先のF8でMessenger Platformが発表され、LINEやSlackなどと同様、プラットフォーム上でのボット実装が可能になった。
- ビジネスアカウント (Facebookページ) のメッセンジャー開放
- メッセージの送受信API公開
- 人工知能ボットエンジン (https://wit.ai/ )の開放
などが上記のリリースには含まれる。
今回はボットエンジンは利用せず、自分で簡単な処理を書いて試した。
参考: wit.aiとの連携を試している方の記事。
Facebook bot に wit.ai のボットエンジンを連携させてみる - Qiita
実装
というわけで、ボットを実装してみる。
基本的には、Messenger Platformのドキュメントに書いてある手順どおり。
FacebookアプリとFacebookページの作成
Facebookアプリを新規作成(もちろん既存のアプリを使用してもよい)。アプリの設定ページの左メニューから"Messenger"を選択、"Get Started"。
また、ボットに対応させるFacebookページのプロフィール画像が、そのままボットのアイコンになる。
Webhookの設定
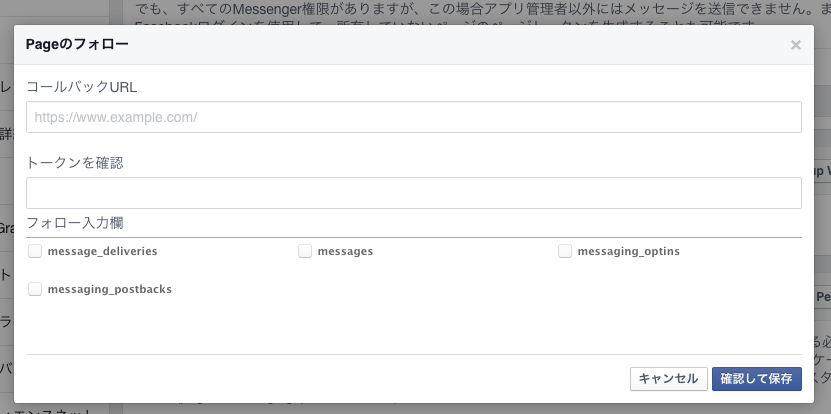
Messenger Platformでは(LINEとかでも同じ)、ボットに話しかけると特定のURLにWebhookでリクエストが飛んでくる仕組みになっている。そのURLとトークンを設定する。
※「フォロー入力欄 (= Subscription Fields)」のとこのチェックマークには全部チェックを入れておく
今回は、Sinatraで簡単なアプリを作成してWebhookに対応。面倒だったので、ローカルでサーバ起動したものをngrokで外部公開して試している。
Sinatraアプリ
アプリ側の設定。
Facebookは、Webhook設定画面の「確認して保存」ボタンを押すと、指定したコールバックURLにGETリクエストを飛ばして検証を行う。その際、入力したトークンがパラメータに含まれていることを確認してから、リクエストに含まれるパラメータ(params["hub.challenge"])をそのままレスポンスとして返すことで、検証が成功する。
コールバックURLは、/callbackというパスにした。
gem "sinatra"
gem "sinatra-contrib"
require "sinatra"
require "sinatra/reloader" if development?
get "/callback" do
if params["hub.verify_token"] != "<VALIDATION TOKEN>"
return "Error, wrong validation token"
end
params["hub.challenge"]
end
ローカルでサーバを起動し (4567番ポート)、ngrokで公開。
ruby main.rb
ngrok http 4567
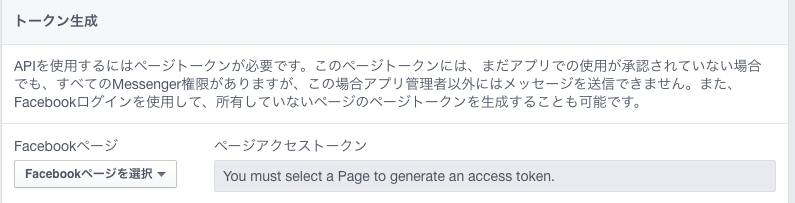
Facebookページのページアクセストークンの取得
ボットを利用するFacebookページを指定し、ページアクセストークンを生成。メモっておく。
Facebookアプリとページの連携 (Subscribe the App to the Page)
先ほどのページアクセストークンを利用して、curlでリクエスト。アプリがFacebookページのアップデートを購読できるようになる(= ボットが起動する)。
curl -ik -X POST "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/me/subscribed_apps?access_token=<FACEBOOK PAGE TOKEN>"
メッセンジャーアプリで検索するとFacebookページが出てくるので、選択して「Get Started」。ボットとの会話ができるようになる。
以降、メッセージを送信すると、設定したコールバックURLにPOSTリクエストでWebhookが飛んでくるようになる。
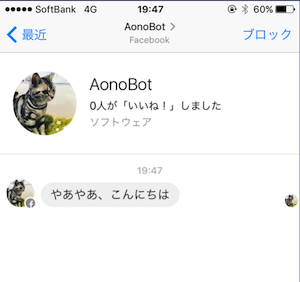
Welcome Screenの設定
ボットとのチャット画面の初回表示 (Welcome Screen) を設定可能。メッセージ or ボタン付きメッセージを出した状態で、会話スタートをすることができる。
設定はcurlコマンドで可能。今回はメッセージを表示した状態に設定。
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"setting_type":"call_to_actions",
"thread_state":"new_thread",
"call_to_actions":[
{
"message":{
"text":"やあやあ、こんにちは"
}
}
]
}' "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/<FACEBOOK PAGE ID>/thread_settings?access_token=<FACEBOOK PAGE TOKEN>"
