マルチシグのウォレットコントラクトをローカル開発環境から操作します。
以前SafeのSDKを使ってトランザクションを実行する記事を書きましたが、いくつか課題を感じました。
- Safeがオフチェーンの署名をインデックスするトランザクションサービスAPIが対応しているネットワークでない場合、SDKの活用は難しい。
- トランザクションサービスはオープンソースなのでフォークして運用可能だが、複雑。
- SDKを活用せずSafeコントラクトを直接利用することも可能?(要検証)。
今回は別のアプローチでマルチシグを使った開発を入門してみます。
目標
簡易的なマルチシグのコントラクトをデプロイして、トランザクションをhardhatから実行します。
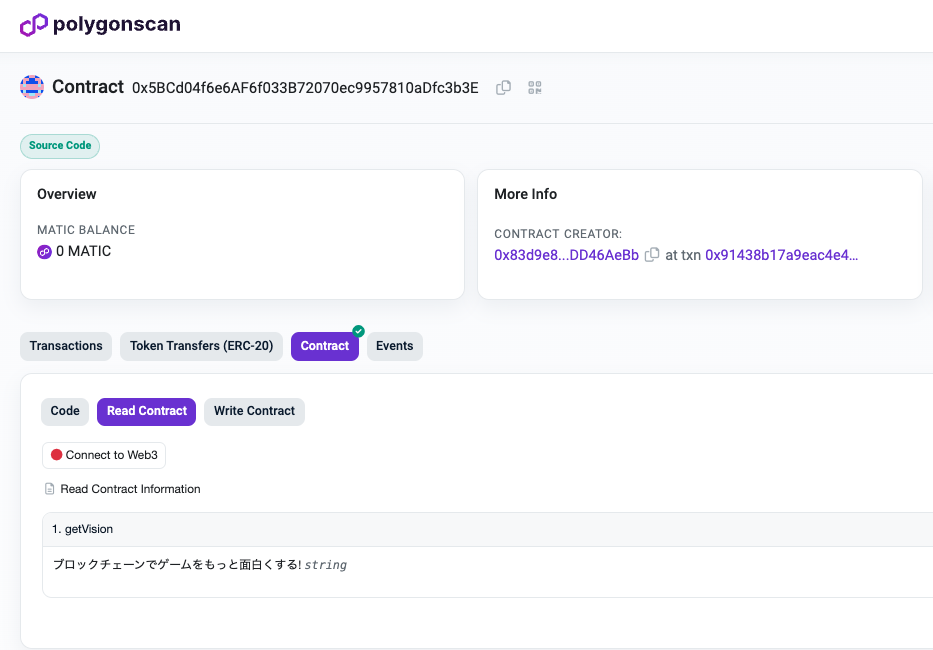
CryptoGamesのVisionを書き込む為のテストネットのコントラクトを予めデプロイしました。このコントラクトのsetVision関数を使ってマルチシグの動作確認をしていきます。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract CryptoGamesVision {
// Solidityのバージョン0.8.20から、
// ユニコード文字列リテラルにはunicodeプレフィックスをつける必要がある。
string private vision = unicode"ブロックチェーンで〇〇をもっと〇〇する!";
function setVision(string memory _vision) public {
vision = _vision;
}
function getVision() public view returns (string memory) {
return vision;
}
}
*「ブロックチェーンでゲームをもっと面白くする!」がCryptoGamesのビジョンです。
*CryptoGames公式のコントラクトではないので、コントラクト上のVision変数を書き換えても何も起きません。
マルチシグコントラクトを準備
こちらのコントラクトを参考にミニマムの内容でマルチシグのウォレットコントラクトを準備します。
内容はシンプルです。
- submitTransaction: 対象のトランザクションを提案。
- confirmTransaction: 対象のトランザクションを承認。
- executeTransaction: 対象のトランザクションを実行。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract MultiSigWallet {
event Deposit(address indexed sender, uint amount, uint balance);
event SubmitTransaction(
address indexed owner,
uint indexed txIndex,
address indexed to,
uint value,
bytes data
);
event ConfirmTransaction(address indexed owner, uint indexed txIndex);
event RevokeConfirmation(address indexed owner, uint indexed txIndex);
event ExecuteTransaction(address indexed owner, uint indexed txIndex);
address[] public owners;
mapping(address => bool) public isOwner;
uint public numConfirmationsRequired;
struct Transaction {
address to;
uint value;
bytes data;
bool executed;
uint numConfirmations;
}
// mapping from tx index => owner => bool
mapping(uint => mapping(address => bool)) public isConfirmed;
Transaction[] public transactions;
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(isOwner[msg.sender], "not owner");
_;
}
modifier txExists(uint _txIndex) {
require(_txIndex < transactions.length, "tx does not exist");
_;
}
modifier notExecuted(uint _txIndex) {
require(!transactions[_txIndex].executed, "tx already executed");
_;
}
modifier notConfirmed(uint _txIndex) {
require(!isConfirmed[_txIndex][msg.sender], "tx already confirmed");
_;
}
constructor(address[] memory _owners, uint _numConfirmationsRequired) {
require(_owners.length > 0, "owners required");
require(
_numConfirmationsRequired > 0 &&
_numConfirmationsRequired <= _owners.length,
"invalid number of required confirmations"
);
for (uint i = 0; i < _owners.length; i++) {
address owner = _owners[i];
require(owner != address(0), "invalid owner");
require(!isOwner[owner], "owner not unique");
isOwner[owner] = true;
owners.push(owner);
}
numConfirmationsRequired = _numConfirmationsRequired;
}
receive() external payable {
emit Deposit(msg.sender, msg.value, address(this).balance);
}
// ①提案
function submitTransaction(
address _to,
uint _value,
bytes memory _data
) public onlyOwner {
uint txIndex = transactions.length;
transactions.push(
Transaction({
to: _to,
value: _value,
data: _data,
executed: false,
numConfirmations: 0
})
);
// txIndexを利用して、承認&実行対象のトランザクションを特定。
emit SubmitTransaction(msg.sender, txIndex, _to, _value, _data);
}
// ②承認
function confirmTransaction(
uint _txIndex
) public onlyOwner txExists(_txIndex) notExecuted(_txIndex) notConfirmed(_txIndex) {
Transaction storage transaction = transactions[_txIndex];
transaction.numConfirmations += 1;
isConfirmed[_txIndex][msg.sender] = true;
