Spring Security は 5.4 以降、設定の書き方に大幅な変更が入っています。
詳しくは @suke_masa さんの Spring Security 5.7でセキュリティ設定の書き方が大幅に変わる件 - Qiita を参照してください。
基礎・仕組み的な話
認証・認可の話
Remember-Me の話
CSRF の話
セッション管理の話
レスポンスヘッダーの話
メソッドセキュリティの話
CORS の話
Run-As の話
テストの話
MVC, Boot との連携の話
番外編
Spring Security にできること・できないこと
ドメインオブジェクトセキュリティとは
hasAuthority() などを使った認可処理は、基本的に機能くらいの単位の制御になる。
(ある機能(画面)は ○○ という権限を持っている必要がある、とか)
しかし、実際にシステムを作っているとデータ単位で権限の管理がしたくなることがまれによくある。
例えば、データを作成した人と同じ所属の人しかそのデータを見れないようにする、とか、データの更新は作成者かシステム管理者しかできないようにする、とか。
Spring Security には、このようなデータ単位でのアクセス制御を実現する仕組みが用意されている。
それがドメインオブジェクトセキュリティ、もしくは ACL (Access Control List) と呼ばれている。
Hello World
実装
依存関係
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.security:spring-security-web:4.2.1.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework.security:spring-security-config:4.2.1.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework.security:spring-security-acl:4.2.1.RELEASE' ★追加
compile 'org.springframework:spring-jdbc:4.3.7.RELEASE'
compile 'com.h2database:h2:1.4.193'
}
DB
CREATE TABLE ACL_SID (
ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
PRINCIPAL BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
SID VARCHAR_IGNORECASE(100) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT UNIQUE_UK_1 UNIQUE(SID,PRINCIPAL)
);
CREATE TABLE ACL_CLASS(
ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
CLASS VARCHAR_IGNORECASE(100) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT UNIQUE_UK_2 UNIQUE(CLASS)
);
CREATE TABLE ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY(
ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
OBJECT_ID_CLASS BIGINT NOT NULL,
OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY BIGINT NOT NULL,
PARENT_OBJECT BIGINT,
OWNER_SID BIGINT,
ENTRIES_INHERITING BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT UNIQUE_UK_3 UNIQUE(OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY),
CONSTRAINT FOREIGN_FK_1 FOREIGN KEY(PARENT_OBJECT)REFERENCES ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY(ID),
CONSTRAINT FOREIGN_FK_2 FOREIGN KEY(OBJECT_ID_CLASS)REFERENCES ACL_CLASS(ID),
CONSTRAINT FOREIGN_FK_3 FOREIGN KEY(OWNER_SID)REFERENCES ACL_SID(ID)
);
CREATE TABLE ACL_ENTRY(
ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY BIGINT NOT NULL,
ACE_ORDER INT NOT NULL,
SID BIGINT NOT NULL,
MASK INTEGER NOT NULL,
GRANTING BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
AUDIT_SUCCESS BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
AUDIT_FAILURE BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT UNIQUE_UK_4 UNIQUE(ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER),
CONSTRAINT FOREIGN_FK_4 FOREIGN KEY(ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY) REFERENCES ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY(ID),
CONSTRAINT FOREIGN_FK_5 FOREIGN KEY(SID) REFERENCES ACL_SID(ID)
);
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (99, false, 'SAMPLE_AUTHORITY');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1000, 100, 44, NULL, 9, true);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 1000, 0, 99, 1, true, false, false);
確認用の共通実装
package sample.spring.security.domain;
public class Foo {
private final long id;
public Foo(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Foo{id=" + id + '}';
}
}
-
idを持つだけの単純なクラス。
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
public class MyAclSampleService {
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void logic(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("foo=" + foo);
}
}
- 引数で受け取った
fooを標準出力する -
@PreAuthorizeでメソッドをアノテートし、hasPermission()関数を使ってドメインオブジェクトへのアクセス権限をチェックしている - ここでは引数
fooに対してreadの権限があるかどうかをチェックしている
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.printPrincipal();
this.callServiceLogic(new Foo(44L), req);
this.callServiceLogic(new Foo(45L), req);
}
private void printPrincipal() {
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
String name = auth.getName();
System.out.println("name=" + name);
System.out.println("authorities=" +
auth.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "))
);
}
private void callServiceLogic(Foo foo, HttpServletRequest req) {
try {
this.findServiceBean(req).logic(foo);
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println("AccessDeniedException : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private MyAclSampleService findServiceBean(HttpServletRequest req) {
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(req.getServletContext());
return context.getBean(MyAclSampleService.class);
}
}
- 現在のプリンシパルの情報を出力したあと、
id=44とid=45でFooのインスタンスを生成し、MyAclSampleServiceのlogic()メソッドを実行している -
AccessDeniedExceptionがスローされた場合は、そのことをコンソールに出力している。
設定
namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd">
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:/sql/create_acl_tables.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:/sql/insert_acl_tables.sql" />
</jdbc:embedded-database>
<sec:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled">
<sec:expression-handler ref="expressionHandler" />
</sec:global-method-security>
<bean id="expressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property name="permissionEvaluator">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.AclPermissionEvaluator">
<constructor-arg ref="aclService" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="aclService" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcAclService">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="lookupStrategy" />
</bean>
<bean id="lookupStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
</bean>
<bean id="aclCache" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.SpringCacheBasedAclCache">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.support.NoOpCache">
<constructor-arg value="myCache" />
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
</bean>
<bean id="aclAuthorizationStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="TEST"/>
</bean>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="permissionGrantingStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ConsoleAuditLogger" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService" />
<sec:http>
<sec:intercept-url pattern="/login" access="permitAll" />
