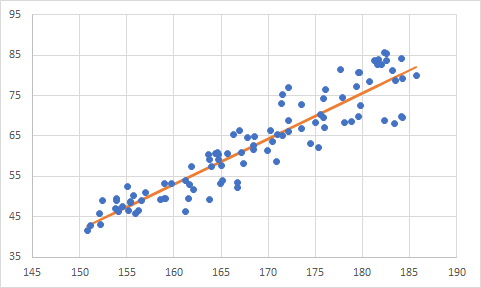
C++による単回帰分析
x(横軸):身長、y(縦軸):体重で示された身2次元データの近似直線を最小二乗法を計算してみた。
clr.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
/* 平均・標準偏差を計算するStatisticsクラス */
class Statistics{
public:
/* 平均を計算 */
float average(vector<float> &f, int N){
float ave = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) ave += f[i]/(float)N;
return ave;
}
/* 2乗の平均を計算 */
float average2(vector<float> &f, int N){
float ave2 = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) ave2 += f[i]*f[i]/(float)N;
return ave2;
}
/* 標準偏差を計算 */
float variance(vector<float> &f, int N){
float ave = average(f, N);
float ave2 = average2(f, N);
float var = ave2 - ave*ave;
return var;
}
/* 共分散を計算 */
float covariance(vector<float> &f, vector<float> &g, int N){
float cov = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) cov += f[i]*g[i]/(float)N;
cov -= average(f, N) * average(g, N);
return cov;
}
};
クラスStatistics
平均(average関数)、2乗平均(average2関数)、分散(variance関数)、共分散(covariance関数)を計算
slr.cpp
/* Statisticsクラスを継承したクラス */
/* Least_squares_method (最小二乗法) クラスで
* 近似直線を計算 */
class Least_squares_method : public Statistics{
public:
/* 傾きを計算 */
float slope(vector<float> &x, vector<float> &y, int N){
float a = 0.0;
float x_var = variance(x, N);
float cov = covariance(x, y, N);
a = cov / x_var;
return a;
}
/* 切片を計算 */
float intercept(vector<float> &x, vector<float> &y, int N){
float b = 0.0;
float x_var = variance(x, N);
float cov = covariance(x, y, N);
float x_ave = average(x, N);
float y_ave = average(y, N);
b = y_ave - (cov / x_var) * x_ave;
return b;
}
};
クラスStatisticsを継承したLeast_squares_methodクラスにより近似直線を計算
以下はファイル読み込み&書き込み
slr.cpp
/* ファイル読み込み */
int read_file(char *filename, vector<float> &x, vector<float> &y){
int N = 0;
float x_tmp = 0.0, y_tmp = 0.0;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if(fp == NULL){
cout << "can't open file ." << endl;
exit(1);
}
while(true){
if(fscanf(fp, "%f, %f\n", &x_tmp, &y_tmp) == EOF) break;
x.push_back(x_tmp);
y.push_back(y_tmp);
N++;
}
fclose(fp);
/* 要素数を返す */
return(N);
}
/* ファイル書き出し */
int write_file(char *filename, vector<float> &x, vector<float> &y, vector<float> &y2, int N){
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(filename, "w");
if(fp == NULL){
cout << "can't open file ." << endl;
exit(1);
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
fprintf(fp, "%f, %f, %f\n", x[i], y[i], y2[i]);
fclose(fp);
return(0);
}
main関数内で近似直線の傾きと切片を表示
ベクトルy2には近似直線を格納、write_file関数にてファイルに書き出される
slr.cpp
int main(void){
vector<float> x, y, y2;
char filename[30] = "height_weight.csv";
/* ファイル読み込み */
int N = read_file(filename, x, y);
/* オブジェクトdata1を生成
* data1オブジェクトにより2次元データの近似直線を計算 */
Least_squares_method data1;
/* 近似直線を計算 */
float a = data1.slope(x, y, N);
float b = data1.intercept(x, y, N);
cout << "slope : " << a << endl;
cout << "intercept : " << b << endl;
/* 近似直線の配列に格納 */
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
y2.push_back(a * x[i] + b);
char filename2[30] = "height_weight_slr.csv";
/* 近似直線のデータを出力 */
write_file(filename2, x, y, y2, N);
return(0);
}