↓ Welcome Screenはこんな感じ
アプリ側でのボットの返答処理
あとは、ユーザからメッセージが飛んできた時の処理をSinatraアプリ側で書けば、なんとなくボットぽくなる。
上で述べたとおり、ユーザが話しかけるとコールバックURL(/callback)にPOSTリクエストでWebhookが飛んでくる。
post "/callback" do
status 201
body ''
end
(とりあえず201ステータスで空のレスポンスを返している)
オウム返し
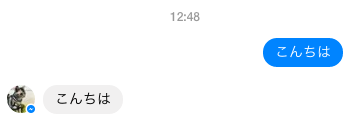
まずは定番?のオウム返し。
こっちからメッセージを送ると、以下の様なJSON形式のリクエストがコールバックURLに飛んで来る。(「こんにちは!」と送っている)
{"object"=>"page", "entry"=>[{"id"=>1682486745345720, "time"=>1460892479519, "messaging"=>[{"sender"=>{"id"=>1133111286733157}, "recipient"=>{"id"=><FACEBOOK PAGE ID>}, "timestamp"=>1460892479500, "message"=>{"mid"=>"mid.1460892479492:6ecbf23e4bac2dbc61", "seq"=>18, "text"=>"こんにちは!"}}]}]}
これをパースしてオウム返しする。
JSONに送り主(ボットにとって相手の宛先)sender, テキストの内容textが含まれている。
メッセージ送信APIのエンドポイントは、POST "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/me/messages?access_token=PAGE_ACCESS_TOKEN"。テキストメッセージ送信の場合、リクエストボディに含むのは上記のsenderとtext(下記text_message_request_bodyメソッド参照)。
require "json"
require 'rest-client'
post "/callback" do
request_body = JSON.parse(request.body.read)
messaging_events = request_body["entry"][0]["messaging"]
messaging_events.each do |event|
sender = event["sender"]["id"]
if !event["message"].nil? && !event["message"]["text"].nil?
text = event["message"]["text"]
bot_response(sender, text)
end
end
status 201
body ''
end
def bot_response(sender, text)
request_endpoint = "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/me/messages?access_token=#{ENV["FACEBOOK_PAGE_TOKEN"]}"
request_body = text_message_request_body(sender, text)
RestClient.post request_endpoint, request_body, content_type: :json, accept: :json
end
def text_message_request_body(sender, text)
{
recipient: {
id: sender
},
message: {
text: text
}
}.to_json
end
これで送ったことをそのまま返してくるボットになった。
画像
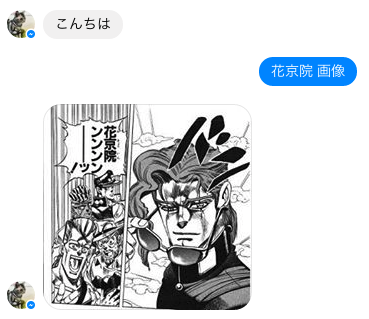
オウム返しの時は、ボットが単純なテキストメッセージを返すのみだったが、画像を返すように変えてみる。
hubot風に、「ほげほげ 画像」と話しかけると、Bingの画像検索APIを利用して画像を返してもらうようにした。テキストメッセージの時と比較すると、リクエストに含めるパラメータの内容は多少増える(image_url_message_request_bodyメソッド)。
gem "bing-search"
require 'bing-search'
BingSearch.account_key = ENV["BING_SEARCH_ACCOUNT_KEY"]
def bot_response(sender, text)
request_endpoint = "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/me/messages?access_token=#{ENV["FACEBOOK_PAGE_TOKEN"]}"
request_body =
if text =~ /(.+)\s+画像/
bing_image = BingSearch.image($&, limit: 10).shuffle[0]
if bing_image.nil?
