概要
マイナンバーの算出方法および各種実装方法については前回記事を参照してください。
SIMD intrinsicでチェックディジットを計算してみる
この記事では、計算用ロジックを再び精査することで、SIMD化におけるポイントを掴みやすくすることを目的とします。
レファレンス実装をもう一度
マイナンバーの算出方法は、次の省令の第五条に明記されています。
プログラムは正しく動くことが重要ですので、それを忠実に再現した実装を考えることは大事なことです。
行政手続における特定の個人を識別するための番号の利用等に関する法律の規定による通知カード及び個人番号カード並びに情報提供ネットワークシステムによる特定個人情報の提供等に関する省令
というわけで、入力チェックも考慮したレファレンス実装を作成してみることにしました。
# include <algorithm>
# include <cctype>
# include <string>
using std::string;
using Digit = std::uint8_t; //1桁の数字を表す
Digit calc_reference(const string &str) {
// 入力チェック
if(str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if(!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return std::isdigit(c);}
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return std::stoi(str.substr(11 - n, 1));
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static auto Q = [](const size_t n) -> Digit {
return static_cast<Digit>(1 <= n && n <= 6 ? n + 1 : 7 <= n && n <= 11 ? n - 5 : n);
};
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
sum += P(str, n) * Q(n);
}
size_t mod = sum % 11;
return static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
なるべく分かりやすく書いたつもりですが、コードについて幾つか補足を書いておきます。
- 冒頭のstd::all_ofは、「第三引数の条件をイテレート全てで満たすかどうか」を判定します。つまり、「全ての文字が数字ならtrue、そうでなければfalse」となります。
- ラムダ式Pおよびラムダ式Qは、省令の要件を忠実に満たすように実装されたものです。std::stoiが処理として重いのは自明ですが、コードとして分かりやすいので採用しています。
-
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n)とループが1オリジンなのも省令通りです。もちろん結果が変化しないのならズラしても構いません。 - 高速化の観点で言うと、最後に剰余処理とif文が出てくるのが厄介ですね……。
文字列→数字変換を修正してみる
C++の規格上、**0~9が連続していることは保証されています**ので、'0'~'9'の間かどうかはisdigit関数を使わなくても判定することができます。
またこれは、「'0'を文字コードから引き算することでstd::stoiの代わりにすることができる」ということでもあります。
この2点を念頭に修正すると、次のようなコードになります。
# include <algorithm>
# include <string>
using std::string;
using Digit = std::uint8_t; //1桁の数字を表す
Digit calc_fix_stoi(const string &str) {
// 入力チェック
if(str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if(!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return ('0' <= c && c <= '9');}
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return str[11 - n] - '0';
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static auto Q = [](const size_t n) -> Digit {
return static_cast<Digit>(1 <= n && n <= 6 ? n + 1 : 7 <= n && n <= 11 ? n - 5 : n);
};
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
sum += P(str, n) * Q(n);
}
size_t mod = sum % 11;
return static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
この段階で(x86でReleaseビルドした後に)Visual Studio 2017 Communityのプロファイラに掛けたところ、「入力チェックより計算部分が倍以上重い」という結果になりました。この辺りにメスを入れられればかなり速くなりそうです。
無駄な計算を省いてみる
実はQ(n)の計算には無駄があります。それは、試行毎に同じ計算を毎回行うのが無駄ということです。
入力が何であれ、Q(n)の値は変化しません。つまり、例えば配列として事前に用意してやれば高速化されるはずです。
また、処理の末尾に剰余処理とif文が出てきますが、sumの値の最大値は高々891(9×9×11)ですので、こちらもテーブル引きすれば余計な計算を省くことができます。
# include <algorithm>
# include <string>
using std::string;
using Digit = std::uint8_t; //1桁の数字を表す
// テーブル引き用のデータを作成する
bool g_digit[256];
Digit g_table[1000];
void init_tabledata() noexcept {
for (size_t i = 0; i < 256; ++i) {
g_digit[i] = ('0' <= i && i <= '9');
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
size_t mod = i % 11;
g_table[i] = static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
}
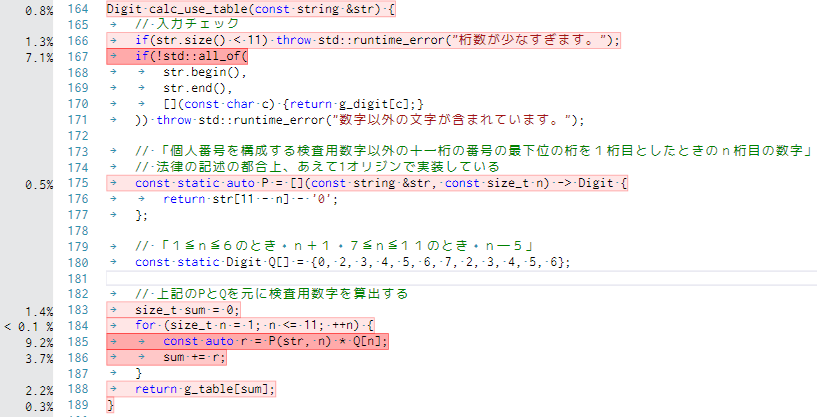
Digit calc_use_table(const string &str) {
// 入力チェック
if(str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if(!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return g_digit[c];}
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return str[11 - n] - '0';
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static Digit Q[] = {0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
const auto r = P(str, n) * Q[n];
sum += r;
}
return g_table[sum];
}
これにより、calc_fix_stoiと比べて負荷が大きく下がりました。それでも入力チェックと積和演算が、相対的に大きなネックになっているのは間違いないようです。
SIMD化を行う
そこで、SIMD演算による高速化を試みます。ここで重要なのは、どういった命令が使えそうかを見極めるということです。
※資料例:x86/x64 SIMD命令一覧表 (SSE~AVX2)
入力チェック
今回対象とする入力はstd::string型……**実質char配列(11文字)**ですので、__m128i型1つに十分収まります。ただ、string内のchar配列がアラインメントされているかは分かりませんので、_mm_load_si128命令(SSE2)ではなく_mm_loadu_si128命令(SSE2)を使用しましょう。
// reinterpret_castは型を跨ぐ強引なキャストのために使用
// 「12文字目以降」に何があるかは保証されないので厳密に言うとリスキーな構文である
const __m128i input = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
