Deployment と Service
アプリケーション自体の Deployment を構成する。
gRPC サービスのため、Pod 自体の Health Check である Readiness Probe では、TCP ソケットがリスンされているかしかチェックできない。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: server1
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: server1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: server1
spec:
containers:
- name: server
image: 74th/try-envoy-server:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 50000
command:
- ./server
- -H
- :50000
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 50000
Service では、Headless Service として構成させる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: server1
spec:
selector:
app: server1
type: ClusterIP
# Headless
clusterIP: None
ports:
- name: server1
protocol: TCP
port: 50000
Envoy の Deployment
Envoy の Deployment では、先の Health Check を Readiness Probe で使うように設定する。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: envoy
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: envoy
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: envoy
spec:
containers:
- name: envoy
image: envoyproxy/envoy-alpine:v1.14.1
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 443
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/envoy
- name: cert
mountPath: /etc/ssl/envoy
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTPS
path: /
httpHeaders:
- name: x-envoy-livenessprobe
value: healthz
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 3
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTPS
path: /
httpHeaders:
- name: x-envoy-livenessprobe
value: healthz
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 10
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "100M"
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "1G"
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: envoy-config
- name: cert
configMap:
name: envoy-cert
なお、Envoy の設定である envoy.yaml と TLS の自己証明書は、ConfigMap として登録する(TLS の自己証明書に秘密鍵が含まれているが、この TLS にアクセスするのは Ingress のみであり、認証等に使っていないため、ConfigMap で登録している。
本来は TLS を必要としないが、GKE Ingress の場合、HTTP2 を有効にすると自動的に TLS が有効になっている必要がある。
configMapGenerator:
- name: envoy-cert
files:
- ./cert.pem
- ./key.pem
- name: envoy-config
files:
- envoy.yaml
Envoy の Service と Ingress
Ingress を Pod と繋ぐためには、NodePort の Service を構築する。
Service の annotation には、 HTTP2 を使うように設定をする。
HTTP2 を有効にした場合、自動的に TLS を使って Health Check が行われるようになる。
また、ここで port に 443 を指定することで、Ingress で HTTPS が使えるようになる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: envoy
annotations:
cloud.google.com/neg: '{"envoy": {"443":{}}}'
cloud.google.com/app-protocols: '{"envoy": "HTTP2"}'
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: envoy
ports:
- name: envoy
protocol: TCP
port: 443
targetPort: 443
Ingress では Service を指定するのみで、特別な設定は必要としない。
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: try-envoy
annotations:
# HTTPS になる
kubernetes.io/ingress.allow-http: "false"
# Static IP
kubernetes.io/ingress.global-static-ip-name: try-envoy-ip
# Managed Cert
networking.gke.io/managed-certificates: try-envoy-cert
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: envoy
servicePort: 443
むすび
Envoy で Lua を使うことで、gRPC のサービス出会ったとしても、Ingress での Health Check を満たすことができる。
何がともあれ、早く GCP の Health Check で gRPC ベースのものが出てくるのを願うばかりである。