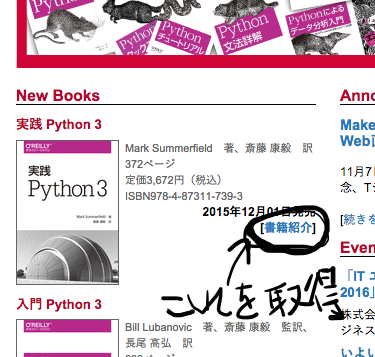
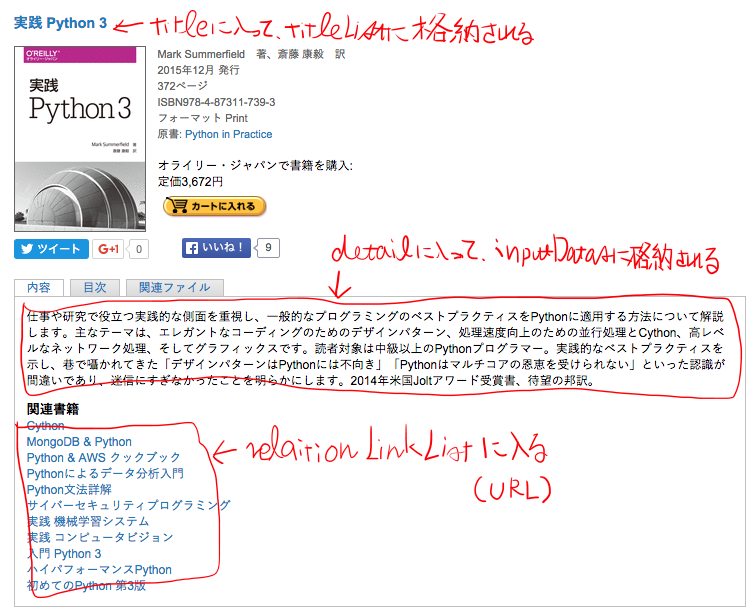
目標
O'Reilly JapanのHPから本の情報を取得して、
取得した情報から本を非階層クラスタリングで分類してみます。
手順は以下のとおり。
・Webのトップページから本の詳細情報情報にアクセスし、
本紹介の文章をリストで取得する
・本ごとに本紹介の文章を単語レベルに分解して、各々の単語に重み付けする
・上記情報をもとに、クラスタリングで本を分類する
言語はPythonを利用します。
Webから情報を取得する
※クローリングとスクレイピングで調べるといろいろ情報が出てくると思います。
1.まず、トップページにある新刊本の詳細ページへのURLを全て取得、
allBookLinksの中に配列で格納する。
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import mechanize
import MeCab
import util
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.cluster import AffinityPropagation
# get O'Reilly new books from Top page
page = mechanize.Browser()
page.open('http://www.oreilly.co.jp/index.shtml')
response = page.response()
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.read(), "html.parser")
allBookLinks = []
bibloLinks = soup.find_all("p", class_="biblio_link")
for bibloLink in bibloLinks:
books = bibloLink.find_all("a", href=re.compile("http://www.oreilly.co.jp/books/"))
for book in books:
allBookLinks.append( book.get("href") )
2.上記で取得した本の詳細ページURLに移動し、移動先のページから
titleListに本のタイトル・inputDatasに紹介文を格納する。
関連書籍情報のURLも取得し、1階層分だけリストに加える。
def get_detail_sentence_list( detailPageLink ):
page.open( detailPageLink )
detailResponse = page.response()
detailSoup = BeautifulSoup( detailResponse.read(), "html.parser" )
# get title
titleTag = detailSoup.find("h3", class_="title")
title = titleTag.get_text().encode('utf-8')
# get detail
detailDiv = detailSoup.find("div", id="detail")
detail = detailDiv.find("p").get_text().encode('utf-8')
# get relation book links
relationLinks = detailDiv.find_all("a")
relationLinkList = []
for relationLink in relationLinks:
href = relationLink.get("href")
if href.find('/books/') > 0:
relationLinkList.append(href[href.find('/books/') + len('/books/'):])
return [ title, detail, relationLinkList ]
# crolling books info
titleList = []
inputDatas = []
for bookLink in allBookLinks:
title, detail, relationLinkList = get_detail_sentence_list( bookLink )
# save
if not (title in titleList):
titleList.append(title)
inputDatas.append( detail )
# go to relation book links
for relationLink in relationLinkList:
title, detail, relationLinkList = get_detail_sentence_list( 'http://www.oreilly.co.jp/books/' + relationLink )
# save
if not (title in titleList):
titleList.append(title)
inputDatas.append( detail )
TF-IDF法で本ごとの紹介文を重み付けする
TfidfVectorizerを使ったXの中身は、
・len( X )=探索した本の数
・len( X[0] )=本の紹介文の単語の数
・X[0][0]=0番目の本の0番目に出てくる単語(terms[0]に格納されている単語)のTF-IDFの値