また、各文字が数字の0~9に収まっているかの判定ですが、要するに「'0'より文字コードが小さい文字」か「'9'より文字コードが大きい文字」が1つでもあればアウトなわけです。それを並列に処理するための命令はSSE2にありますし、「いずれかのビットが立っているか」は_mm_testz_si128命令(SSE4)を使用すれば簡単に判断できます。
// 判定用の定数
const static __m128i min_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
const static __m128i max_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('9');
const static __m128i bit_mask = _mm_set_epi8(
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff,
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff
);
// 判定1:'0'未満なら0xff、'0'以上なら0x00
const __m128i cmp1 = _mm_cmplt_epi8(input, min_digit);
// 判定2:'9'より上なら0xff、'0'以上なら0x00
const __m128i cmp2 = _mm_cmpgt_epi8(input, max_digit);
// OR文で重ね合わせる(数字としての条件を満たさない箇所があれば0xff)
const __m128i cmp3 = _mm_or_si128(cmp1, cmp2);
// 後ろ5バイトは関係ないのでマスクしておく
// マスク後のビットが全て0に等しければセーフ、さもないとアウト
if (_mm_testz_si128(cmp3, bit_mask) != 1)
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
ただし、一般に「a <= c && c <= b」は「(c - a) <= (b - a)」と置き換え可能ですので、これを利用すれば条件分岐を更に減らすことができます。
追記:(c-a)する段階で符号なし整数にキャストする場合ならともかく、今回はそうではないため以下のコードは使えません。
// 判定用の定数
const static __m128i min_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
const static __m128i diff_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('9' - '0');
const static __m128i bit_mask = _mm_set_epi8(
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff,
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff
);
// inputからmin_digitを減算する(飽和させなくていい)
const __m128i temp = _mm_sub_epi8(input, min_digit);
// 判定:('9' - '0')より大きいなら0xff、そうでないなら0x00
const __m128i cmp = _mm_cmpgt_epi8(temp, diff_digit);
// 後ろ5バイトは関係ないのでマスクしておく
// マスク後のビットが全て0に等しければセーフ、さもないとアウト
if (_mm_testz_si128(cmp, bit_mask) != 1)
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
PnとQnとの掛け算処理
$P_n$は要するに読み込む方向を逆にしただけですし、$Q_n$はただの定数ですので、8bitづつの掛け算を行えば済むのですが、あいにくSIMDには8ビットづつの乗算命令が存在しないんですよね……。
そこで、8bitづつ掛け算を行う命令をでっちあげることにしました。参考にしたのは次のページです。
x86 - SSE multiplication 16 x uint8_t - Stack Overflow
// 8ビット毎の掛け算命令
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8193601/sse-multiplication-16-x-uint8-t
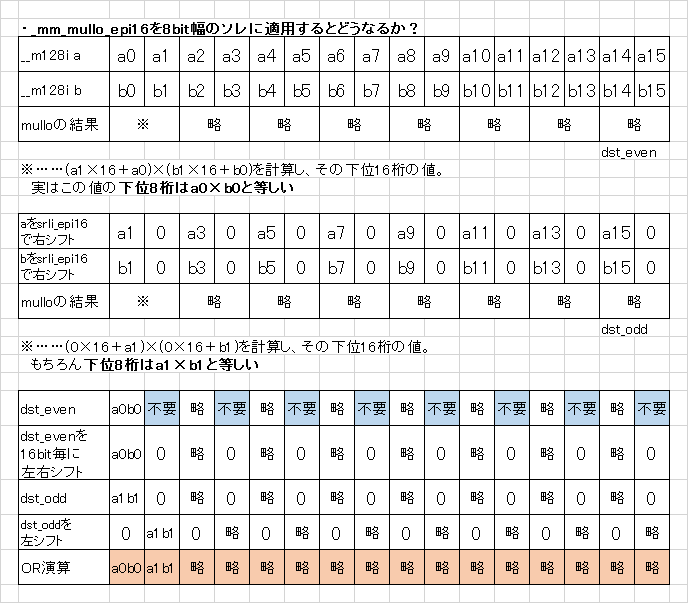
const static auto mullo_epi8 = [](const __m128i &a, const __m128i &b) -> __m128i {
// unpack and multiply
__m128i dst_even = _mm_mullo_epi16(a, b);
__m128i dst_odd = _mm_mullo_epi16(_mm_srli_epi16(a, 8), _mm_srli_epi16(b, 8));
// repack
return _mm_or_si128(_mm_slli_epi16(dst_odd, 8), _mm_srli_epi16(_mm_slli_epi16(dst_even, 8), 8));
};
// q_nはどうせ定数なので決め打ちする
// p_nは反転処理すらしてないので注意
static const __m128i q_n = _mm_set_epi8(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// p_nとq_nとの掛け算
const __m128i mul_pq = mullo_epi8(p_n, q_n);
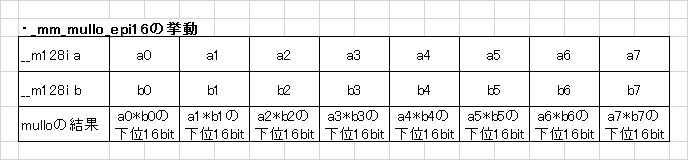
このラムダ式(mullo_epi8)における黒魔術を読み解く鍵は_mm_mullo_epi16です。この命令は要するに次のような操作を行います。
そして不思議なことに、この操作を上記コードのように適用すると、8ビット毎の掛け算命令と化すのです。
ちなみにSIMD intrinsicにおけるシフト演算は、128bit全体を動かすものと8/16/32/64bitの枠毎に動かすものとは別ですので、黒魔術を読み解く際は注意しましょう。
合計処理と検査用数字の計算処理
後は掛け算した結果の各要素を合計すればいい……のですが、_mm_store_si128命令などで変数に書き出してから足し算するのは効率が悪いです。
そこで、ここでもSIMD演算をフル活用することになります(Chikuzenさんからの情報提供)。
検査用数字の算出は……前述のテーブル引きで十分でしょう。2つを表すコードはこんな感じ。
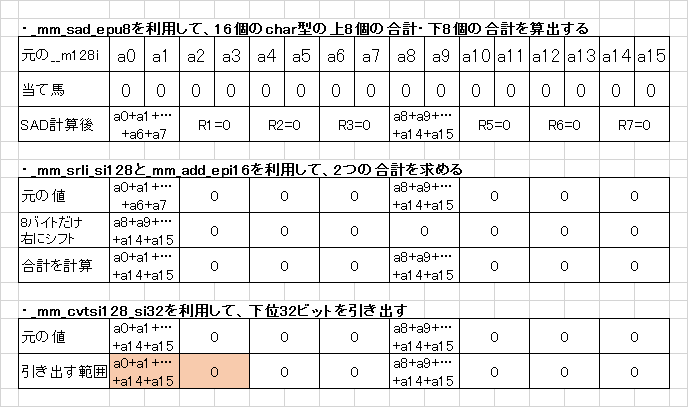
// 総和を計算する
__m128i temp = _mm_sad_epu8(mul_pq, _mm_setzero_si128());
temp = _mm_add_epi16(temp, _mm_srli_si128(temp, 8));
return g_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(temp)];
他の方のコード
※ここの部分では、後述するベンチマーク用にコードを編集したりはしていません。
proelbtnさん
参考URL:http://qiita.com/proelbtn/items/2ad39ef8c9db5358582f
unsigned short Q(unsigned char n) {
if(1 <= n && n <= 6) return n + 1;
else if (7 <= n && n <= 11) return n - 5;
else return -1;
}
bool CheckDigit(const std::array<int, 12>& P) {
unsigned short sum = 0;
sum += (unsigned short)P[10] * (unsigned short)Q(1);
sum += (unsigned short)P[9] * (unsigned short)Q(2);
sum += (unsigned short)P[8] * (unsigned short)Q(3);
sum += (unsigned short)P[7] * (unsigned short)Q(4);
sum += (unsigned short)P[6] * (unsigned short)Q(5);
sum += (unsigned short)P[5] * (unsigned short)Q(6);
sum += (unsigned short)P[4] * (unsigned short)Q(7);
sum += (unsigned short)P[3] * (unsigned short)Q(8);
sum += (unsigned short)P[2] * (unsigned short)Q(9);
sum += (unsigned short)P[1] * (unsigned short)Q(10);
sum += (unsigned short)P[0] * (unsigned short)Q(11);
return (unsigned short)P[11] == sum % 11 <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - sum % 11;
}