<sec:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="isAuthenticated()" />
<sec:form-login />
<sec:logout />
</sec:http>
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="" />
<sec:user name="bar" password="bar" authorities="SAMPLE_AUTHORITY" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans
Java Configuration
package sample.spring.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import java.util.Collections;
@EnableWebSecurity
@Import(MyGlobalMethodSecurityConfig.class)
public class MySpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin();
}
@Bean
public MyAclSampleService myAclSampleService() {
return new MyAclSampleService();
}
@Autowired
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("foo")
.password("foo")
.authorities(Collections.emptyList())
.and()
.withUser("bar")
.password("bar")
.authorities("SAMPLE_AUTHORITY");
}
}
package sample.spring.security;
import org.springframework.cache.support.NoOpCache;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded.EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded.EmbeddedDatabaseType;
import org.springframework.security.access.PermissionEvaluator;
import org.springframework.security.acls.AclPermissionEvaluator;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ConsoleAuditLogger;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.SpringCacheBasedAclCache;
import org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.LookupStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AclCache;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.PermissionGrantingStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)
public class MyGlobalMethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()
.generateUniqueName(true)
.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2)
.setScriptEncoding("UTF-8")
.addScripts("/sql/create_acl_tables.sql", "/sql/insert_acl_tables.sql")
.build();
}
@Bean
public PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator(AclService aclService) {
return new AclPermissionEvaluator(aclService);
}
@Bean
public AclService aclService(DataSource dataSource, LookupStrategy lookupStrategy) {
return new JdbcAclService(dataSource, lookupStrategy);
}
@Bean
public LookupStrategy lookupStrategy(DataSource dataSource, AclCache aclCache, AclAuthorizationStrategy aclAuthorizationStrategy, PermissionGrantingStrategy permissionGrantingStrategy) {
return new BasicLookupStrategy(
dataSource,
aclCache,
aclAuthorizationStrategy,
permissionGrantingStrategy
);
}
@Bean
public AclCache aclCache(PermissionGrantingStrategy permissionGrantingStrategy, AclAuthorizationStrategy aclAuthorizationStrategy) {
return new SpringCacheBasedAclCache(
new NoOpCache("myCache"),
permissionGrantingStrategy,
aclAuthorizationStrategy
);
}
@Bean
public AclAuthorizationStrategy aclAuthorizationStrategy() {
return new AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("TEST"));
}
@Bean
public PermissionGrantingStrategy permissionGrantingStrategy() {
return new DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy(new ConsoleAuditLogger());
}
}
動作確認
foo ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセスする。
name=foo
authorities=
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
id=44, id=45 どちらもアクセスが拒否された。
続いて bar ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセスする。
name=bar
authorities=SAMPLE_AUTHORITY
foo=Foo{id=44}
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
id=44 は logic() メソッドの実行に成功し、 id=45 はアクセスが拒否された。
仕組み
テーブル
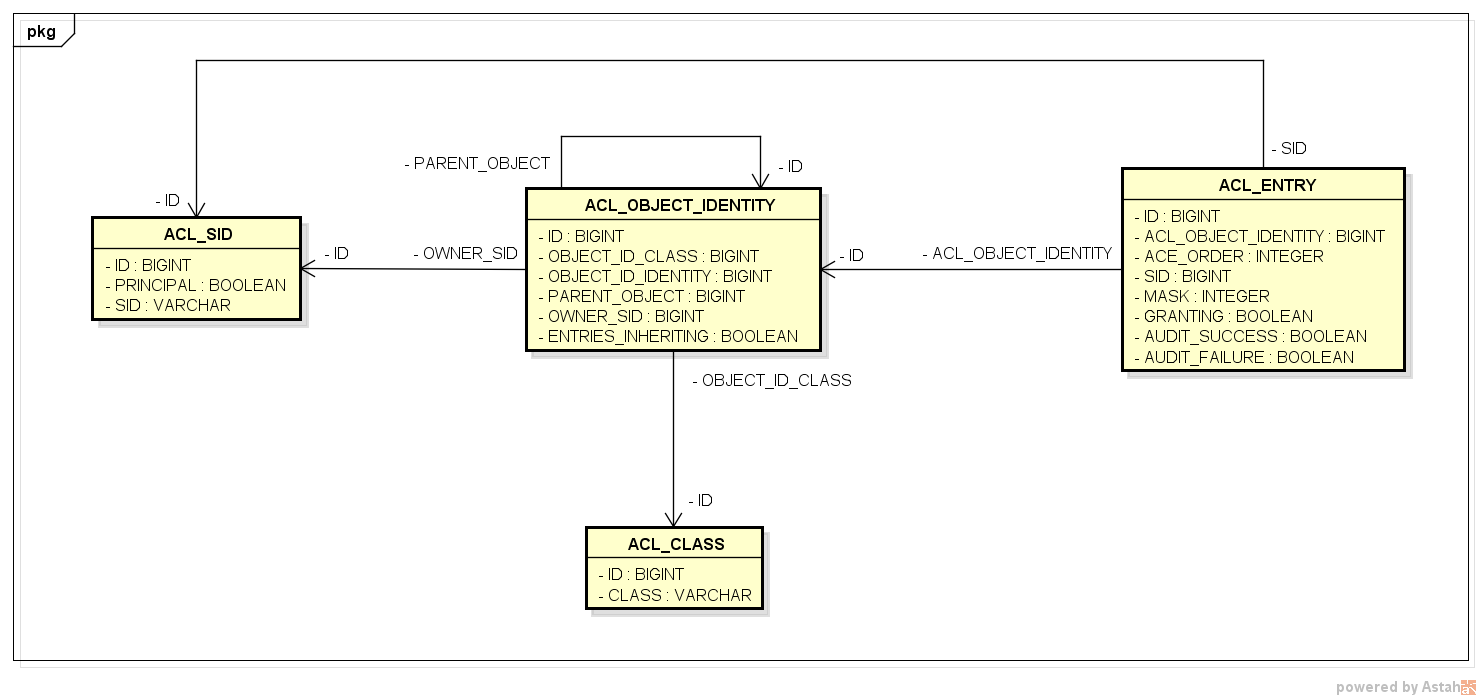
登場するのは次の4つ。
ACL_SIDACL_CLASSACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYACL_ENTRY
テーブル構造は下のような感じ。
※クラス図を利用した ER 図もどきです。雰囲気で読んでください。
矢印は FK を表していて、矢印の元が参照元テーブル、矢印の先が参照先テーブル。
それぞれのテーブルとカラムの意味は以下のような感じ。
※ID の説明は省略
ACL_CLASS
- ドメインオブジェクトの Java クラス名(FQCN)を記録するテーブル
| カラム | 意味 |
|---|---|
CLASS |
ドメインオブジェクトの Java クラス名(FQCN) |
ACL_SID
- パーミッションを付与する対象を定義するテーブル
- 権限(
GrantedAuthority)かプリンシパルを登録する - SID は
Security Identityの略
| カラム | 意味 |
|---|---|
PRINCIPAL |
このレコードがプリンシパルかどうかを区別するフラグtrue → プリンシパルfalse → GrantedAuthority
|
SID |
SID を表現する文字列。 プリンシパルなら username、 GrantedAuthority ならその文字列表現が設定される |
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY
- ドメインオブジェクトの各インスタンスを保持するテーブル
| カラム | 意味 |
|---|---|
OBJECT_ID_CLASS |
ドメインオブジェクトのクラスを指すカラム。ACL_CLASS に外部参照している。 |
OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY |
インスタンスを識別するID |
PARENT_OBJECT |
親の ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY の ID |
OWNER_SID |
このインスタンスを生成した ACL_SID の ID |
ENTRIES_INHERITING |
このインスタンスが他のインスタンスと権限の継承関係を持つかどうかのフラグ |
ACL_ENTRY
-
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYごとにACL_SIDに割り当てるパーミッションを定義したテーブル
| カラム | 意味 |
|---|---|
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY |
このパーミッション定義を適用する ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY の ID |
ACE_ORDER |
1つの ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY に複数の ACL_ENTRTY が紐づく場合の順序 |
SID |
このパーミッション定義を適用する ACL_SID の ID |
MASK |
パーミッション定義を表す整数値(詳細後述) |
GRANTING |
「付与」か「拒否」かのフラグ |
AUDIT_SUCCESS |
このパーミッション定義が付与されたときに監査ログを出力するかのフラグ |
AUDIT_FAILUER |
このパーミッション定義が拒否されたときに監査ログを出力するかのフラグ |
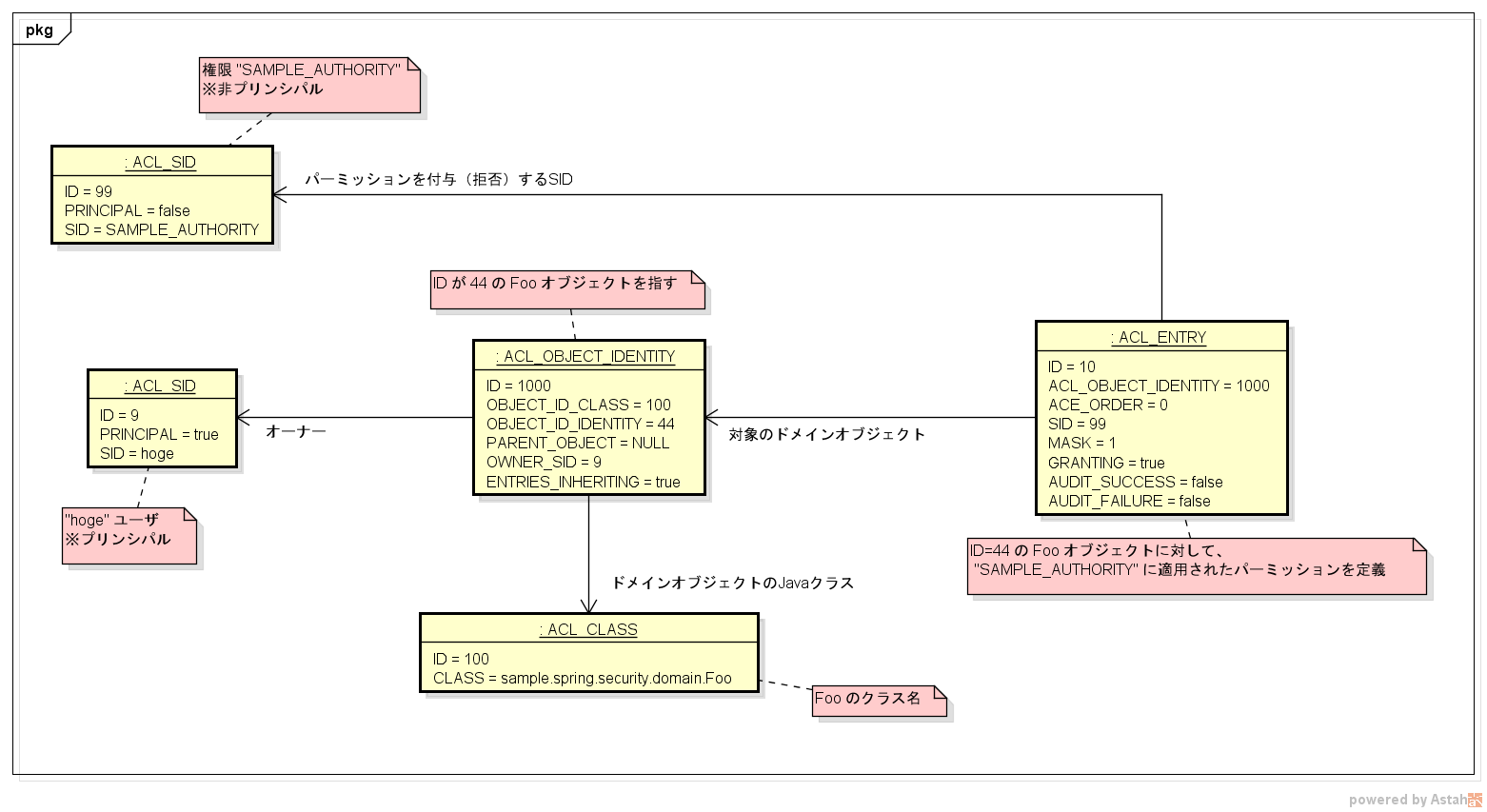
Hello World のデータ
Hello World で使用したデータは、↓のような構造になっていた。
-
ACL_SIDテーブルに2つのレコードを登録している- 1つは
hogeという名前のユーザ(プリンシパル)で、もう1つはSAMPLE_AUTHORITYという名前の権限を表している
- 1つは
-
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYにはid=44のFooオブジェクトを表すレコードを登録している-
hogeをオーナーとして設定している - オーナーとは、そのレコードを作成したプリンシパルを指している
-
-
id=44のFooオブジェクトに設定するパーミッションを定義しているのが、ACL_ENTRYになる-
MASKがパーミッションの定義になっている- 詳細は後述するが、
1は「read(読み取り)」を表している
- 詳細は後述するが、
-
GRANTINGが、パーミッションを「付与」にするのか「拒否」にするのかを表している-
trueは「付与」
-
-
SIDに、パーミッションを適用するACL_SIDを設定している- ここでは
SAMPLE_AUTHORITYを指すようにしている
- ここでは
- つまり、この
ACL_ENTRYのデータは「SAMPLE_AUTHORITY権限を持っていればid=44のFooオブジェクトの読み取りを許可する」という意味になる
-
ドメインオブジェクトの識別子の型
- ドメインオブジェクトの識別子として、
OBJECT_ID_IDENTITYには数値が格納されることになっている - Java でいうと
long型に対応する - 数値型以外で識別しているドメインオブジェクトがある場合はどうなるかというと、公式リファレンスには以下のように記載されている
We do not intend to support non-long identifiers in Spring Security’s ACL module, as longs are already compatible with all database sequences, the most common identifier data type, and are of sufficient length to accommodate all common usage scenarios.