みたいな感じの行列。
ロジック組んでTF-IDFを計算しても良いけど、このライブラリを使うと楽。
def get_word_list( targetText ):
tagger = MeCab.Tagger()
wordList = []
if len(targetText) > 0:
node = tagger.parseToNode(targetText)
while node:
if len(util.mytrim(node.surface)) > 0:
wordList.append(node.surface)
node = node.next
return wordList
tfidfVectonizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer=get_word_list, min_df=1, max_df=50)
X = tfidfVectonizer.fit_transform( inputDatas )
terms = tfidfVectonizer.get_feature_names()
#coding:utf-8
def mytrim( target ):
target = target.replace(' ','')
return target.strip()
クラスタリングで本を分類する
K-meansとAffinityPropagationの両方で試してみた。
K-meansは先に何個に分類するか決まっているときに利用、
決まっていないときはAffinityPropagationを使うとかなりうまくいく。
今回の場合はAffinityPropagationのほうが適していたと思う。
# clustering by KMeans
k_means = KMeans(n_clusters=5, init='k-means++', n_init=5, verbose=True)
k_means.fit(X)
label = k_means.labels_
clusterList = {}
for i in range(len(titleList)):
clusterList.setdefault( label[i], '' )
clusterList[label[i]] = clusterList[label[i]] + ',' + titleList[i]
print 'By KMeans'
for key, value in clusterList.items():
print key
print value
print 'By AffinityPropagation'
# clustering by AffinityPropagation
af = AffinityPropagation().fit(X)
afLabel = af.labels_
afClusterList = {}
for i in range(len(titleList)):
afClusterList.setdefault( afLabel[i], '' )
afClusterList[afLabel[i]] = afClusterList[afLabel[i]] + ',' + titleList[i]
for key, value in afClusterList.items():
print key
print value
いちおう、AffinityPropagation使ったほうの実行結果
なんかそれっぽくなった!
- 分類1
- 実践 機械学習システム
- ハイパフォーマンスPython
- 初めてのコンピュータサイエンス
- Make: Electronics――作ってわかる電気と電子回路の基礎
- キャパシティプランニング――リソースを最大限に活かすサイト分析・予測・配置
- 詳説 イーサネット 第2版
- JavaScriptによるデータビジュアライゼーション入門
- 分類2
- 実践 Python 3
- Cython――Cとの融合によるPythonの高速化
- MongoDB & Python
- Python & AWS クックブック
- Pythonによるデータ分析入門――NumPy、pandasを使ったデータ処理
- Python文法詳解
- 実践 コンピュータビジョン
- 入門 Python 3
- 初めてのPython 第3版
- Pythonチュートリアル 第2版
- Arduinoをはじめよう 第3版
- Processingをはじめよう
- Python クックブック 第2版
- 入門 自然言語処理
- OpenStack Swift――Swiftオブジェクトストレージの管理と開発
- SAN & NAS ストレージネットワーク管理
- 分類3
- Prototyping Lab――「作りながら考える」ためのArduino実践レシピ
- ウェブオペレーション――サイト運用管理の実践テクニック
- 実践 Metasploit――ペネトレーションテストによる脆弱性評価
- ビジュアライジング・データ――Processingによる情報視覚化手法
- ビューティフルビジュアライゼーション
- 分類4
- メタプログラミングRuby 第2版
- Rubyベストプラクティス――プロフェッショナルによるコードとテクニック
- アンダースタンディング コンピュテーション――単純な機械から不可能なプログラムまで
- 初めてのRuby
- プログラミング言語 Ruby
- 分類5
- Seleniumデザインパターン & ベストプラクティス
- 実践 Selenium WebDriver
- テスタブルJavaScript
- ビューティフルテスティング――ソフトウェアテストの美しい実践