ポイントとしては、ループ展開で高速化を狙ったことでしょうか。入力フォーマットが前述までの前提とは違うので、後述するベンチマークの際には「'0'を引く方式」で入力処理を変更しています。
yumetodoさん
参考URL:
http://qiita.com/yumetodo/items/600ca0df422010cbc4c1
https://github.com/yumetodo/benchmark_calc_check_degit/blob/master/benchmark_calc_check_degit/Source.cpp
std::uint8_t calc_check_digit_yumetodo(const std::string& n) noexcept(false) {
if (11 != n.size()) throw std::runtime_error("n.digit must be 11");
for(auto e : n) if(e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("in function calc_check_digit_yumetodo : iregal charactor detect.(" + n + ')'); }
const std::uint8_t r = std::accumulate(n.rbegin(), n.rend(), std::pair<int, int>{}, [](const auto& s, const char& e) -> std::pair<int, int>{
return {s.first + (e - '0') * ((5 < s.second) ? s.second - 4 : s.second + 2), s.second + 1};
}).first % 11;
return (0 == r || 1 == r) ? 0 : 11 - r;
}
このコードのポイントとしては、C++らしくstd::accumulateを使って合計を計算しているところでしょう。更にこの方は、SIMD化したバージョンも公開してくださりました。
SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR auto make_qn() {
alignas(16) sprout::array<std::uint16_t, 16> re{};
for (std::uint8_t i = 0, n = 1; i < re.size(); ++i, ++n) re[i] = (n < 7) ? n + 1 : n - 5;
return re;
}
SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR sprout::array<std::uint8_t, 1000> make_mod_table_yumetodo() {
sprout::array<std::uint8_t, 1000> re{};
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
re[i] = i % 11;
}
return re;
}
std::uint8_t calc_check_digit_yumetodo_kai_simd(const std::string& n) noexcept(false) {
static SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR auto mod_table = make_mod_table_yumetodo();
SPROUT_CONSTEXPR std::size_t num_of_digits = 11;
if (num_of_digits != n.size()) throw std::runtime_error("n.digit must be 11");
for (auto e : n) if (e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("in function calc_check_digit_yumetodo_kai_simd : illegal character detected.(" + n + ')'); }
alignas(16) static SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR auto qn = make_qn();//0-7
alignas(16) std::uint16_t n1[sizeof(__m256i) / sizeof(std::uint16_t)];
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < num_of_digits; ++i) n1[i] = std::uint16_t(n[num_of_digits - 1 - i]);//reverse
const __m256i pn1 = _mm256_sub_epi16(_mm256_load_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(n1)), _mm256_set1_epi16('0'));
alignas(16) std::uint16_t tmp[sizeof(__m256i) / sizeof(std::uint16_t)];//0-63
const __m256i qn1 = _mm256_load_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(qn.data()));
const auto re = _mm256_mullo_epi16(pn1, qn1);
_mm256_storeu_si256(reinterpret_cast<__m256i*>(tmp), re);
std::uint16_t r = 0;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < num_of_digits; ++i) r += tmp[i];
r = mod_table[r];
return (0 == r || 1 == r) ? 0 : 11 - r;
}
コードを読み解いた結果、
- $Q_n$算出と剰余演算にテーブルを使用
- 別途用意したアラインメント済みの配列に代入してからloadし、即座に'0'の__m256iで引き算する
- mullo後にstoreして普通に合計してから剰余演算してif文で結果を返す
といった実装だと判明しました。__m128iでなく__m256iを使用したのは、前述したように8bit毎のmul処理が素で存在しないからだと思われます。
(※Sproutを導入する手間を考慮した結果、こちらは後述のベンチでSprout成分を廃した形で導入します……ごめんなさい)
MaverickTseさん
std::uint8_t calc_check_digit_mavtse(const std::string& query)
{
unsigned long long as_value{ 0 };
std::array<short, 16> simd_result{}; // the 16bit intermediate results from SIMD
if (11 != query.length()) throw std::runtime_error("str.digit must be 11");
for (auto e : query) if (e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("in function calc_check_digit_mavtse : illegal character detecteded.(" + query + ')'); }
__m128i vP = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*> (query.c_str()));
__m128i vzero = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
vP = _mm_sub_epi8(vP, vzero);
// Set Q, beware of order
__m128i vQ = _mm_set_epi8(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// Multiply-add vP and vQ
__m128i vR = _mm_maddubs_epi16(vP, vQ);
// Store vR
_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(simd_result.data()), vR);
// our result
int result{ 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
{
result += simd_result[i];
}
result %= 11;
if (result <= 1)
{
return 0;
}
result = 11 - result;
return static_cast<std::uint8_t>(result);
}
こちらもSIMD路線ですが、特徴的なのはコードの短さでしょうか。_mm_maddubs_epi16を撃てばストアするだけで合計が求まる……というシンプルさは魅力的です。
