はじめに
1年以上前に、
Codeaを使ってiPadでアプリ開発(概要)
という記事を書いたのですが、概要の紹介だけで終わっていました。
今回はもう少し詳しく、Codeaで開発する際の実際のコードを紹介したいと思います。
なお、Codeaのリファレンスはアプリ上で見られる他、以下のページで確認できます。
Codea Reference
setup
まずはHelloWorld。
CodeaはMainのsetupという関数が最初に呼ばれます。
function setup()
print("Hello World!")
end
実行すると、「アウトプット」欄にHello World!が出力されているはずです。
draw
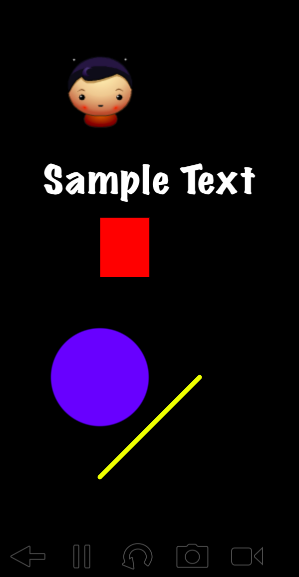
次に描画です。Codeaでは、draw関数が毎フレーム毎に呼び出されます。
function draw()
-- 黒で塗りつぶす
background(0, 0, 0)
-- ########## 線を引く ##########
-- rgba
stroke(255, 255, 0, 255)
-- 線の太さ
strokeWidth(5)
-- 線の端のスタイル
lineCapMode(ROUND)
-- x=100,y=100 -> x=200,y=200 の位置に線を引く
line(100, 100, 200, 200)
-- ########## 円を描く ##########
-- 円の縁の線をなしに
noStroke()
-- 円の塗りつぶしの色
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
-- x=100,y=200, 直径=100 の円を描く
ellipse(100, 200, 100)
-- ########## 四角を描く ##########
-- 四角の塗りつぶしの色
fill(255, 0, 0, 255)
-- x=100,y=300,width=50,height=100 の四角を描く
rect(100, 300, 50, 60)
-- ########## 文字を描く ##########
-- 文字色
fill(255, 255, 255, 255)
-- 文字サイズ
fontSize(40)
-- フォント
font("MarkerFelt-Wide")
-- x=150,y=400 の位置に文字を描画
text("Sample Text", 150, 400)
-- ########## 画像を描画 ##########
-- x=100,y=500 の位置に画像を描画
sprite("Planet Cute:Character Boy", 100, 500)
end
Codeaは円が綺麗に描けるのが、個人的には気に入っています。
最初にbackgroundやrect等で背景を塗りつぶさないと、一度描画したものが残り続けます。
fillやstroke等で設定した内容は、それ以降ずっと有効となったままです。
そのため、一時的に色やスタイルを変え、描画後に戻したい場合はpushStyle、popStyleで挟むと良いです。
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
pushStyle()
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
rect(100, 100, 100)
popStyle()
end
Touch
タッチイベントは、Mainのtouchedという関数で受け取ります。
function touched(touch)
if touch.state == BEGAN then
print("BEGAN : " .. touch.x .. ", " .. touch.y)
elseif touch.state == MOVING then
print("MOVING : " .. touch.x .. ", " .. touch.y)
elseif touch.state == ENDED then
print("ENDED : " .. touch.x .. ", " .. touch.y)
end
end
引数のtouchオブジェクトの中身は以下を参照してください
http://twolivesleft.com/Codea/Reference/Touch.html#touch
stateの値は、タッチ開始がBEGAN、ドラッグ中がMOVING、離すとENDEDとなります。
そのため、タッチ1回だけの取得であれば、touch.stage == ENDEDの場合のみ処理を実行すれば良いかと思います。
アニメーション
Codeaでオブジェクトを動かしたい場合、基本的な考え方は、drawでずらしながら描画するという方法です。
function setup()
x = 100
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(x, 100, 100)
-- x = 100 -> 300 まで移動
x = x + DeltaTime * 100
if x > 300 then
x = 300
end
end
しかしこれを毎回実装するのは面倒です。
そこでtween関数を使います。tweenを使うと、指定時間でオブジェクトの値を変化させる処理を
簡単に書くことができます。
上記と同じような処理をtweenで書き直すと、以下のようになります。
function setup()
obj = {x = 100, y = 100}
-- 2秒かけて、objのxを300まで変化させる
tween(2, obj, {x = 300})
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(obj.x, obj.y, 100)
end
tweenではeasingを指定することもできます。
function setup()
obj = {x = 100, y = 300}
tween(2, obj, {y = 100}, tween.easing.bounceOut)
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(obj.x, obj.y, 100)
end
easingは結構種類があります。
http://twolivesleft.com/Codea/Reference/Animation.html#3
さらにloopを指定することで、アニメーションを繰り返し実行することができます。
loopには、tween.loop.forever、tween.loop.pingpong を指定することができ、
pingpong は以下のように行ったり来たりを繰り返します。
function setup()
obj = {x = 100, y = 300}
tween_id = tween(0.5, obj, {y = 100}, {easing=tween.easing.cubicInOut, loop=tween.loop.pingpong})
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(obj.x, obj.y, 100)
end
tweenでは、さらにアニメーション完了時のコールバックを指定できます。
tween(0.5, obj, {y = 100}, tween.easing.liner, function()
print("complete.")
