概要
Spring Bootを利用した複数のデータベースを扱うウェブアプリケーションのサンプルコードです。
環境
- Windows10 Professional
- