TensorFlowの初心者向けチュートリアルをTensorBoardで出力
TensorFlowの初心者向けチュートリアルMNIST For ML BeginnersをTensorBoardに出力して見える化しました。ですが、TensorBoardの見方(特にGraph以外)をほとんど理解していないのでコードと簡単な解説のみです。Deep Learningを実践していくと、非常に有用そうですが、そこまでのレベルに達していないので・・・
環境:python3.5 tensorflow1.1
参考リンク
- TensorFlowをWindowsにインストール Python初心者でも簡単だった件
- 【入門者向け解説】TensorFlow基本構文とコンセプト
- 【入門者向け解説】TensorFlowチュートリアルMNIST(初心者向け)
- TensorFlow APIメモ
- 【TensorBoard入門】TensorFlow処理を見える化して理解を深める
- 【TensorBoard入門:image編】TensorFlow画像処理を見える化して理解を深める
- 【TensorBoard入門:Projector編】TensorFlow処理をかっこよく見える化
- 【入門者向け解説】TensorFlowチュートリアルDeep MNIST
- TensorFlow理解のために柏木由紀さん顔特徴を調べてみた【前編】
コード
書いたコードは↓です。公式サイトの「TensorBoard: Visualizing Learning」を参考にしています。
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# MNISTデータ読込
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
# TensorBoard情報出力ディレクトリ
log_dir = '/tmp/tensorflow/mnist/logs/mnist_beginner'
# 指定したディレクトリがあれば削除し、再作成
if tf.gfile.Exists(log_dir):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(log_dir)
tf.gfile.MakeDirs(log_dir)
# 変数を加工してTensorBoard出力する関数
def variable_summaries(var):
# 変数Summaries
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var) #Scalar出力(平均)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) #Scalar出力(標準偏差)
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) #Scalar出力(最大値)
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) #Scalar出力(最小値)