(訳)
我々は、 Spring Security の ACL モジュールでlongでない識別子をサポートするつもりはありません。
longは全てのデータベースシーケンスで既に互換性があり、最も一般的なデータ型であり、全ての一般的な利用シナリオを格納するのに十分な長さを持ちます。
- ということで、ドメインオブジェクトの識別子が
longであることが前提となっている
ACL を有効にするための Bean 設定
SecurityExpressionHandler の拡張
<sec:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled">
<sec:expression-handler ref="expressionHandler" />
</sec:global-method-security>
<bean id="expressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property name="permissionEvaluator">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.AclPermissionEvaluator">
<constructor-arg ref="aclService" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
-
hasPermission()を@PreAuthorize()などの式の中で使えるようにするためには、SecurityExpressionHandlerを拡張する必要がある -
hasPermission()式は、PermissionEvaluatorによって評価される - しかし、
DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandlerが持つデフォルトのPermissionEvaluatorはDenyAllPermissionEvaluatorというクラスで、全ての評価結果をfalseとする実装になっている- つまり、デフォルトだと
hasPermission()式は動作しない(常にfalseと評価される)
- つまり、デフォルトだと
- このため、
DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandlerが持つPermissionEvaluatorを本物の実装に差し替える必要がある - そのために設定するのが、上の
AclPermissionEvaluatorになる
AclService の定義
<bean id="aclService" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcAclService">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="lookupStrategy" />
</bean>
-
AclServiceは ACL の機能を提供する -
JdbcAclServiceは、 JDBC を使ってデータベースに定義された情報にアクセスし、 ACL の機能を実現する - そのため、コンストラクタ引数に
DataSourceを渡す必要がある
LookupStrategy
<bean id="lookupStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
</bean>
- ACL の定義情報(
ACL_CLASSとか)の検索処理は、AclService自身は行わずLookupStrategyに委譲するようになっている -
BasicLookupStrategyは JDBC を使って ACL の定義情報を検索する実装になっている- そのため、コンストラクタ引数に
DataSourceを渡している
- そのため、コンストラクタ引数に
キャッシュの仕組み
<bean id="aclCache" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.SpringCacheBasedAclCache">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.support.NoOpCache">
<constructor-arg value="myCache" />
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
</bean>
- 前述のテーブル定義から想像できる通り、テーブルのデータ件数はかなり大きくなる(オブジェクトごとにデータを登録するので)
- そのため、検索処理を高速化するため、デフォルトでキャッシュの仕組みが組み込まれている
- キャッシュは
AclCacheインターフェースによって表現される - このインターフェースを実装したクラスとして、
SpringCacheBasedAclCacheとEhCacheBasedAclCacheの2つが標準で用意されている- 今回は ACL の動作検証が目的なので、
SpringCacheBasedAclCacheを利用した - 実際のキャッシュの実装には
NoOpCacheを使用している- これは
NoOpとあるように実際はキャッシュを一切しない空実装になっている
- これは
- 実際は
EhCacheBasedAclCacheを利用したりすることになりそう
- 今回は ACL の動作検証が目的なので、
AclAuthorizationStrategy と PermissionGrantingStrategy
-
SpringCacheBasedAclCacheがキャッシュするのはAclImplというクラスのオブジェクトになる - この
AclImplのフィールド定義を見ると、次のようになっている
private Acl parentAcl;
private transient AclAuthorizationStrategy aclAuthorizationStrategy;
private transient PermissionGrantingStrategy permissionGrantingStrategy;
private final List<AccessControlEntry> aces = new ArrayList<AccessControlEntry>();
private ObjectIdentity objectIdentity;
private Serializable id;
private Sid owner; // OwnershipAcl
private List<Sid> loadedSids = null; // includes all SIDs the WHERE clause covered,
-
AclImplはAclインターフェースを実装しており、AclはSerializableを継承している - よって
AclImplはシリアライズ可能でなければならず、上のフィールドはどれも基本的にシリアライズ可能となっている - ただし、
aclAuthorizationStrategyとpermissionGrantingStrategyはtransientで修飾されているため、シリアライズの対象からは除外される - キャッシュがオブジェクトをシリアライズして格納する場合、キャッシュから取り出すときにこの2つのフィールドは失われることになる
- つまり、キャッシュはデシリアライズ時にこの2つのフィールドをキャッシュ前と同じ状態に戻す必要がある
- そのため、キャッシュには
AclAuthorizationStrategyとPermissionGrantingStrategyのインスタンスをコンストラクタ引数で渡す必要がある - ここで指定したインスタンスは、
AclImplがキャッシュから取り出された時に再設定するために利用されている
ちなみに BasicLookupStrategy も AclAuthorizationStrategy と PermissionGrantingStrategy のインスタンスをコンストラクタ引数で受け取る必要がある。
<bean id="lookupStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy">
...
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
</bean>
これは、 BasicLookupStrategy がデータベースの情報から AclImpl オブジェクトを再構築したときに設定するために利用されている。
AclAuthorizationStrategy
<bean id="aclAuthorizationStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="TEST"/>
</bean>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
-
AclAuthorizationStrategyは、 ACL の定義を変更するときに、現在のプリンシパルがその権限を持つかどうかをチェックする役割を持つ - つまり、今回の Hello World では実質利用されていない
- 詳細な説明は後述
PermissionGrantingStrategy
<bean id="permissionGrantingStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ConsoleAuditLogger" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
-
PermissionGrantingStrategyは、hasPermission()で指定したパーミッションを、現在のプリンシパルが持つかどうか具体的に判定する処理を提供する
AuditLogger
-
AuditLoggerは、パーミッションの判定結果をログに残す処理を提供する -
ConsoleAuditLoggerは、唯一提供されている実装クラスで、結果をコンソールに出力する - 詳細は後述
ここまでの話をまとめたクラス図
こんな感じ。
hasPermission()
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void logic(Foo foo) {
- ACL の判定には
hasPermission()式を使用する - 第一引数にはドメインオブジェクトを、第二引数にはパーミッションを指定する
ドメインオブジェクトから ID が取得される方法
-
hasPermission()にドメインオブジェクトが渡されると、 ACL モジュールはドメインオブジェクトにgetId()というメソッドがないかリフレクションで検索する - メソッドがあれば、そのメソッドを実行し、戻された値をドメインオブジェクトの ID として使用する
- 該当するメソッドがないか、戻された値が
Serializableを実装していない場合は例外がスローされる - 要は、ドメインオブジェクトには
long getId()というメソッドを用意しておく必要がある、ということ
ID だけで指定する
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#id, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo', read)")
public void logic(long id) {
- まだドメインオブジェクトのインスタンスができていない場面などでは、 ID を指定する
hasPermission()が利用できる - 第一引数が、ドメインオブジェクトの識別子
- 第二引数が、ドメインオブジェクトの FQCN
- 第三引数が、検証するパーミッション
パーミッションの指定
- パーミッションの指定には
readという定数を指定している - これは
SecurityExpressionRootに定義されている
public final String read = "read";
public final String write = "write";
public final String create = "create";
public final String delete = "delete";
public final String admin = "administration";
パーミッションの定義
パーミッション(read, write, create, delete, administration)の定義は、整数値で表現する。
データベース上は ACL_ENTRY の MASK カラムに保存される。
各パーミッションは、以下のように2進数の各ビットと紐づいている
|5bit目|4bit目|3bit目|2bit目|1bit目|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|administration|delete|create|write|read|
つまり、
| パーミッション | 2進数表現 | 10進数表現 |
|---|---|---|
read |
00001 |
1 |
write |
00010 |
2 |
create |
00100 |
4 |
delete |
01000 |
8 |
administration |
10000 |
16 |
「じゃあ、 read と write の2つのパーミッションを持たせるなら 00011 (10進数で 3)なのかな?」と思うかもしれないがそうではない。
あくまで、各 ACL_ENTRY のレコードの MASK には上記5つのどれかが入る。
複数のパーミッションを付与する場合は、その数だけレコードを登録することになる。
(これはマスクというのか?)