Chikuzenさん
参考URL:
https://twitter.com/mtfmk/status/850698403931594754
// 11文字に'0'から'9'以外が含まれていればfalseを返す
static inline bool validate(const __m128i& x, const __m128i& zero, const __m128i& nine, const __m128i& mask)
{
__m128i t = _mm_or_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(x, nine), _mm_cmplt_epi8(x, zero));
return _mm_test_all_zeros(t, mask) == 1;
}
uint8_t calc_check_digit(const std::string& str) noexcept
{
static const __m128i c_zero = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
static const __m128i c_nine = _mm_set1_epi8('9');
static const __m128i mask = _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0);
static const __m128i q_n0 = _mm_setr_epi16(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5);
static const __m128i q_n1 = _mm_setr_epi16(4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
if (str.size() != 11) {
return 0xFE;
}
__m128i p_n0 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
if (!validate(p_n0, c_zero, c_nine, mask)) {
return 0xFF;
}
const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128();
p_n0 = _mm_subs_epu8(p_n0, c_zero);
__m128i p_n1 = _mm_unpackhi_epi8(p_n0, zero);
p_n0 = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(p_n0, zero);
__m128i sum = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_madd_epi16(p_n0, q_n0), _mm_madd_epi16(p_n1, q_n1));
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 4));
int ret = 11 - _mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum) % 11;
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ret > 9 ? 0 : ret);
}
ポイントとしては、積和処理が前述のSIMD化とは違う方向性だということです。
- _mm_unpackhi_epi8および_mm_unpacklo_epi8でデータを「0と」交互に並び替える
- それを_mm_madd_epi16で積和し、_mm_add_epi32と_mm_srli_si128で足し合わせることにより下位32ビットに結果を集める
- 後は_mm_cvtsi128_si32で中身を引き出せば積和終了
追記:_mm_maddubs_epi16命令によって更に高速化したとのこと
static inline bool validate(const __m128i& x)
{
__m128i t = _mm_sub_epi8(x, _mm_min_epu8(x, _mm_set1_epi8(9)));
return _mm_test_all_zeros(t, _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0)) == 1;
}
uint8_t calc_check_digit(const std::string& str) noexcept
{
if (str.size() != 11) {
return 0xFE;
}
__m128i p_n = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
p_n = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8('0'));
if (!validate(p_n)) {
return 0xFF;
}
__m128i sum = _mm_maddubs_epi16(p_n, _mm_setr_epi8(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0));
sum = _mm_sad_epu8(sum, _mm_setzero_si128());
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
int ret = 11 - _mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum) % 11;
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ret > 9 ? 0 : ret);
}
追記:最終版
※C++でマイナンバーのチェックデジットを計算するの追記コメント:
「@MaverickTse, @mtfmk, @YSRKEN 氏の格闘の結果、超高速されたものが登場しました。」
SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR sprout::array<std::uint8_t, 1000> make_mod_table_ysr() {
sprout::array<std::uint8_t, 1000> re{};
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
size_t mod = i % 11;
re[i] = static_cast<std::uint8_t>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
return re;
}
static inline bool validate(const __m128i& x)
{
__m128i t = _mm_sub_epi8(x, _mm_min_epu8(x, _mm_set1_epi8(9)));
return _mm_test_all_zeros(t, _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0)) == 1;
}
uint8_t calc_check_digit_mtfmk_ysrken(const std::string& str) noexcept
{
static SPROUT_CXX14_CONSTEXPR auto mod_table = make_mod_table_ysr();
if (str.size() != 11) {
return 0xFE;
}
__m128i p_n = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
p_n = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8('0'));
if (!validate(p_n)) {
return 0xFF;
}
__m128i sum = _mm_maddubs_epi16(p_n, _mm_setr_epi8(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0));
sum = _mm_sad_epu8(sum, _mm_setzero_si128());
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
return mod_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum)];
}
ベンチマーク結果
- 後述するベンチマーク用コードを使用した。入力に誤りがある際は例外を投げるようにする
- 動作環境はWindows 10 Pro + Core i7-4790K
- コンパイラはVisual Studio 2017の物を使用。x86ビルドとx64ビルドの両方で確かめた
- コンパイルオプションはデフォルトのものを採用
- 20回試行した平均値と標本標準偏差を掲載する
- noneは「何も計算しない」(入力チェックすら行わない)ものの記録
- 前述したようにsimd_yumetodoではSprout部分を事前計算で代用している
| 種類(x86) | 平均値 | 標本標準偏差 |
|---|---|---|