end)
Class
Codeaのアプリ上では、「新規クラスを作成」というボタンがあり、Classを作成して処理を分割することができます。
「新規クラスを作成」を実行すると、以下のような雛形が生成されます。
TestClass = class()
function TestClass:init(x)
-- you can accept and set parameters here
self.x = x
end
function TestClass:draw()
-- Codea does not automatically call this method
end
function TestClass:touched(touch)
-- Codea does not automatically call this method
end
このクラスはCodea独特のもので、以下のような特徴があります。
- 作ったクラスは自動で
requireされる - クラス名() でインスタンスを生成できる (例:TestClass() )
- initはコンストラクタ相当のもので、引数はインスタンス生成時に指定する
- 雛形で生成される
draw、touchedは勝手に呼ばれないので、Mainから呼び出す処理を書く
クラスの例
-- Main
function setup()
test = TestClass(100, 100)
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
test:draw()
end
function touched(touch)
test:touched(touch)
end
-- TestClass
TestClass = class()
function TestClass:init(x, y)
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.tween_id = tween(0.5, self, {y = 300}, {easing=tween.easing.linear, loop=tween.loop.pingpong})
end
function TestClass:draw()
pushStyle()
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(self.x, self.y, 100)
popStyle()
end
function TestClass:touched(touch)
if touch.state == ENDED and self.tween_id then
tween.stop(self.tween_id)
self.tween_id = nil
end
end
なお、class(親クラス) とすることで、クラスを継承することができます。
-- TestClass2
TestClass2 = class(TestClass)
補足
説明上、「クラス」「継承」と記載していますが、Luaにクラスは存在せず、実態はただのLuaのテーブルです。
当然クラスの継承というものもありません。
Codeaではclass()関数で特別なテーブルを生成しており、それにより、上記のような
オブジェクト指向的な書き方ができるようになっています。
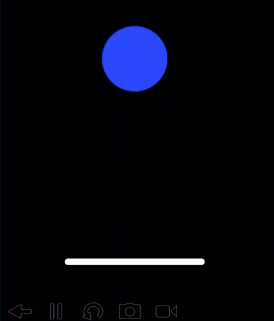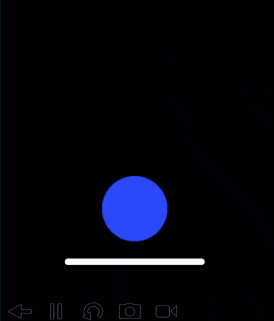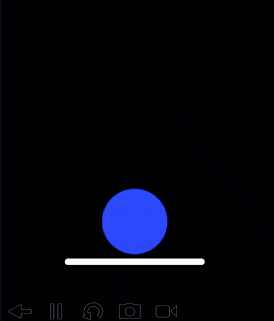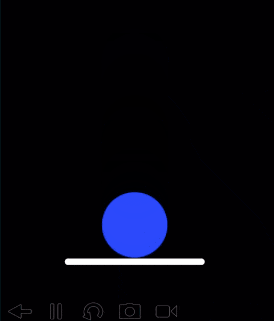
物理エンジン(Physics)
Codeaでは物理エンジンを使うこともできます。物理エンジンはBox2Dを使っています。
-- Main
function setup()
physics.gravity(0, -100) -- 重力
-- ボール
ball = physics.body(CIRCLE, 50)
ball.x = 200
ball.y = 400
ball.gravityScale = 10 -- 重力10倍
ball.restitution = 0.7 -- 反発係数
-- 床
flr = physics.body(EDGE, vec2(100, 100), vec2(300, 100))
flr.w = 10
end
function draw()
background(0, 0, 0)
-- ボール描画
pushStyle()
fill(0, 0, 255, 255)
ellipse(ball.x, ball.y, ball.radius * 2)
-- 床描画
pushStyle()
stroke(255, 255, 255, 255)
strokeWidth(flr.w)
local p = flr.points
line(p[1].x, p[1].y - 5, p[2].x, p[2].y - flr.w * 0.5)
popStyle()
end
Physicsはリファレンス等を見ても情報が少なく、使う方がわかりづらいのですが、
物理エンジンはBox2Dのため、Box2Dの使い方を調べればだいたいわかります。
おわりに
Codeaでゲームを開発する際の、基本的なAPIを紹介してみました。
他にもストレージやネットワーク、サウンド等、色々と便利なAPIがあるため、
興味がある方はリファレンスを一通り見てみると良いと思います。
最後に、Codeaで簡単な数字パズル的なゲームを作ってリリースしてみたので紹介しておきます。
Chain Numbers
以上