emit ConfirmTransaction(msg.sender, _txIndex);
}
// ③実行
function executeTransaction(
uint _txIndex
) public onlyOwner txExists(_txIndex) notExecuted(_txIndex) {
Transaction storage transaction = transactions[_txIndex];
require(
transaction.numConfirmations >= numConfirmationsRequired,
"cannot execute tx"
);
transaction.executed = true;
(bool success, ) = transaction.to.call{value: transaction.value}(
transaction.data
);
require(success, "tx failed");
emit ExecuteTransaction(msg.sender, _txIndex);
}
function revokeConfirmation(
uint _txIndex
) public onlyOwner txExists(_txIndex) notExecuted(_txIndex) {
Transaction storage transaction = transactions[_txIndex];
require(isConfirmed[_txIndex][msg.sender], "tx not confirmed");
transaction.numConfirmations -= 1;
isConfirmed[_txIndex][msg.sender] = false;
emit RevokeConfirmation(msg.sender, _txIndex);
}
function getOwners() public view returns (address[] memory) {
return owners;
}
function getTransactionCount() public view returns (uint) {
return transactions.length;
}
function getTransaction(
uint _txIndex
)
public
view
returns (
address to,
uint value,
bytes memory data,
bool executed,
uint numConfirmations
)
{
Transaction storage transaction = transactions[_txIndex];
return (
transaction.to,
transaction.value,
transaction.data,
transaction.executed,
transaction.numConfirmations
);
}
}
CREATE2を利用したファクトリーコントラクトの準備
ウォレットを複数のチェーンを横断して利用したい際に同じアドレスを使えると便利なので、今回はCREATE2を使ってコントラクトをデプロイしていきます。
CREATE2はopcodeの1つで、予測可能なスマートコントラクトアドレスを実現します。
概要は、openzeppelinのドキュメントを参考にしてください。
通常の場合:
nonceによって毎回アドレスが変わります。
new_address = hash(sender, nonce)
create2 の場合:
nonceが関係なくなります。
new_address = hash(0xFF, sender, salt, bytecode)
openzeppelinのライブラリを利用したファクトリーコントラクトの例です。
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.20;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Create2.sol";
import "./MultiSigWallet.sol";
contract MultiSigWalletFactory {
address public latestAddress;
mapping(bytes32 => address) public deployedAddresses;
modifier isWalletNotDeployed(bytes32 _salt) {
require(deployedAddresses[_salt] == address(0), "Wallet token already deployed for this salt");
_;
}
// ウォレットコントラクトのデプロイ。デプロイするコントラクトのコンストラクターによって引数を変える。
function deploy(bytes32 _salt, address[] memory _owners, uint _numConfirmationsRequired)
external
isWalletNotDeployed(_salt)
returns (address)
{
latestAddress = Create2.deploy(
0,
_salt,
abi.encodePacked(type(MultiSigWallet).creationCode, abi.encode(_owners, _numConfirmationsRequired))
);
deployedAddresses[_salt] = latestAddress;
return latestAddress;
}
// デプロイ後のアドレスを予測
function computeAddress(bytes32 _salt, address[] memory _owners, uint _numConfirmationsRequired)
public
view
returns (address)
{
return Create2.computeAddress(
_salt,
keccak256(abi.encodePacked(type(MultiSigWallet).creationCode, abi.encode(_owners, _numConfirmationsRequired)))
);
}
}
今回は採用しませんでしたが、CREATE2でデプロイしてくれるhardhatのpluginもあるようです。
各種コントラクトのデプロイ
CREATE2ファクトリーコントラクトのデプロイ
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
async function main() {
const Factory = await ethers.getContractFactory("MultiSigWalletFactory")
const txs = await Factory.deploy()
await txs.waitForDeployment();
console.info(`Factory address: ${txs.target}`)
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy/deployMultiSigWalletFactory.ts --network mumbai
マルチシグコントラクトのデプロイ
import { ethers } from 'hardhat'
import * as multiSigWalletFactoryArtifact from '../../artifacts/contracts/MultiSigWalletFactory.sol/MultiSigWalletFactory.json';
const FACTORY_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0xd8Fd441A3F1Dc49943D57d84DD63bB5Ef471339c"
const FACTORY_CONTRACT_ABI = multiSigWalletFactoryArtifact.abi
async function main() {
const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners();
const factoryContract = new ethers.Contract(
FACTORY_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
FACTORY_CONTRACT_ABI,
signer
);
// デプロイするコントラクトのsaltを生成。例として簡単な数値を使用
const salt = ethers.encodeBytes32String('1234');
const deployerAddress = signer.address;
//コントラクトアドレスの予測
const precomputeAddress = await factoryContract.computeAddress(salt, [deployerAddress], 1)
console.log("デプロイ後のコントラクトアドレス: ", precomputeAddress)
// ファクトリーコントラクトを使って新しいコントラクトをデプロイ
// 今回は検証の都合上、1 of 1のマルチシグコントラクトになっています。
// トランザクション実行に必要な承認が1の設定です。
const tx = await factoryContract.deploy(salt, [deployerAddress], 1);
await tx.wait();
console.log("Tx hash: ", tx.hash);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy/deployMultiSigWallet.ts --network mumbai
マルチシグの操作
必要なコントラクトが揃ったので、冒頭で紹介したテスト用コントラクトのsetVision関数を実行してみましょう。
①提案
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const multiSigWalletAddress = "0x1f6FC2dE0ced12b02b04505feBbC49666DE00167";
const cryptoGamesVisionAddress = "0x5BCd04f6e6AF6f033B72070ec9957810aDfc3b3E";
const newVisionText = "ブロックチェーンでゲームをもっと面白くする!";
const multiSigWallet = await ethers.getContractAt("MultiSigWallet", multiSigWalletAddress);
const cryptoGamesVision = await ethers.getContractAt("CryptoGamesVision", cryptoGamesVisionAddress);
const data = cryptoGamesVision.interface.encodeFunctionData("setVision", [newVisionText]);
// MultiSigWalletを介してトランザクションを提案する
const tx = await multiSigWallet.submitTransaction(cryptoGamesVisionAddress, 0, data);
const receipt = await tx.wait();
console.log(receipt)
console.log(`Transaction hash: ${receipt.hash}`);
console.log(`submitTransactionのTxIndex: ${receipt.logs[0].topics[2]}`);
// この時点では実際にトランザクションが実行されていない事を確認
// https://mumbai.polygonscan.com/address/0x5BCd04f6e6AF6f033B72070ec9957810aDfc3b3E#readContract
}
// メイン関数を実行し、エラーがあればログに記録
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
npx hardhat run scripts/multisig/submit.ts --network mumbai
②承認
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const multiSigWalletAddress = "0x1f6FC2dE0ced12b02b04505feBbC49666DE00167";
const txIndex = 5; // TODO: submitTransactionを実行した際に取得したトランザクションのインデックス
const multiSigWallet = await ethers.getContractAt("MultiSigWallet", multiSigWalletAddress);
// トランザクションを承認する
const confirmTx = await multiSigWallet.confirmTransaction(txIndex);
console.log(`Confirm Transaction Hash: ${confirmTx.hash}`);
await confirmTx.wait();
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
npx hardhat run scripts/multisig/confirm.ts --network mumbai
③実行
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const multiSigWalletAddress = "0x1f6FC2dE0ced12b02b04505feBbC49666DE00167";
const txIndex = 5; // TODO: submitTransactionを実行した際に取得したトランザクションのインデックス
const multiSigWallet = await ethers.getContractAt("MultiSigWallet", multiSigWalletAddress);
// 必要な数の確認が得られている場合のみ成功。
const executeTx = await multiSigWallet.executeTransaction(txIndex);
console.log(`Execute Transaction Hash: ${executeTx.hash}`);
await executeTx.wait();
// 実行結果を確認
// https://mumbai.polygonscan.com/address/0x5BCd04f6e6AF6f033B72070ec9957810aDfc3b3E#readContract
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
npx hardhat run scripts/multisig/execute.ts --network mumbai
最終的にこのコントラクトのvision関数を書き換えることができていてれば成功です!
最後に
コントラクトを開発運用する上でセキュリティは重要です。今回紹介したマルチシグもセキュリティを向上させるための手段の一つです。この記事が役に立つと嬉しいです。
掲載したコントラクトは一部監査などを通していません。利用する際は自己責任でお願いします。