検証
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (98, false, 'AUTHORITY_10101');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (99, false, 'AUTHORITY_01010');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1000, 100, 44, NULL, 9, true);
-- AUTHORITY_10101
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 1000, 0, 98, 1, true, false, false); -- read(00001 = 1)
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (11, 1000, 1, 98, 4, true, false, false); -- create(00100 = 4)
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (12, 1000, 2, 98, 16, true, false, false); -- administration(10000 = 16)
-- AUTHORITY_01010
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (13, 1000, 3, 99, 10, true, false, false); -- write, delete(01010 = 10)
-
AUTHORITY_10101にread(1),create(4),administration(16)のパーミッションをそれぞれ個別に付与 -
AUTHORITY_01010にwrite(2),delete(8)のパーミッションを合体させた01010 = 10を付与
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
...>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="AUTHORITY_10101" />
<sec:user name="bar" password="bar" authorities="AUTHORITY_01010" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
-
fooユーザにAUTHORITY_10101の権限を、 -
barユーザにはAUTHORITY_01010の権限を付与
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
public class MyAclSampleService {
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void read(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("[read] foo=" + foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, write)")
public void write(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("[write] foo=" + foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, create)")
public void create(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("[create] foo=" + foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, delete)")
public void delete(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("[delete] foo=" + foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, admin)")
public void admin(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("[admin] foo=" + foo);
}
}
- メソッドごとに
hasPermission()で必要なパーミッションを指定
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.printPrincipal();
MyAclSampleService serviceBean = this.findServiceBean(req);
Foo foo = new Foo(44L);
this.callServiceLogic("read", () -> serviceBean.read(foo));
this.callServiceLogic("write", () -> serviceBean.write(foo));
this.callServiceLogic("create", () -> serviceBean.create(foo));
this.callServiceLogic("delete", () -> serviceBean.delete(foo));
this.callServiceLogic("admin", () -> serviceBean.admin(foo));
}
private void printPrincipal() {
...
}
private void callServiceLogic(String methodName, Runnable runnable) {
try {
System.out.println("* invoke " + methodName + "()");
runnable.run();
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println("AccessDeniedException : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private MyAclSampleService findServiceBean(HttpServletRequest req) {
...
}
}
-
MyAclSampleServiceの各メソッドを実行して結果を標準出力に表示する
動作確認
name=foo
authorities=AUTHORITY_10101
* invoke read()
[read] foo=Foo{id=44}
* invoke write()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke create()
[create] foo=Foo{id=44}
* invoke delete()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke admin()
[admin] foo=Foo{id=44}
- 個別で付与したパーミッションだけメソッドが実行できた
name=bar
authorities=AUTHORITY_01010
* invoke read()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke write()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke create()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke delete()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
* invoke admin()
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
-
writeとdeleteもブロックされた
マスクがビットマスクでない理由
GitHub のこの Issue に理由が書いてあった。
英語力低いので合っているか怪しいが、だいたい以下のような感じっぽい気がする気もしなくもない感じ。
- パーミッションの継承を利用したときに親のパーミッションを子のパーミッションで拒否するときに、ビットマスクだとどの権限を拒否しているのかが判別しづらくなる(らしい)
- SQL で検索するときに、ビットマスクだと検索が大変になる
ということで、 MASK と言いつつも、実際は整数値の区分のような感じになっている。
結局、「拡張ポイントを用意したので、どうしてもビットマスクで判定したい場合はそいつを利用してくれ」ということになっている。
SEC-1166: Provide strategy interface for AclImpl isGranted() method.
ACL の CRUD
ここまでは、 ACL_ENTRY などのデータはあらかじめ SQL で INSERT 文を用意して登録していた。
しかし、実際の開発でこれらのテーブルを直接編集するのは仕様などを正しく理解しなければならず大変。
なので、これらのデータをメンテナンスするための API が用意されている。
新たにインスタンスの ACL を登録する
実装
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.ObjectIdentity;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
public MyAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
this.aclService = aclService;
}
public void createObjectIdentity() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
MutableAcl acl = this.aclService.createAcl(objectIdentity);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
}
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req, MyAclSampleService.class);
service.createObjectIdentity();
this.printTables(req);
}
private void printTables(HttpServletRequest req) {
this.printTable(req, "ACL_SID");
this.printTable(req, "ACL_CLASS");
this.printTable(req, "ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY");
this.printTable(req, "ACL_ENTRY");
}
private void printTable(HttpServletRequest req, String table) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = this.findServiceBean(req, JdbcTemplate.class);
List<Map<String, Object>> records = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from " + table + " order by id asc");
System.out.println("\n[" + table + "]");
records.forEach(System.out::println);
}
private <T> T findServiceBean(HttpServletRequest req, Class<T> clazz) {
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(req.getServletContext());
return context.getBean(clazz);
}
}
namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<tx:annotation-driven />
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:/sql/create_acl_tables.sql" />
</jdbc:embedded-database>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
...
<bean id="aclService" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcMutableAclService">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="lookupStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
</bean>
...
<bean class="sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService">
<constructor-arg ref="aclService" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
...
</beans>
Java Configuration
package sample.spring.security;
...
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
...
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Import(MyGlobalMethodSecurityConfig.class)
public class MySpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
...
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public MyAclSampleService myAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
return new MyAclSampleService(aclService);
}
...
}
package sample.spring.security;
...
import org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcMutableAclService;
...
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)
public class MyGlobalMethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
...
@Bean
public AclService aclService(DataSource dataSource, LookupStrategy lookupStrategy, AclCache aclCache) {
return new JdbcMutableAclService(dataSource, lookupStrategy, aclCache);
}
...
}
動作確認
MyAclServlet を実行するようにアクセスする。
acl = AclImpl[
id: 1;
objectIdentity: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl[
Type: sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
Identifier: 10
];
owner: PrincipalSid[
foo
];
no ACEs;
inheriting: true;
parent: Null;
aclAuthorizationStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl@2c7d9da4;
permissionGrantingStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy@634b81ac
]
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
※Acl の出力は実際は1行で出力されますが、見やすいように改行をいれています
説明
トランザクションの有効化
- ACL のテーブルを更新する場合はトランザクションの制御が必要になるので、アノテーションベースの宣言的トランザクションを有効にしている
package sample.spring.security.service;
...
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
...
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
...
- クラスを
@Transactionalでアノテート
namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans ...
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
...
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<tx:annotation-driven />
...
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
...
-
<annotation-driven>でアノテーションベースのトランザクションを有効にする -
transactionManagerという名前でPlatformTransactionManagerの実装(DataSourceTransactionManager)を Bean 登録
Java Configuration
...
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
...
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
...
@EnableTransactionManagement
...
public class MySpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
-
@EnableTransactionManagementでトランザクション管理を有効に -
PlatformTransactionManagerの実装であるDataSourceTransactionManagerを Bean 登録
JdbcMutableAclService の定義
namespace
<bean id="aclService" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcMutableAclService">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="lookupStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
</bean>
Java Configuration
import org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.JdbcMutableAclService;
...
@Bean
public AclService aclService(DataSource dataSource, LookupStrategy lookupStrategy, AclCache aclCache) {
return new JdbcMutableAclService(dataSource, lookupStrategy, aclCache);
}
-
JdbcAclServiceのサブクラスとして ACL を更新するためのメソッドが追加されたJdbcMutableAclServiceというクラスがある -
JdbcAclServiceの代わりにこのクラスのオブジェクトを Bean として登録する - コンストラクタ引数で
AclCacheを渡しているが、これは ACL を削除する処理を実行したときにJdbcMutableAclServiceがキャッシュからもその情報を削除するため必要になる
ObjectIdentity の登録
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.ObjectIdentity;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
public MyAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
this.aclService = aclService;
}
public void createObjectIdentity() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
MutableAcl acl = this.aclService.createAcl(objectIdentity);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
}
-
ObjectIdentityのオブジェクトを作成する(ObjectIdentityImpl)-
ObjectIdeneityImplのコンストラクタは、1つ目がドメインオブジェクトのClassオブジェクト、 - 2つ目がドメインオブジェクトの識別子(
ID)
-
-
MutableAclServiceのcreateAcl(ObjectIdentity)メソッドに作成したObjectIdentityを渡す -
createAcl()を実行した時点でACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYに情報が保存される-
ACL_CLASSも、情報が存在しない場合は一緒に作成される
-
- 戻り値として、
MutableAclが返される
オーナー
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
{ID=2, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=11, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
- よく見ると、作成された
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYのOWNER_SIDにはSID=fooのACL_SIDが設定されている - これは、
MutableAclServiceのcreateAcl()を実行したときのログインユーザ(プリンシパル)の情報で記録されている
ACL の Java クラス
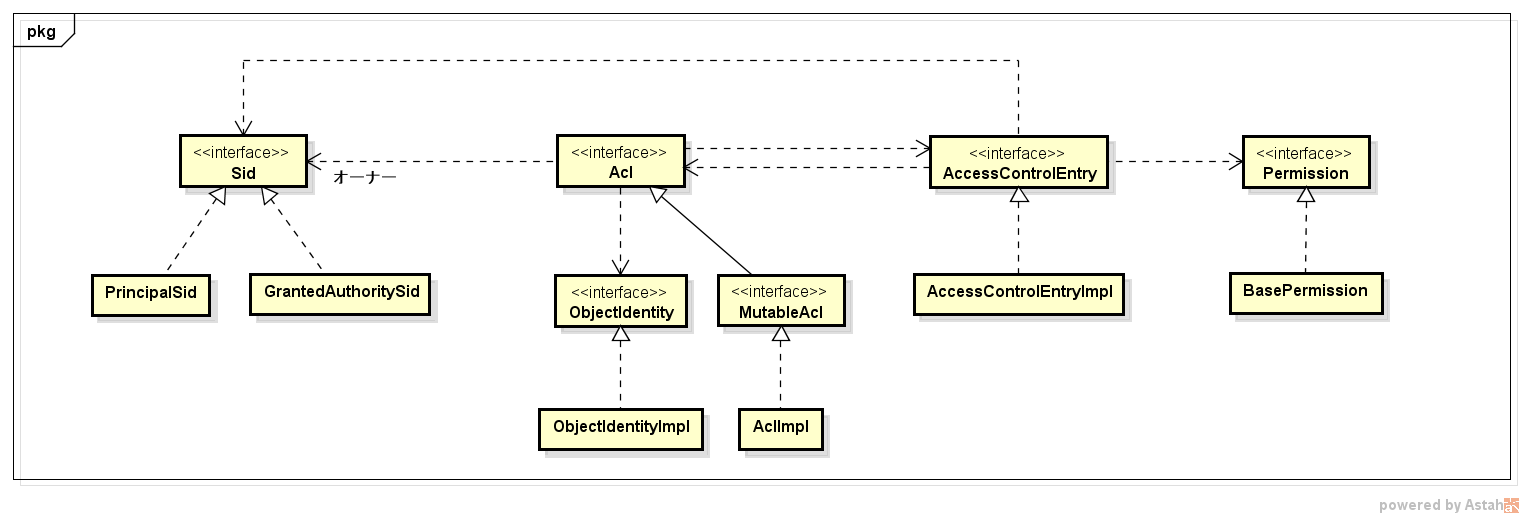
ACL の情報は下のようなクラス構造でモデル化されている。
-
ObjectIdentity- ドメインオブジェクトの識別子を表すオブジェクト
- ドメインオブジェクトの識別子とクラス名を参照できる
-
Acl- ACL のメインとなるオブジェクト
-
ObjectIdentityに対して関連付けられた全てのパーミッションをまとめあげている
-
AccessControlEntry-
Aclに対してSidに割り当てられた個々のパーミッションを表すオブジェクト
-
-
Permission- 具体的なパーミッション情報を持つオブジェクト
-
Sid- パーミッションを割り当てる対象を表すオブジェクト
- プリンシパルか
GrantedAuthorityのいずれか
MutableAclService の createAcl() を実行すると、引数で指定した ObjectIdentity に紐づく形で Acl, AccessControlEntry, Permission, Sid がそれぞれ構築されている。
既存の ACL を検索する
実装
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.Acl;
...
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
...
public void createObjectIdentity() {
...
}
public void findAcl() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
Acl acl = aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
}
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req, MyAclSampleService.class);
service.createObjectIdentity();
this.printTables(req);
service.findAcl();
}
...
}
動作確認
acl = AclImpl[
id: 1;
objectIdentity: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl[
Type: sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
Identifier: 10
];
owner: PrincipalSid[
foo
];
no ACEs;
inheriting: true;
parent: Null;
aclAuthorizationStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl@2c7d9da4;
permissionGrantingStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy@634b81ac
]
説明
public void findAcl() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
Acl acl = aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
-
AclServiceにAclを検索するためのメソッドが用意されている -
readAclById(ObjectIdentity)で、ObjectIdentityに紐づくAclを検索できる
パーミッションを追加する
実装
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.GrantedAuthoritySid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.PrincipalSid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AccessControlEntry;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.Acl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.ObjectIdentity;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
import java.util.List;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
...
public void createObjectIdentity() {
...
}
public void findAcl() {
...
}
public void addPermission() {
// 更新する ACL を検索して、
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
MutableAcl acl = (MutableAcl) aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
// 権限 "HOGE_AUTHORITY" に CREATE のパーミッションを付与
List<AccessControlEntry> entries = acl.getEntries();
GrantedAuthoritySid grantedAuthoritySid = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("HOGE_AUTHORITY"));
acl.insertAce(entries.size(), BasePermission.CREATE, grantedAuthoritySid, true);
// プリンシパル "test_user" に対して WRITE のパーミッションを付与
PrincipalSid principalSid = new PrincipalSid("test_user");
acl.insertAce(entries.size(), BasePermission.WRITE, principalSid, true);
// ACL の変更を保存する
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
}
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req, MyAclSampleService.class);
service.createObjectIdentity();
this.printTables(req);
service.findAcl();
service.addPermission();
this.printTables(req);
}
...
}
動作確認
★パーミッション追加前
acl = AclImpl[
id: 1;
objectIdentity: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl[
Type: sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
Identifier: 10
];
owner: PrincipalSid[
foo
];
no ACEs;
inheriting: true;
parent: Null;
aclAuthorizationStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl@162ff71c;
permissionGrantingStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy@742976d3
]
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
...
★パーミッション追加後
acl = AclImpl[
id: 1;
objectIdentity: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl[
Type: sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
Identifier: 10
];
owner: PrincipalSid[
foo
];
AccessControlEntryImpl[
id: null;
granting: true;
sid: PrincipalSid[
test_user
];
permission: BasePermission[
..............................W.=2
];
auditSuccess: false;
auditFailure: false
]
AccessControlEntryImpl[
id: null;
granting: true;
sid: GrantedAuthoritySid[
HOGE_AUTHORITY
];
permission: BasePermission[
.............................C..=4
];
auditSuccess: false;
auditFailure: false
]
inheriting: true;
parent: Null;
aclAuthorizationStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl@162ff71c;
permissionGrantingStrategy: org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy@742976d3
]
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
{ID=2, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=test_user}
{ID=3, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=HOGE_AUTHORITY}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=1, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=2, MASK=2, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=2, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=3, MASK=4, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
説明
public void addPermission() {
// 更新する ACL を検索して、
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
MutableAcl acl = (MutableAcl) aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
// 権限 "HOGE_AUTHORITY" に CREATE のパーミッションを付与
List<AccessControlEntry> entries = acl.getEntries();
GrantedAuthoritySid grantedAuthoritySid = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("HOGE_AUTHORITY"));
acl.insertAce(entries.size(), BasePermission.CREATE, grantedAuthoritySid, true);
// プリンシパル "test_user" に対して WRITE のパーミッションを付与
PrincipalSid principalSid = new PrincipalSid("test_user");
acl.insertAce(entries.size(), BasePermission.WRITE, principalSid, true);
// ACL の変更を保存する
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
System.out.println("acl = " + acl);
}
-
MutableAclのinsertAce(int, Permission, Sid, boolean)を実行することでAclにパーミッションを追加できる- 内部的には
AclにAccessControlEntryが追加される
- 内部的には
- 最初の
intは、パーミッションの挿入位置を0始まりのインデックスで指定する- パーミッション(
AccessControlEntry)はAcl内部でListで保持されており、add(int, E)メソッドの第一引数に渡される - なので、
0より小さい値やsize()より大きい値を渡すとエラーになる(size()と同じなら末尾に追加される) - DB だと
ACL_ENTRYのACE_ORDERになる
- パーミッション(
-
Permissionは、実装クラスであるBasePermissionに定義された定数を指定できる -
SidはGrantedAuthoritySidかPrincipalSidを指定する- 権限に対してパーミッションを割り当てるなら
GrantedAuthoritySid - プリンシパルに対してパーミッションを割り当てるなら
PrincipalSidを使用する
- 権限に対してパーミッションを割り当てるなら
- 最後の
booleanは、パーミッションを「付与」にするのか「拒否」にするのかを指定している-
trueは付与、falseは拒否
-
拒否のパーミッションと ACE_ORDER
実装
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.GrantedAuthoritySid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.NotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.ObjectIdentity;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
public MyAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
this.aclService = aclService;
}
public void addPermission() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
try {
this.aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
} catch (NotFoundException e) {
MutableAcl acl = this.aclService.createAcl(objectIdentity);
GrantedAuthoritySid deniedRead = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("DENIED_READ"));
acl.insertAce(0, BasePermission.READ, deniedRead, false);
GrantedAuthoritySid permitRead = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("PERMIT_READ"));
acl.insertAce(1, BasePermission.READ, permitRead, true);
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
}
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void read(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("read(" + foo + ")");
}
}
- 初回は
readAclById()で ACL が取得できずNotFoundExceptionがスローされるので、そのときだけパーミッションを登録-
DENIED_READ権限にはreadの権限を「拒否」で登録し、 -
PERMIT_READ権限にはreadの権限を「付与」で登録している - また、順番は
DENIED_READを0にして先にくるようにしている
-
- 既に ACL が登録されている場合は何もしない
- また
read()メソッドを@PreAuthorizeでアノテートし、hasPermission()でreadの権限があるかチェックしている
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.printPrincipal();
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req, MyAclSampleService.class);
service.addPermission();
this.printTables(req);
try {
service.read(new Foo(10L));
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
...