text_message_request_body(sender, "残念、画像は見つかりませんでした")
else
image_url_message_request_body(sender, bing_image.media_url)
end
else
text_message_request_body(sender, text)
end
# 略
end
def image_url_message_request_body(sender, url)
{
recipient: {
id: sender
},
message: {
attachment: {
type: "image",
payload: {
url: url
}
}
}
}.to_json
end
以下のように画像を返してくれる。
Structured Message (Button Template)
ボタン付きのインタラクティブなメッセージも送信でき、これを'Structured Message'と呼ぶ。
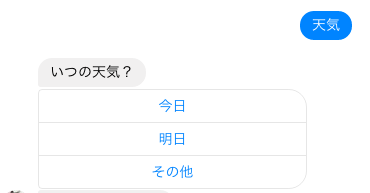
ボットに「天気」と尋ねたら、ボタン付きの返事が返ってくるようにする。
def bot_response(sender, text)
request_endpoint = "https://graph.facebook.com/v2.6/me/messages?access_token=#{ENV["FACEBOOK_PAGE_TOKEN"]}"
request_body =
if text =~ /天気/
button_structured_message_request_body(sender, "いつの天気?", *weather_buttons)
elsif text =~ /(.+)\s+画像/
bing_image = BingSearch.image($&, limit: 10).shuffle[0]
if bing_image.nil?
text_message_request_body(sender, "残念、画像は見つかりませんでした")
else
image_url_message_request_body(sender, bing_image.media_url)
end
else
text_message_request_body(sender, text)
end
# 略
end
def button_structured_message_request_body(sender, text, *buttons)
{
recipient: {
id: sender
},
message: {
attachment: {
type: "template",
payload: {
template_type: "button",
text: text,
buttons: buttons
}
}
}
}.to_json
end
def weather_buttons
[
{
type: "postback",
title: "今日",
payload: "today_weather"
},
{
type: "postback",
title: "明日",
payload: "tomorrow_weather"
},
{
type: "web_url",
url: "http://www.jma.go.jp/jp/week/319.html",
title: "その他"
}
]
end
ボタンを表示するためのパラメータetc.をセット(button_structured_message_request_body, weather_buttonsメソッド)。
↓ 以下のようなメッセージが来る。
ボタンを押した時のアクションは
- Webページへの遷移 (
type: "web_url") - コールバック処理 (
type: "postback")
の2種類。
type: "postback"の方のボタンを押すと、もう1回コールバックURLにリクエストが飛んで来る。postbackというパラメータが入っているか否かで、ボタンによるコールバックなのかどうかは判断可能。また、上記のweather_buttonsメソッド内で指定したpayloadというパラメータの文字列もそのままリクエストに含まれているので、それを利用してどのボタンによるアクションか区別し、処理を分岐させる。
post "/callback" do
request_body = JSON.parse(request.body.read)
messaging_events = request_body["entry"][0]["messaging"]
messaging_events.each do |event|
sender = event["sender"]["id"]
if !event["postback"].nil?
case event["postback"]["payload"]
when "today_weather"
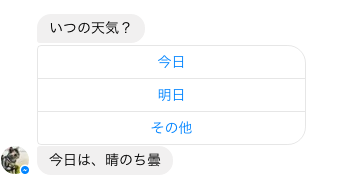
fetch_weather(:today) {|weather| bot_response(sender, "今日は、#{weather}") }
when "tomorrow_weather"
fetch_weather(:tomorrow) {|weather| bot_response(sender, "明日は、#{weather}") }
end
elsif !event["message"].nil? && !event["message"]["text"].nil?
# 略
end
end
# 略
end
def fetch_weather(date_sym)
date = {
today: "今日",
tomorrow: "明日"
}
request_endpoint = "http://weather.livedoor.com/forecast/webservice/json/v1?city=130010"
RestClient.get request_endpoint do |response, request, result, &block|
json = JSON.parse response
weather = "分かりません"
json["forecasts"].each do |forecast|
if forecast["dateLabel"] == date[date_sym]
weather = forecast["telop"]
end
end
yield weather
end
end
ライブドアの天気APIを利用し、postbackのpayloadの値を見て「今日」or「明日」の天気を取得。それを通常のテキストメッセージで返却している。
これで、主要なメッセージ送信APIを試した。
おわり
というわけで、Sinatraを使って簡単なMessengerボットを作ってみた。
できることがまだ多くはないので、どういうアイデアのボットがこれから出てくるのか気になるところ。