始めに
Embulkを使ってCloudtrailログをelasticsearchに放り込むのが便利だったのでので、やり方をまとめておきます。
準備
-
elasticsearchとkibanaをインストールしておく。手順は下記リンクなどを参考に。
-
elasticsearch上にマッピングを作成。kibanaで分析する場合は各フィールド適宜not_analyzed を指定する。今回は以下ののmappingを使用。
{
"mappings": {
"log": {
"properties": {
"eventName": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"eventSource": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"awsRegion": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"sourceIPAddress": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"errorCode": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"requestID": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"eventID": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"userType": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"userArn": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"userName": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"accesskeyid": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"userAgent": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"eventTime": {
"type": "date",
"format": "dateOptionalTime"
},
"errorMessage": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}
えんばるくる(Embulkの実行)
Embulkをインストールする。
$ curl –create-dirs. –o ~/.embulk/bin/embulk –L http://dl.embulk.org/embulk-latest.jar
$ chmod +x ~/.embulk/bin/embulk
$ echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.embulk/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
S3 input、json parser、elasticsearch output のプラグインをインストールする。
$ embulk gem install embulk-input-s3
$ embulk gem install embulk-output-elasticsearch
$ embulk gem install embulk-parser-json
設定ファイルを書く。
in:
type: s3
bucket: <bucket name>
path_prefix: <path to cloudtrail log>
endpoint: <s3 region endpoint>
access_key_id: <access key>
secret_access_key: <secret key>
decoders:
- {type: gzip}
parser:
type: json
root: $.Records
schema:
- {name: eventName, type: string}
- {name: eventSource, type: string}
- {name: awsRegion, type: string}
- {name: sourceIPAddress, type: string}
- {name: eventTime, type: string}
- {name: requestID, type: string}
- {name: eventID, type: string}
- {name: userType, path: userIdentity.type, type: string}
- {name: userArn, path: userIdentity.arn, type: string}
- {name: userName, path: userIdentity.userName, type: string}
- {name: accesskeyid, path: userIdentity.accessKeyId, type: string}
- {name: userAgent, type: string}
- {name: errorCode, type: string}
- {name: errorMessage, type: string}
out:
type: elasticsearch
cluster_name: <clustername>
nodes:
- {host: "localhost", port: 9300}
index: cloudtrail
index_type: log
previewコマンドでinput側のdry-runができる。
$ embulk preview config.yml
問題なさそうであればデータロードの実行。
$embulk run config.yml -o config.yml
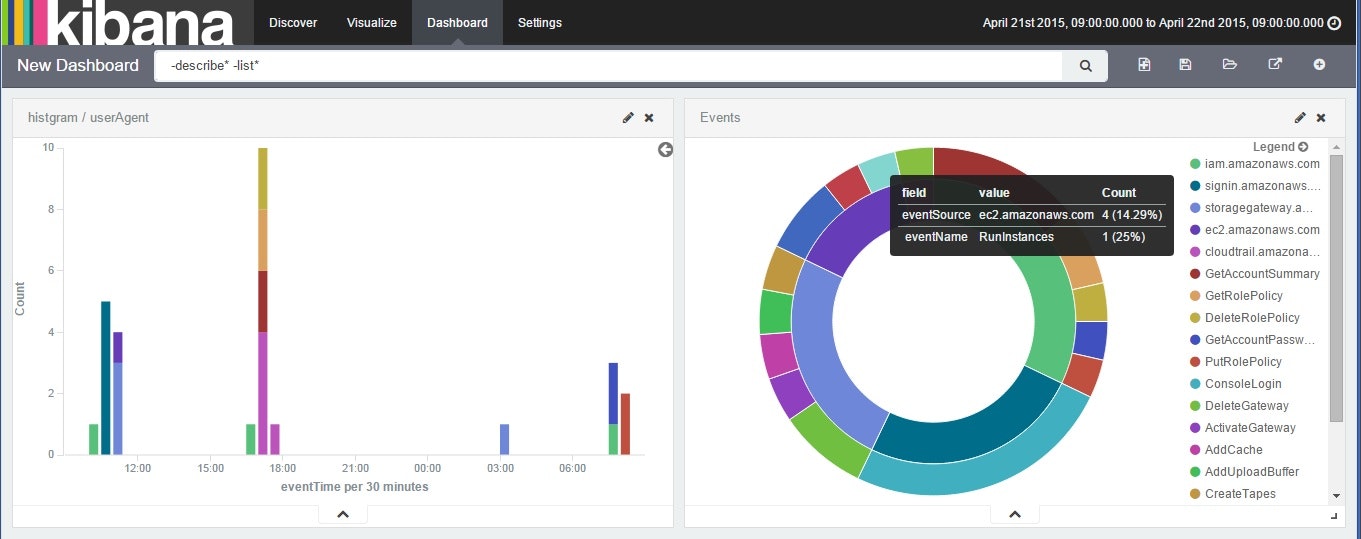
ロードが終わったら、kibanaで眺める。
注意事項
kibana上ではローカルタイムゾーンでの時刻表示となるようです https://github.com/elastic/kibana/issues/1600
UTCとずれて表示されるのご注意ください。
雑感
- Embulk、初めて触ったけどとんでもなく簡単だし便利。設定ファイル書き換えればELBやCloudFrontログを解析することもすぐにできそう。
- Redshiftのoutputプラグインもあるので、Redshiftで分析することもたぶん可能。Pluginが増えると使い方がどんどん広がる。
参考リンク等
Embulk公式
https://github.com/embulk/embulk
http://treasure-data.hateblo.jp/entry/2015/02/02/133635 #紹介記事
http://www.embulk.org/plugins/ #plug-inのリスト。
今回使ったEmbulk plug-in
https://github.com/embulk/embulk-input-s3
https://github.com/takumakanari/embulk-parser-json
https://github.com/muga/embulk-output-elasticsearch
定期的にログをkibanaで分析したい場合はLambdaもお勧めです
Lambdaを使ってCloudtrailログをElasticsearchに投下する