}
- 現在のプリンシパルの情報を出力し(
printPrincipal()) - ACL を登録(
addPermission()) - テーブルに登録された情報を出力(
printTables()) -
read()メソッドを実行し、AccessDeniedExceptionがスローされた場合はメッセージ出力
という実装
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
...>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="PERMIT_READ" />
<sec:user name="bar" password="bar" authorities="PERMIT_READ,DENIED_READ" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
-
fooとbarの2つのユーザを定義 -
fooユーザにはPERMIT_READ権限を設定 -
barユーザにはPERMIT_READとDENIED_READの両方の権限を設定
動作確認
foo ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセスする。
name=foo
authorities=PERMIT_READ
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
{ID=2, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=DENIED_READ}
{ID=3, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=PERMIT_READ}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=1, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=2, MASK=1, GRANTING=false, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=2, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=3, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
read(Foo{id=10})
read() メソッドが実行できている
続いて bar ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセスする。
name=bar
authorities=DENIED_READ, PERMIT_READ
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
{ID=2, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=DENIED_READ}
{ID=3, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=PERMIT_READ}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=1, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=2, MASK=1, GRANTING=false, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=2, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=3, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
Access is denied
アクセスは拒否された。
説明
MutableAcl acl = this.aclService.createAcl(objectIdentity);
GrantedAuthoritySid deniedRead = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("DENIED_READ"));
acl.insertAce(0, BasePermission.READ, deniedRead, false);
GrantedAuthoritySid permitRead = new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("PERMIT_READ"));
acl.insertAce(1, BasePermission.READ, permitRead, true);
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="PERMIT_READ" />
<sec:user name="bar" password="bar" authorities="PERMIT_READ,DENIED_READ" />
-
ACE_ORDERは順序が先の方が優先して適用されるもよう -
barユーザーにはPERMIT_READも設定されていたが、DENIED_READのほうがPERMIT_READよりもACE_ORDERが先だったため、パーミッションは「拒否」と判定された
使いどころは?
- 最初この仕組み(拒否のパーミッションと
ACEの順序設定)を見たとき、あまり使いどころが思いつかなかった- アクセスを拒否したいだけなら、単純にパーミッションを与えなければいいだけなので、あえて「拒否」のパーミッションを与える場面が分からなかった
- 唯一思いついたのが、↑のような「完全に拒否する」権限を定義する使い方
- 「付与」系のパーミッションは末尾に追加し、「拒否」系のパーミッションは先頭に追加するようにしていれば、「拒否」のパーミッションが常に優先されるようになる
- そして「拒否」のパーミッションを権限(
GrantedAuthority)と紐づけておけば、「その権限を与えられると基本的にアクセスができなくなる」みたいな振る舞いになる - そんな場面があるのかは分からないが、「アクセスを基本拒否したい」ときに「この権限を設定すればアクセス不可にできる」みたいな制御ができる気がする
ACL の更新で行われる権限のチェック
ACL の更新は誰でもできるわけではない。
実装
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (19, true, 'admin');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1000, 100, 10, NULL, 9, true);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10000, 1000, 0, 19, 16, true, false, false); -- admin ユーザに administration(16) のパーミッションを付与
-
ID=10のFooオブジェクトについてのACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYを作成 - オーナーに
hogeプリンシパルを設定 -
adminプリンシパルにはadministrationのパーミッションを付与
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
...>
...
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:/sql/create_acl_tables.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:/sql/insert_acl_tables.sql" />
</jdbc:embedded-database>
...
<bean id="aclAuthorizationStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="PERMISSION_MANAGER"/>
</bean>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="hoge" password="hoge" authorities="" />
<sec:user name="fuga" password="fuga" authorities="" />
<sec:user name="piyo" password="piyo" authorities="PERMISSION_MANAGER" />
<sec:user name="admin" password="admin" authorities="" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
-
AclAuthorizationStrategyImplのコンストラクタ引数でPERMISSION_MANAGERを渡している -
hoge,fuga,adminユーザは権限なし -
piyoユーザにだけPERMISSION_MANAGER権限を付与
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.GrantedAuthoritySid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.PrincipalSid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AlreadyExistsException;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.ObjectIdentity;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
public MyAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
this.aclService = aclService;
}
public void addPermission() {
ObjectIdentity objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 10L);
MutableAcl acl = (MutableAcl) this.aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
acl.insertAce(
acl.getEntries().size(),
BasePermission.READ,
new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("test")),
true
);
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
}
}
-
id=10のFooオブジェクトを検索し、insertAce()でパーミッションを追加している
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.NotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req, MyAclSampleService.class);
this.printPrincipal();
this.printTables(req);
try {
System.out.println("service.addPermission()");
service.addPermission();
this.printTables(req);
} catch (AccessDeniedException | NotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("e.class = " + e.getClass() + ", message = " + e.getMessage());
}
}
...
}
- 処理の前にログインしているユーザの情報とデータベースの状態を出力
-
MyAclSampleServiceのaddPermission()メソッドを実行したのち、データーベースの状態を再度出力 -
addPermission()で例外が発生した場合は、その情報を出力
動作確認
hoge ユーザでアクセスした場合
★ユーザーの情報
name=hoge
authorities=
★更新前のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10000, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
★メソッド実行
service.addPermission()
★更新後のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
{ID=20, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=test}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10001, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=10002, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=20, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
- パーミッションの追加が成功している
fuga ユーザでアクセスした場合
★ユーザーの情報
name=fuga
authorities=
★更新前のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10000, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
★メソッド実行
service.addPermission()
★エラーの情報
e.class = class org.springframework.security.acls.model.NotFoundException, message = Unable to locate a matching ACE for passed permissions and SIDs
- パーミッションの追加はできず、例外(
NotFoundException)がスローされた
piyo ユーザでアクセスした場合
★ユーザーの情報
name=piyo
authorities=PERMISSION_MANAGER
★更新前のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10000, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
★メソッド実行
service.addPermission()
★更新後のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
{ID=20, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=test}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10001, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=10002, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=20, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
- パーミッションの更新が成功している
admin ユーザでアクセスした場合
★ユーザーの情報
name=admin
authorities=
★更新前のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10000, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
★メソッド実行
service.addPermission()
★更新後のテーブルの状態
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=19, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=admin}
{ID=20, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=test}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=10, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10001, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=19, MASK=16, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
{ID=10002, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=1, SID=20, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
- パーミッションの更新が成功している
説明
- パーミッションの更新には、次の要素が関わってくる
- 更新しようとしている ACL のオーナーかどうか
- 更新しようとしている ACL に対して
administrationのパーミッションが付与されているかどうか -
AclAuthorizationStrategyImplのコンストラクタ引数で指定した権限を持っているかどうか - ACL の更新種別(一般、所有、監査)
- そして、次のような順序で更新可能かどうかが判断されている
- 現在のプリンシパルが更新しようとしている ACL のオーナーの場合、 ACL の更新種別が「一般」 or 「所有」の場合は、許可
- そうでない場合、
AclAuthorizationStrategyImplで指定した権限を持っていれば許可 - そうでない場合、更新しようとしている ACL に対して
administrationのパーミッションが付与されていれば許可 - そうでない場合は 不許可
更新の種類
ACL の更新の種類には、次の3つがある。
- 一般
- 所有
- 監査
そして、 ACL を更新するメソッドは、それぞれ以下のように分類されている。
| メソッド | 更新の種類 |
|---|---|
insertAce() |
一般 |
updateAce() |
一般 |
deleteAce() |
一般 |
setParent() |
一般 |
setEntriesInheriting() |
一般 |
setOwner() |
所有 |
updateAuditing() |
監査 |
ちなみに、この3つの種類は AclAuthorizationStrategy インターフェースに定義されている。
public interface AclAuthorizationStrategy {
int CHANGE_OWNERSHIP = 0; 所有
int CHANGE_AUDITING = 1; 監査
int CHANGE_GENERAL = 2; 一般
AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl で指定する権限
<bean id="aclAuthorizationStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="PERMISSION_MANAGER"/>
</bean>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
-
AclAuthorizationStrategyImplのコンストラクタで渡していたGrantedAuthorityは、 ACL を更新するときに利用されている - 更新しようとしているログインユーザがここで指定した権限を持っていれば、更新が許可されるようになっている。
更新の種類ごとに権限を指定する
上記例では PERMISSION_MANAGER という権限だけを指定してる。
この場合、この権限を持っていれば全ての更新の種類(一般、所有、監査)が許可されることになる。
もし「"一般" の更新の場合は●●という権限が必要で、 "所有" の更新のときは▲▲、 "監査" のときは★★が必要」といった制御がしたい場合は、次のように Bean を定義する。
<bean id="aclAuthorizationStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="PERMISSION_MANAGER_OWNERSHIP"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="PERMISSION_MANAGER_AUDIT"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority">
<constructor-arg value="PERMISSION_MANAGER_GENERAL"/>
</bean>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
- コンストラクタ引数に渡す
GrantedAuthorityの数を3つにする(2つや4つだとエラーになるので注意) - 以下のように、指定した
GrantedAuthorityの位置により、どの更新種別に権限が紐づけられるかが決まる- 「所有」に関する更新の場合に必要になる権限を指定する
- 「監査」に関する更新の場合に必要になる権限を指定する
- 「一般」に関する更新の場合に必要になる権限を指定する
更新が不許可となった場合の挙動について
前述の例では、更新が不許可となった場合 NotFoundException がスローされていた。
不許可の場合、常に NotFoundException がスローされるかというと、実は違う。
もし更新対象の ACL に administration のパーミッションが「拒否」で設定されていた場合、 AccessDeniedException がスローされる。
これは実はバグで、本当はどちらの場合でも AccessDeniedException がスローされるのが正しい。
GitHub の issue を検索するとこのバグが起票されている。
しかし、 2017/07/09 現在この issue は OPEN のままで、対応されている様子はない。
この問題が認識されたのは、 2009 年のことらしいので、完全に放置されている(これに限らず、 ACL 関係の issue はどれも長期間放置されていて、あまりメンテする気はないのかもしれない)。
これ以外にも、 ACL の更新に関する権限チェックには ロールの階層化を利用していた場合に親のロールが参照されない といったバグが上げられている(こちらも長期間放置されている)。
この辺を正しい動作で利用したい場合は、既存の AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl をコピーして、問題箇所を修正した独自実装クラスを作り、 AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl の代わりに利用するといった対応が必要になると思われる。
(もしくは修正版を本家に Pull Request するか)
パーミッションに継承関係を持たせる
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY には、継承関係を持たせることができる。
Hello World
実装
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (98, false, 'READONLY');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1000, 100, 44, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1001, 100, 45, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1002, 100, 46, 1000, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1003, 100, 47, 1000, 9, true);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 1000, 0, 98, 1, true, false, false);
-
id=44...47のACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYを定義している -
id=44にだけREADONLY権限に対してreadのパーミッションを付与している -
id=45は、親オブジェクトなどを一切指定していない -
id=46は、親オブジェクトのID だけPARENT_OBJECTで指定している(ENTRIES_INHERITINGはfalse) -
id=47は、親オブジェクトを指定したうえでENTRIES_INHERITINGをtrueにしている
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void read(Foo foo) {
System.out.println("read(" + foo + ")");
}
}
- 引数で受け取る
Fooオブジェクトに対してreadのパーミッションを持っていることをチェックする
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.printPrincipal();
this.printTables(req);
this.callServiceLogic(req, 44L);
this.callServiceLogic(req, 45L);
this.callServiceLogic(req, 46L);
this.callServiceLogic(req, 47L);
}
private void callServiceLogic(HttpServletRequest req, long id) {
try {
System.out.println("id=" + id);
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req);
Foo foo = new Foo(id);
service.read(foo);
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println("AccessDeniedException : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
...