| none | 16.20 | 0.951 |
| reference | 8922.05 | 179.281 |
| none_stoi | 312.40 | 14.199 |
| use_table | 220.25 | 9.978 |
| proelbtn | 238.80 | 11.010 |
| yumetodo | 234.20 | 13.610 |
| simd_yumetodo | 322.95 | 6.525 |
| simd_mavericktse | 192.50 | 9.902 |
| simd_ysrken | 75.05 | 10.262 |
| simd_chikuzen | 89.05 | 3.203 |
| simd_chikuzen2 | 81.85 | 4.955 |
| ysr_chiku_mave | 45.10 | 4.973 |
| 種類(x64) | 平均値 | 標本標準偏差 |
|---|---|---|
| none | 15.35 | 0.988 |
| reference | 7406.55 | 286.752 |
| none_stoi | 307.15 | 8.798 |
| use_table | 215.70 | 14.925 |
| proelbtn | 176.65 | 8.048 |
| yumetodo | 238.70 | 8.112 |
| simd_yumetodo | 269.10 | 5.428 |
| simd_mavericktse | 148.40 | 3.912 |
| simd_ysrken | 63.20 | 3.105 |
| simd_chikuzen | 76.90 | 4.494 |
| simd_chikuzen2 | 76.10 | 2.511 |
| ysr_chiku_mave | 41.70 | 2.557 |
……自分のコードが一番速いという手前味噌な結果になってしまいましたが、これは皆さんのコードとリプのやり取りあってのものです。本当にありがとうございます。
ちなみにChikuzenさんのコードの末尾をテーブル引きにしたら最速になってなにそれこわい
追記:3人のコードのいいとこ取りをした最終版が最速になりました。
おまけ:ベンチマーク用コード
# include <cassert>
# include <cctype>
# include <chrono>
# include <cstdint>
# include <algorithm>
# include <array>
# include <iostream>
# include <random>
# include <string>
# include <numeric>
# include <immintrin.h>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using Digit = std::uint8_t;
// ループ回数
const size_t LOOP_COUNT = 10000 * 1000;
// ベンチマークする回数
const size_t BENCH_TIMES = 20;
// ベンチマーク用データ
string g_benchdata[LOOP_COUNT];
bool g_digit[256];
Digit g_table[1000];
// 検査用数字計算用関数のテンプレ
using calc_check_digit_func = Digit(*)(const std::string&);
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 mt(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dist(0u, 9u);
// ランダムな数字を11桁並べた文字列を返す
string get_rand_digit() {
string str;
str.resize(11);
std::generate(str.begin(), str.end(), []() -> char { return '0' + dist(mt); });
return str;
}
// テストを行うための土台
// 引数に関数名を渡せば、関数の動作をテストしてくれる
void test(const string name, const calc_check_digit_func &func) {
cout << name << " ";
bool flg = true;
static string data_list[] = {
"314159265050", "314159265158", "314159265255", "314159265352", "314159265450",
"314159265557", "314159265654", "314159265751", "314159265859", "314159265956",
};
for (const auto &data : data_list) {
const auto input = data.substr(0, 11);
const auto output = static_cast<Digit>(std::stoi(data.substr(11, 1)));
if (func(input) != output) {
cout << input << " " << (int)func(input) << " " << (int)output << endl;
flg = false;
break;
}
}
cout << (flg ? "OK" : "NG") << endl;
}
// ベンチマーク用のデータを作成する
void init_benchdata() noexcept {
for (size_t i = 0; i < LOOP_COUNT; ++i) {
g_benchdata[i] = get_rand_digit();
}
}
// テーブル引き用のデータを作成する
void init_tabledata() noexcept {
for (size_t i = 0; i < 256; ++i) {
g_digit[i] = ('0' <= i && i <= '9');
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
size_t mod = i % 11;
g_table[i] = static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
}
// ベンチマークするための土台
// 引数に関数名を渡せば、それに従い計算を行い、時間を計測する
void bench(const string name, const calc_check_digit_func &func) {
cout << name << endl;
using hrc = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock;
Digit dst;
for (size_t n = 0; n < BENCH_TIMES; ++n) {
const auto begin_time = hrc::now();
for (size_t i = 0; i < LOOP_COUNT; ++i) {
dst = func(g_benchdata[i]);
}
const auto end_time = hrc::now();
const auto duaration_time = end_time - begin_time;
cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(duaration_time).count() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 「何もしない」実装
Digit calc_none(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
return 0;
}
// リファレンス実装
// http://law.e-gov.go.jp/announce/H26F11001000085.html
Digit calc_reference(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
// 入力チェック
if (str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if (!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return std::isdigit(c); }
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return std::stoi(str.substr(11 - n, 1));
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static auto Q = [](const size_t n) -> Digit {
return static_cast<Digit>(1 <= n && n <= 6 ? n + 1 : 7 <= n && n <= 11 ? n - 5 : n);
};
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
sum += P(str, n) * Q(n);
