はじめに
ブロックチェーンは信頼できる第三者を仮定しない書き換えが極めて困難なストレージである。この記事では世界的に広く用いられているBitcoinのブロックチェーンに対して、任意の80byteデータを書き込む方法について紹介する。なおこの方法には少量のBitcoinが必要であるため、すでにBitcoinを持っている方が望ましい。
この記事を読んでよく分からない部分や疑問、改善するべき点を見つけた場合は気軽にコメントなどで教えてほしい。
ブロックチェーン
ブロックチェーンについてはいろいろ複雑な説明があると思うが、ここではこの点だけをおさえておけば十分である。
- 公平な第三者がいなくとも過去に書いた内容を変更できない
このような絶対に削除や改変ができない石板のようなストレージに、暗号通貨は送金のリンクを記録することで暗号通貨として成り立っている。
BitcoinのpubScript
先ほどの説明では、Bitcoinのような暗号通貨は削除不可能なストレージに送金のリンクを記録していると書いたが、少なくともBitcoinに限って言えばこれはやや適切ではない。BitcoinにはpubScriptという仕組みがあり、これにより送金以外のこともできる。pubScriptとはスタックベースの非チューリング完全な機械語であり、次のサイトに利用できる機械語の一覧がある。
たとえば、次の機械語を見てみる。
OP_1 OP_2 OP_3 OP_ADD OP_SUB
\def\AtSOne#1\csod{%
\begin{array}{c|}
\hline
#1\\
\hline
\end{array}
}%
\def\AtSTwo#1,#2\csod{%
\begin{array}{c|c|}
\hline
#1 & #2\\
\hline
\end{array}
}%
\def\AtSThree#1,#2,#3\csod{%
\begin{array}{c|c|c|}
\hline
#1 & #2 & #3\\
\hline
\end{array}
}
\def\SOne#1{\AtSOne#1\csod}
\def\STwo#1{\AtSTwo#1\csod}
\def\SThree#1{\AtSThree#1\csod}
これは次のような意味となる。
- $1$をスタックへプッシュ(
OP_1) → $\SOne{1}$ - $2$をスタックへプッシュ(
OP_2) → $\STwo{2, 1}$ - $3$をスタックへプッシュ(
OP_3) → $\SThree{3, 2, 1}$ - スタックの先頭から2つを取り出し、足し算して結果をスタックの先頭にプッシュ(
OP_ADD) → $\STwo{5, 1}$ - スタックの先頭から2つを取り出し、引き算して結果をスタックの先頭にプッシュ(
OP_SUB) → $\SOne{4}$
Bitcoinはこのように柔軟な命令をブロックチェーンに記録することができる。そして、機械語を評価して最終的にスタックの先頭が1以上であれば受理するという仕組みになっている。
OP_RETURN
Bitcoinの機械語にはOP_RETURNという命令が存在する。これはスタックマシンを停止させる命令であり、この命令の後には任意の80byteデータを入れてよいということになっている。これを用いることで、ブロックチェーン上に任意の80byteデータを記録することができる。
データの書き込み
この節の内容は次のブログの投稿を元にした。
準備
まずPython3をインストールする。
$ brew install python3
そして、Python3のパッケージマネージャーであるpip3からpycoinを次のようにインストールする。
$ pip3 install --upgrade 'pycoin<0.70'
うまくいけばkuというコマンドラインツールを使うことができる。このツールを用いてBitcoinのアドレスと秘密鍵を生成する。
$ ku create -j | grep -i -e "wif\"" -e "btc_address\""
warning: can't open gpg, can't use as entropy source
"BTC_address": "12hvDk49ngLag3Mw6267bZTWbGMN1sWYc4",
"wif": "L3gzupeV1C55n7JTPFuCkhbRx1FRKf9K9qAjzcWXsJ5Vw7RR5bro",
このような出力があるので、これをどこかに控えておく。そして、次のようにしてop_return.pyというプログラムをダウンロードする。
$ wget https://gist.githubusercontent.com/y-yu/35cd269b2e4bfe229c677196d7c3b586/raw/6cc3273588044957991fc6fed6c9f4339b45bb5c/op_return.py
これは次のようなプログラムになっている。
# !/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# This script is based on https://gist.githubusercontent.com/harding/d34b581d8cfbb8919812/raw/send-op-return.py
from sys import exit, argv
from os import system
from pycoin.services.blockchain_info import spendables_for_address
from pycoin.tx import script, Tx
from pycoin.tx.tx_utils import sign_tx
from pycoin.tx.TxOut import TxOut, standard_tx_out_script
from binascii import hexlify
## This is the address and key you generated before
bitcoin_address = "ADDRESS"
bitcoin_private_key = "PRIVATE_KEY"
## The fee that will be given to the miner in bitcoin
bitcoin_fee = 15000 # In satoshis
## Get the message
if(len(argv) is not 2):
exit("usage: python3 send-op-return.py \"MESSAGE\"")