}
-
id=44...47でFooオブジェクトを生成し、MyAclSampleServiceのread()メソッドを実行する
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
...>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="READONLY" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
-
fooユーザにREADONLY権限を付与
動作確認
foo ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセスする。
name=foo
authorities=READONLY
[ACL_SID]
{ID=9, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=hoge}
{ID=98, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=READONLY}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=100, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1000, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=44, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=false}
{ID=1001, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=45, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=false}
{ID=1002, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=46, PARENT_OBJECT=1000, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=false}
{ID=1003, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=100, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=47, PARENT_OBJECT=1000, OWNER_SID=9, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=10, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1000, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=98, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
id=44
read(Foo{id=44})
id=45
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
id=46
AccessDeniedException : Access is denied
id=47
read(Foo{id=47})
-
id=44, 47のみメソッドが実行できて、id=45, 46は拒否された
説明
...
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1000, 100, 44, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1001, 100, 45, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1002, 100, 46, 1000, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (1003, 100, 47, 1000, 9, true);
- パーミッションに継承関係を持たせるには、
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYに次の2つの設定を追加する-
PARENT_OBJECTに、親となるACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYのIDを設定する -
ENTRIES_INHERITINGにtrueを設定する
-
- これにより、子供の
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYに関するパーミッションのチェックが行われるときに、親までさかのぼってパーミッションの判定をするようになる
デフォルトのパーミッションとしての利用
- パーミッションの継承を利用すれば、例えば「デフォルトのパーミッション」みたいなことが実現でき、定義情報を一か所で管理することができる
-
使い方として正しいかは謎だが、
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYのOBJECT_IDENTITYは別に実在するidでなくても登録はできる - 仮に
OBJECT_IDENTITY=-1などのあり得ない値でACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYを登録しておいて、他の通常のACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYはこのデフォルトのACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYを継承するようにすれば、デフォルトパーミッションが実現できる - ただ、継承を何層にも重ねてしまうと、 SQL だけで「その
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITYに設定されている全てのパーミッション」を特定することが困難になる気がする(階層の最大値が決まっているなら、その数だけLEFT JOINすればイケる?) - 階層はなるべく少なくしておいたほうが無難な気がする
プログラムで親を設定する
実装
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.GrantedAuthoritySid;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ObjectIdentityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAcl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.MutableAclService;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
@Transactional
public class MyAclSampleService {
private MutableAclService aclService;
public MyAclSampleService(MutableAclService aclService) {
this.aclService = aclService;
}
public void init() {
ObjectIdentityImpl parentId = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 44L);
MutableAcl parentAcl = this.aclService.createAcl(parentId);
parentAcl.insertAce(
parentAcl.getEntries().size(),
BasePermission.READ,
new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("READONLY")),
true
);
this.aclService.updateAcl(parentAcl);
ObjectIdentityImpl childId = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 45L);
MutableAcl childAcl = this.aclService.createAcl(childId);
childAcl.setParent(parentAcl);
this.aclService.updateAcl(childAcl);
}
}
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req);
service.init();
this.printTables(req);
}
...
}
動作確認
/acl にアクセス
[ACL_SID]
{ID=1, PRINCIPAL=true, SID=foo}
{ID=2, PRINCIPAL=false, SID=READONLY}
[ACL_CLASS]
{ID=1, CLASS=sample.spring.security.domain.Foo}
[ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY]
{ID=1, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=44, PARENT_OBJECT=null, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
{ID=2, OBJECT_ID_CLASS=1, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY=45, PARENT_OBJECT=1, OWNER_SID=1, ENTRIES_INHERITING=true}
[ACL_ENTRY]
{ID=1, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY=1, ACE_ORDER=0, SID=2, MASK=1, GRANTING=true, AUDIT_SUCCESS=false, AUDIT_FAILURE=false}
説明
public void init() {
ObjectIdentityImpl parentId = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 44L);
MutableAcl parentAcl = this.aclService.createAcl(parentId);
parentAcl.insertAce(
parentAcl.getEntries().size(),
BasePermission.READ,
new GrantedAuthoritySid(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("READONLY")),
true
);
this.aclService.updateAcl(parentAcl);
ObjectIdentityImpl childId = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 45L);
MutableAcl childAcl = this.aclService.createAcl(childId);
childAcl.setParent(parentAcl); // ★ここで親を設定
this.aclService.updateAcl(childAcl);
}
- ある ACL に親の ACL を設定するには、
MutableAclのsetParent()メソッドを使用する -
ENTRIES_INHERITINGは、 ACL を新規に作成するとデフォルトがtrueなので、新規作成なら明示は不要(一応setEntriesInheriting()メソッドで設定が可能)
監査ログ
パーミッションを付与したか拒否したかのタイミングで、その情報を監査ログとして出力する仕組みが用意されている。
Hello World
実装
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (98, false, 'READONLY');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (999, 100, 44, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 999, 0, 98, 1, true, true, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (11, 999, 1, 98, 2, false, false, true);
-
Fooのid=44について、READONLY権限に対して「readの付与」と「writeの拒否」のパーミッションを設定 - 「
readの付与」のACL_ENTRYは、AUDIT_SUCCESSをtrueに - 「
writeの拒否」のACL_ENTRYは、AUDIT_FAILUREをtrueに設定
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
public class MyAclSampleService {
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void read(Foo foo) {
System.out.println(foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, write)")
public void write(Foo foo) {
System.out.println(foo);
}
}
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
...
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req);
Foo foo = new Foo(44L);
try {
System.out.println("service.read()");
service.read(foo);
System.out.println("service.write()");
service.write(foo);
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
...
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
...>
...