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) #ヒストグラム出力
# 回帰の計算
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('y'):
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
tf.summary.histogram('y', y)
# クロスエントロピー
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
with tf.name_scope('total'):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y))
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
# 訓練
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
# 正解
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
# 全Summariesを出力
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_dir + '/train', sess.graph) #訓練データ
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_dir + '/test') #テストデータ
# 初期化
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
# 10回ごとにテストし、正解率を出力
if i % 10 == 0: # Record summaries and test-set accuracy
summary, acc = sess.run([merged, accuracy], feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels})
test_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
print('Accuracy at step %s: %s' % (i, acc))
# 訓練
else: # Record train set summaries, and train
# 訓練のうち1回/100回は、詳細訓練データを出力
if i % 100 == 99: # Record execution stats
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step],
feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_:batch_ys},
options=run_options,
run_metadata=run_metadata)
train_writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%03d' % i)
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
print('Adding run metadata for', i)
#通常の訓練
else:
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_:batch_ys})
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
# Writerクローズ
train_writer.close()
test_writer.close()
TensorBoard起動
その後にTensorboardを起動します。筆者の環境はAnacondaで構築しているので、まずAnaconda NavigatorからTerminalを起動しています。
で、TerminalからTensorbaordをディレクトリを指定して起動します(Pythonプログラム内変数log_dirにディレクトリを格納しています)。
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tensorflow/mnist/logs/mnist_beginner
起動後にブラウザで http://localhost:6006/ を開くとTensorBoard画面が表示されます。
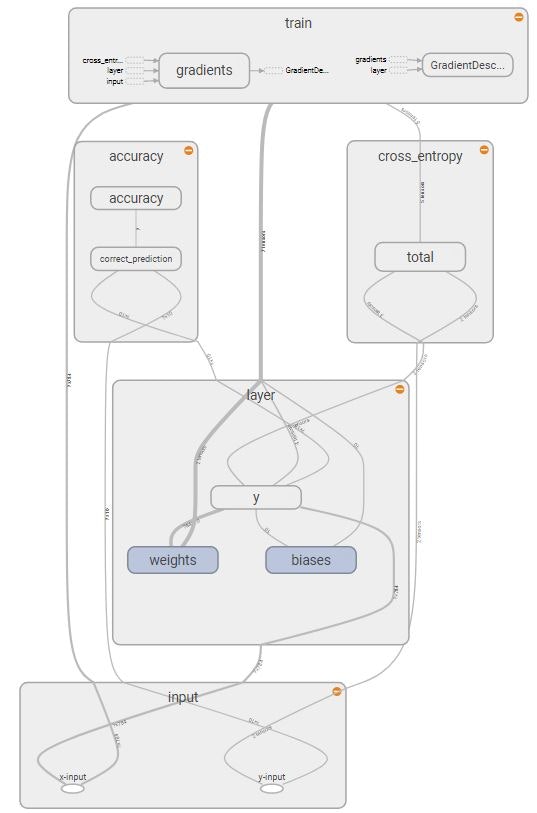
Graph
Computational Graphは下図の形で出力されます。入門記事では、シンプルな計算式だったのでグラフ化の必要性がなかったですが、このくらいの複雑さになると見やすいです。
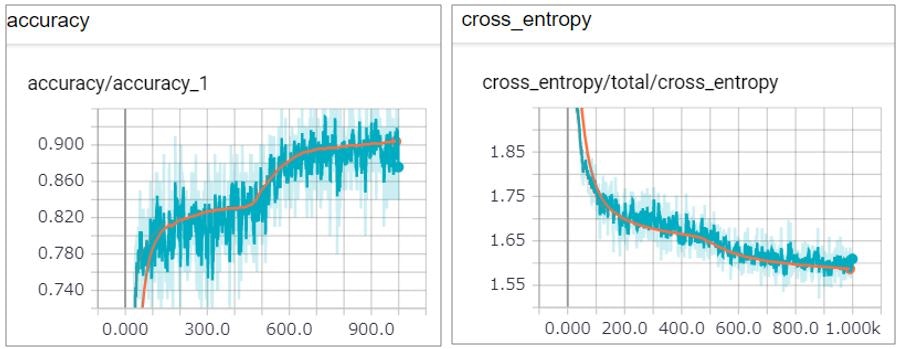
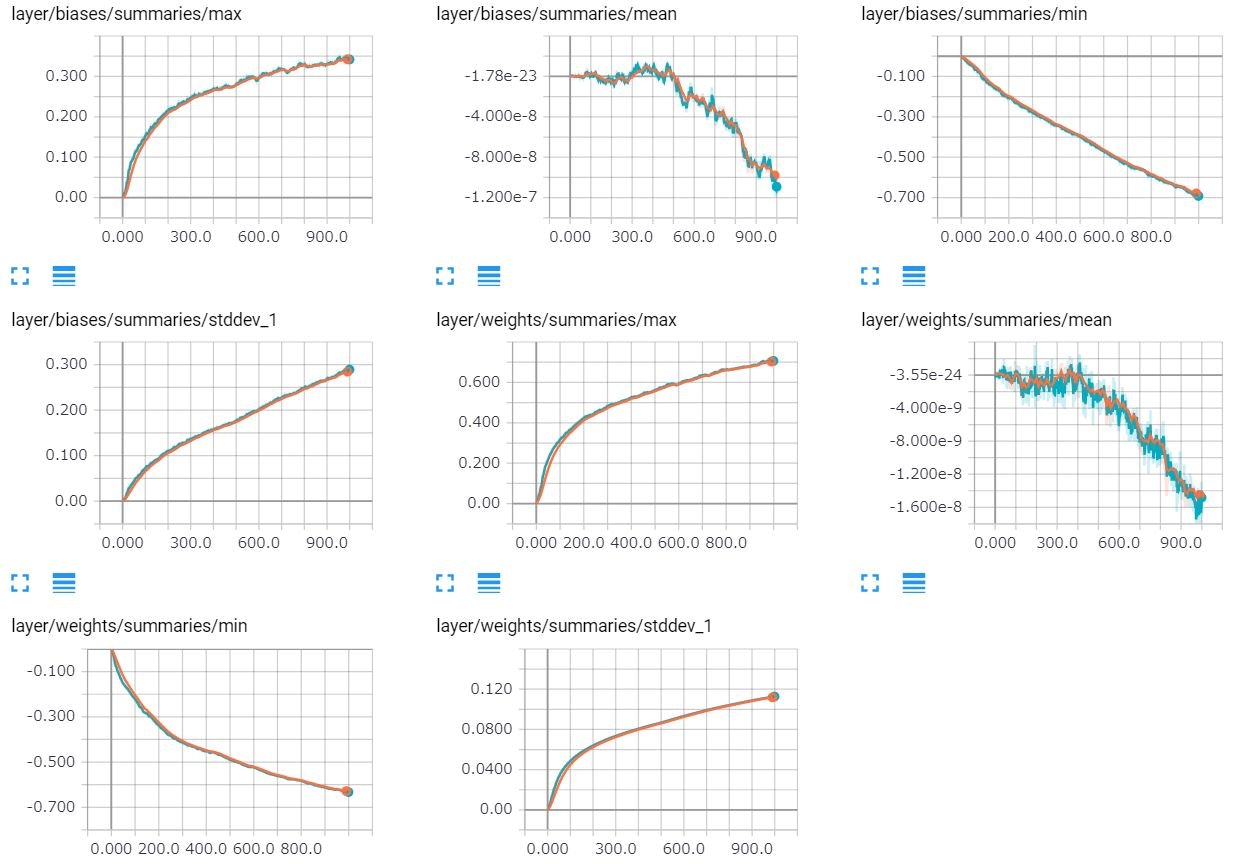
Scalar(折れ線グラフ)
Scalar(折れ線グラフ)で正答率(accuracy)と交差エントロピー(クロスエントロピー)のステップごとの遷移が見られます。
青線が訓練データで、オレンジ線がテストデータです。
同様にバイアス(切片)や重み付けの値の標準偏差等の値の遷移も出力しています。
Distribution(分布)
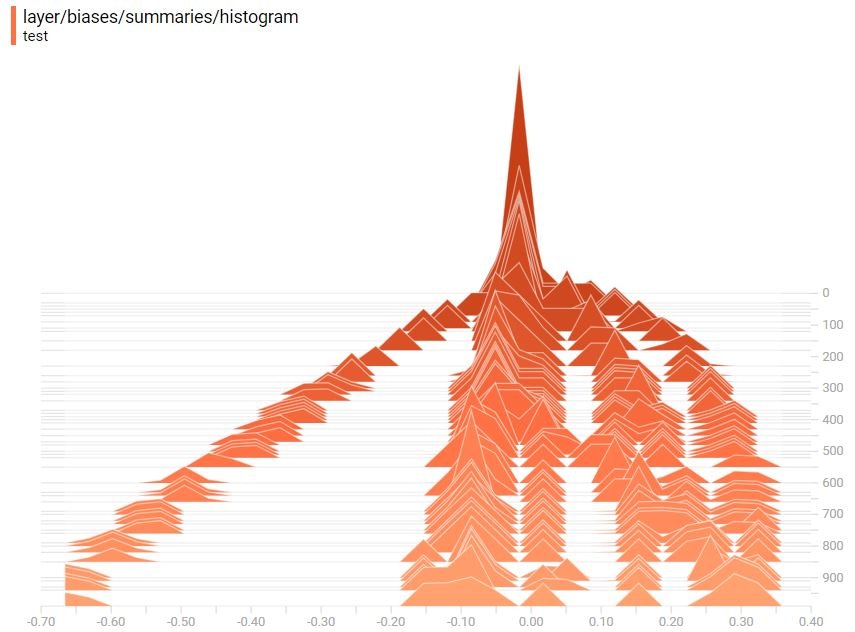
バイアスのDistribution(分布)を見てみましょう。0で初期化しているので0からスタートして、学習していくにつれ、バイアスのテンソルの値が変化していることがわかります。
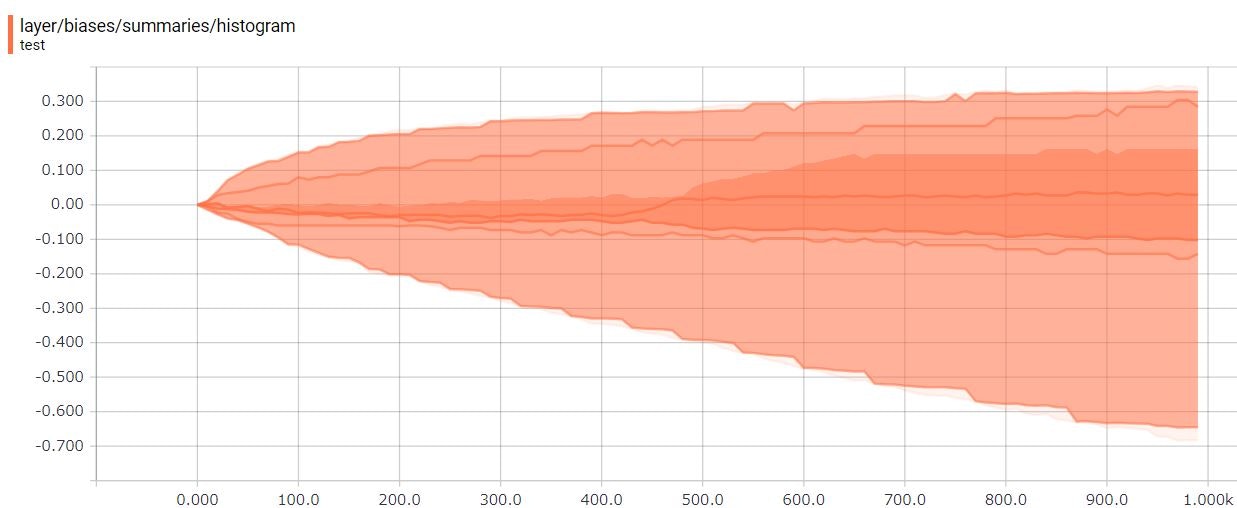
Histogram(ヒストグラム)
同じくバイアスのHistogram(ヒストグラム)を見てみます。3次元の度数分布です。Distribution(分布)で見たように0からスタートして、学習していくにつれ、バイアスのテンソルの値が変化しています。