raw_message = argv[1]
if(len(raw_message) > 80):
exit("Message must be 80 characters or less")
message = hexlify(raw_message.encode()).decode('utf8')
## Get the spendable outputs we are going to use to pay the fee
spendables = spendables_for_address(bitcoin_address)
bitcoin_sum = sum(spendable.coin_value for spendable in spendables)
if(bitcoin_sum < bitcoin_fee):
exit("Not enough satoshis to cover the fee. found: {sum} need: {fee}".format(sum=bitcoin_sum,fee=bitcoin_fee))
## Create the inputs we are going to use
inputs = [spendable.tx_in() for spendable in spendables]
## If we will have change left over create an output to send it back
outputs = []
if (bitcoin_sum > bitcoin_fee):
change_output_script = standard_tx_out_script(bitcoin_address)
outputs.append(TxOut(bitcoin_sum - bitcoin_fee, change_output_script))
## Build the OP_RETURN output with our message
op_return_output_script = script.tools.compile("OP_RETURN %s" % message)
outputs.append(TxOut(0, op_return_output_script))
## Create the transaction and sign it with the private key
tx = Tx(version=1, txs_in=inputs, txs_out=outputs)
tx.set_unspents(spendables)
signed_tx = sign_tx(tx, wifs=[bitcoin_private_key])
## Print the raw transaction
print(tx.as_hex())
このop_return.pyをエディターで開いて、先ほどkuで作成したBitcoinアドレスと秘密鍵(wif)を次の変数に入力する。
bitcoin_address = "12hvDk49ngLag3Mw6267bZTWbGMN1sWYc4"
bitcoin_private_key = "L3gzupeV1C55n7JTPFuCkhbRx1FRKf9K9qAjzcWXsJ5Vw7RR5bro"
Bitcoinの入金
Bitcoinのブロックチェーンに書き込むには手数料を支払う必要がある。手数料は約0.00015 BTCあればよいようなので、0.01 BTCくらい先ほど作成したBitcoinアドレスに入金する必要がある。日本国内のサービスを用いる場合、本人確認などの手続きが必要なのでやや時間が必要であることに注意して欲しい。
データの書き込み
先ほどのプログラムop_return.pyのコマンドライン引数に、ブロックチェーンに記録したいデータを入力する。たとえばI have mental.pokerというデータを書き込む場合は次のようにする。
$ python3 op_return.py "I have mental.poker"
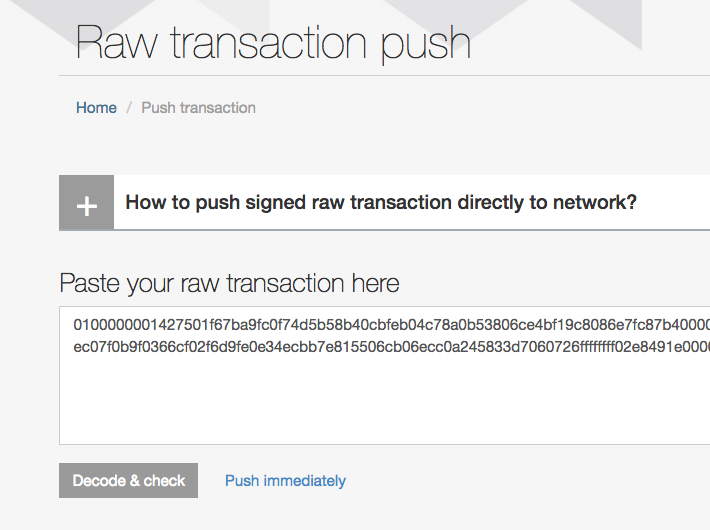
0100000001427501f67ba9fc0f74d5b58b40cbfeb04c78a0b53806ce4bf19c8086e7fc87b4000000006a47304402200d3709cfe38335f255797d0e9ab950c92e7a118695af91870084120bae9da24102205d0762ea88150749accf21f0110f28f1c9dd13d8c119cadb873e73f950837ada012103e0ec07f0b9f0366cf02f6d9fe0e34ecbb7e815506cb06ecc0a245833d7060726ffffffff02e8491e00000000001976a914fcebbb8713269d115c38d50fd795bcd47648ecf688ac0000000000000000156a13492068617665206d656e74616c2e706f6b657200000000
このように出力された取引の内容を適当な方法を用いてBitcoinネットワークに送信する。今回はBlockr.ioを利用する。次のように得られたデータをフォームに入力する。
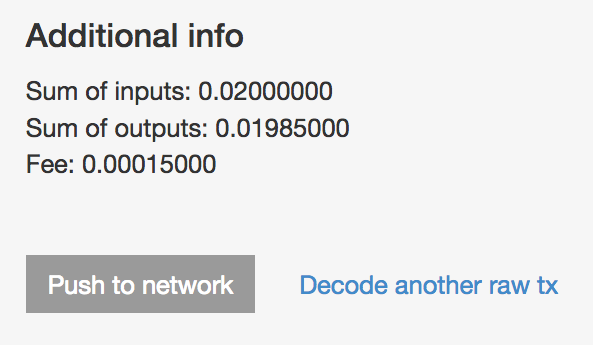
“Decode & check”を押して、内容を確認しよければ“Push to network”を押す。
すると、次のようなトランザクションIDという取引を特定するための数値が発行される。
64a113656256d2220a373d0b18d9a315668260365983cb600f96229e708cfe6c
これをたとえばBitcoin Block ExplorerのようなWebページで確認1し、しばらくするとブロックチェーンに書き込まれる。ブロックチェーンに書き込まれると、次のように確認することができる。
この取引に先ほどの文字列が書き込まれているのが分かる。
まとめ
このようにOP_RETURNを用いて、Bitcoinのブロックチェーン上に削除が不可能と言ってよい80byte以下のデータを書き込むという実験を行った。この削除が非常に難しいという特徴はいろいろな用途が考えられると思うので、それらについて考えてみるのもおもしろいと思う。
参考文献
-
Blockchain.infoというサービスでは、
OP_RETURNの扱いが壊れているようで、表示できないことがある。 ↩