<bean id="permissionGrantingStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ConsoleAuditLogger" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="READONLY" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
動作確認
foo ユーザでログインして /acl にアクセス
service.read()
GRANTED due to ACE: AccessControlEntryImpl[id: 10; granting: true; sid: GrantedAuthoritySid[READONLY]; permission: BasePermission[...............................R=1]; auditSuccess: true; auditFailure: false]
Foo{id=44}
service.write()
DENIED due to ACE: AccessControlEntryImpl[id: 11; granting: false; sid: GrantedAuthoritySid[READONLY]; permission: BasePermission[..............................W.=2]; auditSuccess: false; auditFailure: true]
Access is denied
- 各メソッドの実行前に、パーミッションが付与されたか拒否されたかがコンソールに出力されている
説明
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 999, 0, 98, 1, true, true, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (11, 999, 1, 98, 2, false, false, true);
- 監査ログの出力を有効にするには、
ACL_ENTRYのAUDIT_SUCCESSまたはAUDIT_FAILUREにtrueを設定する -
AUDIT_SUCCESSがtrueの場合、パーミッションの付与が判定されたときにログが出力される -
AUDIT_FAILUREがtrueの場合は、パーミッションの拒否が判定されたときにログが出力される
<bean id="permissionGrantingStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.ConsoleAuditLogger" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
- 監査ログの出力は、
AuditLoggerインターフェースを実装したクラスによって行われる -
AuditLoggerは、DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategyにセットする -
AuditLoggerの実装として標準で用意されているConsoleAuditLoggerクラスは、ログを標準出力に出力する
デフォルトの監査ログ出力の実装
ConsoleAuditLogger の実装は次のようになっている
package org.springframework.security.acls.domain;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AccessControlEntry;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AuditableAccessControlEntry;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class ConsoleAuditLogger implements AuditLogger {
public void logIfNeeded(boolean granted, AccessControlEntry ace) {
Assert.notNull(ace, "AccessControlEntry required");
if (ace instanceof AuditableAccessControlEntry) {
AuditableAccessControlEntry auditableAce = (AuditableAccessControlEntry) ace;
if (granted && auditableAce.isAuditSuccess()) {
System.out.println("GRANTED due to ACE: " + ace);
}
else if (!granted && auditableAce.isAuditFailure()) {
System.out.println("DENIED due to ACE: " + ace);
}
}
}
}
-
AuditLoggerインターフェースにはlogIfNeeded(boolean, AccessControlEntry)メソッドが定義されている- 第一引数には、パーミッションが付与されたのか拒否されたのかのフラグが渡される
- 第二引数には、そのパーミッションの情報を保持する
AccessControlEntryオブジェクトが渡される
- 監査ログを出力するかどうかの設定(
AUDIT_SUCCESS,AUDIT_FAILURE)を取得するには、AuditableAccessControlEntryのisAuditSuccess()かisAuditFailure()のメソッドを使用する(引数のAccessControlEntryをキャストする必要がある) - 実際はログファイルとかに出力する必要があると思うので、この実装を参考にして独自の
AuditLoggerクラスを実装することになる気がする
プログラムから設定する
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.AuditableAcl;
...
ObjectIdentityImpl objectIdentity = new ObjectIdentityImpl(Foo.class, 44L);
AuditableAcl acl = (AuditableAcl) this.aclService.readAclById(objectIdentity);
acl.updateAuditing(0, true, false);
this.aclService.updateAcl(acl);
-
AUDIT_SUCCESSとAUDIT_FAILUREをプログラムから変更するには、AuditableAclのupdateAuditing(int, boolean, boolean)メソッドを使用する- 第一引数が、変更したい
AccessControlEntryを指定するためのインデックス - 第二引数が
AUDIT_SUCCESSに設定する値 - 第三引数が
AUDIT_FAILUREに設定する値
- 第一引数が、変更したい
独自のパーミッションを定義する
デフォルトで使用できるパーミッションは read, write, create, delete, administration の 5 つだけだが、独自のパーミッションを追加で定義することもできる。
32 (二進数表現で 100000)を作ってみる。
実装
package sample.spring.security.acl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.Permission;
public class MyPermission extends BasePermission {
public static final Permission HOGE = new MyPermission(0b100000, 'H');
private MyPermission(int mask, char code) {
super(mask, code);
}
}
-
BasePermissionを継承して独自のPermissionクラスを作成する -
HOGEという定数を作成し、マスクを0b100000(十進数で32)、コードを'H'にしてインスタンスを設定している
INSERT INTO ACL_CLASS (ID, CLASS)
VALUES (100, 'sample.spring.security.domain.Foo');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (9, true, 'hoge');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (98, false, 'READONLY');
INSERT INTO ACL_SID (ID, PRINCIPAL, SID)
VALUES (99, false, 'HOGE');
INSERT INTO ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY (ID, OBJECT_ID_CLASS, OBJECT_ID_IDENTITY, PARENT_OBJECT, OWNER_SID, ENTRIES_INHERITING)
VALUES (999, 100, 44, NULL, 9, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (10, 999, 0, 98, 1, true, false, false);
INSERT INTO ACL_ENTRY (ID, ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY, ACE_ORDER, SID, MASK, GRANTING, AUDIT_SUCCESS, AUDIT_FAILURE)
VALUES (11, 999, 1, 99, 32, true, false, false);
-
READONLY権限に対してreadのパーミッションを付与 -
HOGE権限に対して32(MyPermissionで定義したHOGE)のパーミッションを付与
package sample.spring.security.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
public class MyAclSampleService {
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, read)")
public void read(Foo foo) {
System.out.println(foo);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, 'hoge')")
public void hoge(Foo foo) {
System.out.println(foo);
}
}
-
readとhogeで、それぞれパーミッションをチェック
package sample.spring.security.servlet;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import sample.spring.security.domain.Foo;
import sample.spring.security.service.MyAclSampleService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@WebServlet("/acl")
public class MyAclServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
MyAclSampleService service = this.findServiceBean(req);
Foo foo = new Foo(44L);
this.callMethod("read", () -> service.read(foo));
this.callMethod("hoge", () -> service.hoge(foo));
}
private void callMethod(String method, Runnable runnable) {
try {
System.out.println(method);
runnable.run();
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
...
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
...>
...
<bean id="permissionFactory" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionFactory">
<constructor-arg value="sample.spring.security.acl.MyPermission" />
</bean>
<bean id="expressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property name="permissionEvaluator">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.AclPermissionEvaluator">
<constructor-arg ref="aclService" />
<property name="permissionFactory" ref="permissionFactory" /> ★
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="lookupStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
<property name="permissionFactory" ref="permissionFactory" /> ★
</bean>
...
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider>
<sec:user-service>
<sec:user name="foo" password="foo" authorities="READONLY" />
<sec:user name="bar" password="bar" authorities="HOGE" />
</sec:user-service>
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
</beans>
-
DefaultPermissionFactoryを Bean として定義- コンストラクタ引数で、自作した
Permission(MyPermission)のClassオブジェクトを指定
- コンストラクタ引数で、自作した
-
DefaultPermissionFactoryの Bean を、AclPermissionEvaluatorとBasicLookupStrategyにそれぞれプロパティとして設定する
動作確認
foo ユーザーでログインして /acl にアクセス
read
Foo{id=44}
hoge
Access is denied
bar ユーザーでログインして /acl にアクセス
read
Access is denied
hoge
Foo{id=44}
説明
独自パーミッションクラスの定義
package sample.spring.security.acl;
import org.springframework.security.acls.domain.BasePermission;
import org.springframework.security.acls.model.Permission;
public class MyPermission extends BasePermission {
public static final Permission HOGE = new MyPermission(0b100000, 'H');
private MyPermission(int mask, char code) {
super(mask, code);
}
}
- 独自のパーミッションを定義する場合は、
BasePermissionを継承したクラスを作成し、そこに定数で追加したいパーミッションを定義する - コンストラクタの第一引数がそのパーミッションに対応するビット値になり、第二引数がパーミッションを一文字であらわした表現を指定する
- 定数名が重要で、ここで指定した定数名が
hasPermission()式の第二引数で指定するパーミッションの名前になる
既存のパーミッションクラスと置き換える
<bean id="permissionFactory" class="org.springframework.security.acls.domain.DefaultPermissionFactory">
<constructor-arg value="sample.spring.security.acl.MyPermission" />
</bean>
<bean id="expressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property name="permissionEvaluator">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.acls.AclPermissionEvaluator">
<constructor-arg ref="aclService" />
<property name="permissionFactory" ref="permissionFactory" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="lookupStrategy" class="org.springframework.security.acls.jdbc.BasicLookupStrategy">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclCache" />
<constructor-arg ref="aclAuthorizationStrategy" />
<constructor-arg ref="permissionGrantingStrategy" />
<property name="permissionFactory" ref="permissionFactory" />
</bean>
- 何もしないと、パーミッションクラスは
BasePermissionが使用される - これを、先ほど作成した自作のパーミッションクラス
MyPermissionに差し替える必要がある - パーミッションクラスを直接利用しているのは
PermissionFactoryインターフェースの実装クラスであるDefaultPermissionFactoryになっている - このクラスのコンストラクタ引数で、使用したいパーミッションクラスの
Classオブジェクトを指定する-
DefaultPermissionFactory内部でパーミッションクラスに定義されている定数をリフレクションで取得するようになっている
-
-
PermissionFactoryはAclPermissionEvaluatorとBasicLookupStrategyクラスで利用されているので、それらのpermissionFactoryプロパティを差し替える
式で利用する
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#foo, 'hoge')")
public void hoge(Foo foo) {
System.out.println(foo);
}
- ここまでの設定で、独自のパーミッションが利用できるようになる
- ただし、他の既存のパーミッションとは違い、独自のパーミッションは
SecurityExpressionRootに定数が定義されていない - なので、シングルクォーテーション(
')で囲って文字列として指定してあげる必要がある - パーミッションクラスに定義した定数名が全て大文字になっていれば、実質大文字小文字の区別はなくて問題ない
- どういうことかというと、実際はまずそのままの形(
hoge)でチェックし、なければ全て大文字にして(HOGE)チェックする、となっている
- どういうことかというと、実際はまずそのままの形(