}
size_t mod = sum % 11;
return static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
// std::stoiを排除した
Digit calc_fix_stoi(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
// 入力チェック
if (str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if (!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return ('0' <= c && c <= '9'); }
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return str[11 - n] - '0';
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static auto Q = [](const size_t n) -> Digit {
return static_cast<Digit>(1 <= n && n <= 6 ? n + 1 : 7 <= n && n <= 11 ? n - 5 : n);
};
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
sum += P(str, n) * Q(n);
}
size_t mod = sum % 11;
return static_cast<Digit>(mod <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - mod);
}
// テーブル引きを導入した
Digit calc_use_table(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
// 入力チェック
if (str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if (!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return g_digit[c]; }
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 「個人番号を構成する検査用数字以外の十一桁の番号の最下位の桁を1桁目としたときのn桁目の数字」
// 法律の記述の都合上、あえて1オリジンで実装している
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return str[11 - n] - '0';
};
// 「1≦n≦6のとき n+1 7≦n≦11のとき n―5」
const static Digit Q[] = { 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
// 上記のPとQを元に検査用数字を算出する
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t n = 1; n <= 11; ++n) {
const auto r = P(str, n) * Q[n];
sum += r;
}
return g_table[sum];
}
// proelbtn版をベンチマーク用に少し書き換えたもの
Digit calc_proelbtn(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
// 入力チェック(便宜上設置)
if (str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
if (!std::all_of(
str.begin(),
str.end(),
[](const char c) {return g_digit[c]; }
)) throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 元の実装は入力がstd::array<int, 12>だったので便宜上設置
const static auto P = [](const string &str, const size_t n) -> Digit {
return str[n] - '0';
};
// Qは元の実装になるべく忠実にした
const static auto Q = [](const unsigned char n) -> unsigned short {
if (1 <= n && n <= 6) return n + 1;
else if (7 <= n && n <= 11) return n - 5;
else return -1;
};
// 計算用ルーチン
unsigned short sum = 0;
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 10)* (unsigned short)Q(1);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 9) * (unsigned short)Q(2);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 8) * (unsigned short)Q(3);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 7) * (unsigned short)Q(4);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 6) * (unsigned short)Q(5);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 5) * (unsigned short)Q(6);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 4) * (unsigned short)Q(7);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 3) * (unsigned short)Q(8);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 2) * (unsigned short)Q(9);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 1) * (unsigned short)Q(10);
sum += (unsigned short)P(str, 0) * (unsigned short)Q(11);
// 元の実装では12桁目と比較して判定結果をboolで返していた
return ((sum % 11) <= 1 ? 0 : 11 - (sum % 11));
}
// yumetodo版をベンチマーク用に少し書き換えたもの
Digit calc_yumetodo(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
if (11 != str.size()) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
for (auto e : str) if (e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。"); }
const std::uint8_t r = std::accumulate(str.rbegin(), str.rend(), std::pair<int, int>{}, [](const auto& s, const char& e) -> std::pair<int, int> {
return { s.first + (e - '0') * ((5 < s.second) ? s.second - 4 : s.second + 2), s.second + 1 };
}).first % 11;
return (0 == r || 1 == r) ? 0 : 11 - r;
}
alignas(16) std::array<std::uint16_t, 16> g_qn{};
std::array<std::uint8_t, 1000> g_mod_table{};
void init_tabledata_yumetodo() {
for (std::uint8_t i = 0, n = 1; i < g_qn.size(); ++i, ++n) g_qn[i] = (n < 7) ? n + 1 : n - 5;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
g_mod_table[i] = i % 11;
}
}
Digit calc_simd_yumetodo(const std::string& n) noexcept(false) {
const std::size_t num_of_digits = 11;
if (num_of_digits != n.size()) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
