まだこちらは金曜日ですが今週のCodeFights用ノートを更新します。忘れがちな関数や他の方の解答で覚えておきたいものを抜粋します。使用言語はC++です。
Conditional Operator
名前も文法もよく忘れるこいつ。日本語でなんていうかわからない🤔
(expression: expression ? expression)
使用例
//年数を世紀に直して返す
int centuryFromYear(int year) {
int century = year / 100;
return (year % 100 == 0 ? century : ++century );
}
//ちなみに別解。みじかっ
int centuryFromYear(int year) {
return (year + 99)/ 100;
}
Palindrome 回文 - string::back と string::substr
与えられたstringが回文ならtrueを返す。それぞれ別解。
bool checkPalindrome(std::string inputString) {
if (inputString.size() < 2)
return true;
if (inputString[0] != inputString.back())
return false;
return checkPalindrome(inputString.substr(1, inputString.size() - 2));
}
- string::back(): Returns a reference to the last character of the string. This function shall not be called on empty strings.
- string::substr: Returns a newly constructed string object with its value initialized to a copy of a substring of this object.
bool checkPalindrome(string is) {
return is == string(is.rbegin(),is.rend());
}
- ひっくり返した文字列を元の文字列と比較してる。なるほどなあ。
std::max
std::max:二つを比べて大きい方を返す。std::minもある。
template <class T> const T& max (const T& a, const T& b) {
return (a<b)?b:a; // or: return comp(a,b)?b:a; for version (2)
}
//例
//与えられた数列の中で、隣り合う数字の積で最大のものを返す。
int adjacentElementsProduct(std::vector<int> inputArray) {
int ans = -987654321;
for (int i = 1; i < inputArray.size(); ++i)
ans = max(ans, inputArray[i] * inputArray[i - 1]);
return ans;
}
std::minmax_element
最大値と最小値のpairをiteratorで返す。pairはutility libraryを含むことで使えるが以下ではautoを使っている。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::minmax_element
#include <array> // std::array
int main () {
std::array<int,7> foo {3,7,2,9,5,8,6};
auto result = std::minmax_element (foo.begin(),foo.end());
// print result:
std::cout << "min is " << *result.first; //2, at position 2
std::cout << ", at position " << (result.first-foo.begin()) << '\n';
std::cout << "max is " << *result.second; //9, at position 3
std::cout << ", at position " << (result.second-foo.begin()) << '\n';
return 0;
}
- 関連
- std::minmax: minmax_elementとほぼ同じだがiteratorではなく値のペアを返す。
- std::min_element: 最小値のiteratorを返す。
- std::max_element: 最大値のiteratorを返す。
- std::lower_bound と std::upper_bound: Returns an iterator pointing to the first element in the range [first,last) which does not compare less than val. 小<大に並び替えられていてはじめて役に立つ、多分。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::lower_bound, std::upper_bound, std::sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
int main () {
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20};
std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20
std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30
std::vector<int>::iterator low,up;
low=std::lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
up= std::upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
std::cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << '\n'; //3
std::cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << '\n'; //6
return 0;
}
2D Vector の行数と列数
std::vector<std::vector<int>> twoDVect;
int row = twoDVect.size(); //行数
int col = twoDVect[0].size(); //列数
そもそもベクトルの基礎が怪しいので参照リンクを貼り付けておく。(http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/)
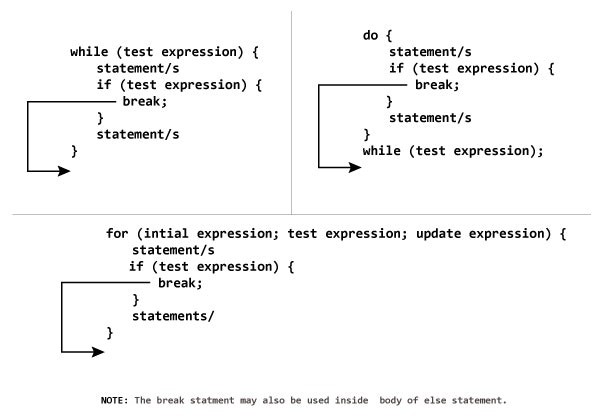
break と continue の違い
continue
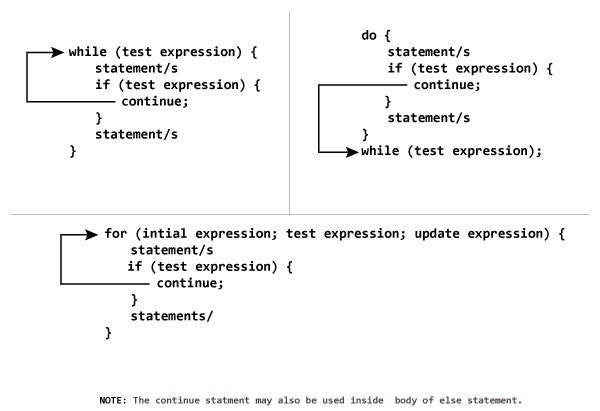
画像参照元
あとがき
今後もこんな感じに自分が覚えておきたいと思ったものを備忘録のような形でまとめていきます。