for (auto e : n) if (e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。"); }
alignas(16) std::uint16_t n1[sizeof(__m256i) / sizeof(std::uint16_t)];
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < num_of_digits; ++i) n1[i] = std::uint16_t(n[num_of_digits - 1 - i]);//reverse
const __m256i pn1 = _mm256_sub_epi16(_mm256_load_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(n1)), _mm256_set1_epi16('0'));
alignas(16) std::uint16_t tmp[sizeof(__m256i) / sizeof(std::uint16_t)];//0-63
const __m256i qn1 = _mm256_load_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(g_qn.data()));
const auto re = _mm256_mullo_epi16(pn1, qn1);
_mm256_storeu_si256(reinterpret_cast<__m256i*>(tmp), re);
std::uint16_t r = 0;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < num_of_digits; ++i) r += tmp[i];
r = g_mod_table[r];
return (0 == r || 1 == r) ? 0 : 11 - r;
}
Digit calc_simd_mavericktse(const std::string& query) noexcept(false) {
unsigned long long as_value{ 0 };
std::array<short, 16> simd_result; // the 16bit intermediate results from SIMD
if (11 != query.length()) throw std::runtime_error("str.digit must be 11");
for (auto e : query) if (e < '0' || '9' < e) { throw std::runtime_error("in function calc_check_digit_mavtse : illegal character detecteded.(" + query + ')'); }
__m128i vP = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*> (query.c_str()));
__m128i vzero = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
vP = _mm_sub_epi8(vP, vzero);
// Set Q, beware of order
__m128i vQ = _mm_set_epi8(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// Multiply-add vP and vQ
__m128i vR = _mm_maddubs_epi16(vP, vQ);
// Store vR
_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(simd_result.data()), vR);
// our result
int result{ 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
{
result += simd_result[i];
}
result %= 11;
if (result <= 1)
{
return 0;
}
result = 11 - result;
return static_cast<std::uint8_t>(result);
}
// SIMD演算を適用-1
Digit calc_simd_ysrken(const string &str) noexcept(false) {
// 入力チェック-1
if (str.size() < 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
// __m128i型にマッピング
const __m128i input = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
// 入力チェック-2
// 判定用の定数
const static __m128i min_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
const static __m128i max_digit = _mm_set1_epi8('9');
const static __m128i bit_mask = _mm_set_epi8(
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1
); // 0xffと書きたいが警告が出るので-1としている
// 判定1:'0'未満なら0xff、'0'以上なら0x00
const __m128i cmp1 = _mm_cmplt_epi8(input, min_digit);
// 判定2:'9'より上なら0xff、'0'以上なら0x00
const __m128i cmp2 = _mm_cmpgt_epi8(input, max_digit);
// OR文で重ね合わせる(数字としての条件を満たさない箇所があれば0xff)
const __m128i cmp3 = _mm_or_si128(cmp1, cmp2);
// 後ろ5バイトは関係ないのでマスクしておく
// マスク後のビットが全て0に等しければセーフ、さもないとアウト
if (_mm_testz_si128(cmp3, bit_mask) != 1)
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
// 8ビット毎の掛け算命令
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8193601/sse-multiplication-16-x-uint8-t
const static auto mullo_epi8 = [](const __m128i &a, const __m128i &b) -> __m128i {
// unpack and multiply
__m128i dst_even = _mm_mullo_epi16(a, b);
__m128i dst_odd = _mm_mullo_epi16(_mm_srli_epi16(a, 8), _mm_srli_epi16(b, 8));
// repack
return _mm_or_si128(_mm_slli_epi16(dst_odd, 8), _mm_srli_epi16(_mm_slli_epi16(dst_even, 8), 8));
};
// 掛け合わせる定数
// p_n(つまりinput2)を反転させてないので、逆にこちらを反転させている
const static __m128i q_n = _mm_set_epi8(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// p_nとq_nとの掛け算
const __m128i mul_pq = mullo_epi8(_mm_sub_epi8(input, min_digit), q_n);
// 総和を計算する
__m128i temp = _mm_sad_epu8(mul_pq, _mm_setzero_si128());
temp = _mm_add_epi16(temp, _mm_srli_si128(temp, 8));
return g_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(temp)];
}
// SIMD演算を適用-2
Digit calc_simd_chikuzen(const std::string& str) noexcept(false) {
static const __m128i c_zero = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
static const __m128i c_nine = _mm_set1_epi8('9');
static const __m128i mask = _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0);
static const __m128i q_n0 = _mm_setr_epi16(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5);
static const __m128i q_n1 = _mm_setr_epi16(4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
if (str.size() != 11) {
throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
}
__m128i p_n0 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
__m128i t = _mm_or_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(p_n0, c_nine), _mm_cmplt_epi8(p_n0, c_zero));
if (_mm_test_all_zeros(t, mask) != 1) {
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
}
const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128();
p_n0 = _mm_subs_epu8(p_n0, c_zero);
__m128i p_n1 = _mm_unpackhi_epi8(p_n0, zero);
p_n0 = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(p_n0, zero);
__m128i sum = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_madd_epi16(p_n0, q_n0), _mm_madd_epi16(p_n1, q_n1));
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 4));
int ret = 11 - _mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum) % 11;
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ret > 9 ? 0 : ret);
//return g_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum)];
}
Digit calc_simd_chikuzen2(const std::string& str) noexcept(false) {
static const __m128i c_zero = _mm_set1_epi8('0');
static const __m128i c_nine = _mm_set1_epi8('9');
static const __m128i mask = _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0);
static const __m128i q_n0 = _mm_setr_epi16(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5);
static const __m128i q_n1 = _mm_setr_epi16(4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
if (str.size() != 11) {
throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
}
__m128i p_n = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
p_n = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8('0'));
__m128i t = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_min_epu8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8(9)));
if (_mm_test_all_zeros(t, _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0)) != 1) {
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
}
__m128i sum = _mm_maddubs_epi16(p_n, _mm_setr_epi8(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0));
sum = _mm_sad_epu8(sum, _mm_setzero_si128());
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
int ret = 11 - _mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum) % 11;
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ret > 9 ? 0 : ret);
//return g_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum)];
}
Digit calc_mtfmk_ysrken(const std::string& str) noexcept(false) {
if (str.size() != 11) throw std::runtime_error("桁数が少なすぎます。");
__m128i p_n = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(str.c_str()));
p_n = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8('0'));
__m128i t = _mm_sub_epi8(p_n, _mm_min_epu8(p_n, _mm_set1_epi8(9)));
if ( _mm_test_all_zeros(t, _mm_setr_epi32(-1, -1, 0x00FFFFFF, 0)) != 1) {
throw std::runtime_error("数字以外の文字が含まれています。");
}
__m128i sum = _mm_maddubs_epi16(p_n, _mm_setr_epi8(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0));
sum = _mm_sad_epu8(sum, _mm_setzero_si128());
sum = _mm_add_epi32(sum, _mm_srli_si128(sum, 8));
return g_table[_mm_cvtsi128_si32(sum)];
}
int main() {
init_tabledata();
init_tabledata_yumetodo();
// 事前に動作テストを行う
cout << "動作テスト:" << endl;
test("none", calc_none);
test("reference", calc_reference);
test("none_stoi", calc_fix_stoi);
test("use_table", calc_use_table);
test("proelbtn", calc_proelbtn);
test("yumetodo", calc_yumetodo);
test("simd_yumetodo", calc_simd_yumetodo);
test("simd_mavericktse", calc_simd_mavericktse);
test("simd_ysrken", calc_simd_ysrken);
test("simd_chikuzen", calc_simd_chikuzen);
test("simd_chikuzen2", calc_simd_chikuzen2);
test("mtfmk_ysrken", calc_mtfmk_ysrken);
// ベンチマーク用データを作成する
cout << "ベンチマーク用データを作成中..." << endl;
init_benchdata();
// ベンチマーク
cout << endl << "ベンチマーク:" << endl;
bench("none", calc_none);
bench("reference", calc_reference);
bench("none_stoi", calc_fix_stoi);
bench("use_table", calc_use_table);
bench("proelbtn", calc_proelbtn);
bench("yumetodo", calc_yumetodo);
bench("simd_yumetodo", calc_simd_yumetodo);
bench("simd_mavericktse", calc_simd_mavericktse);
bench("simd_ysrken", calc_simd_ysrken);
bench("simd_chikuzen", calc_simd_chikuzen);
bench("simd_chikuzen2", calc_simd_chikuzen2);
bench("mtfmk_ysrken", calc_mtfmk_ysrken);
}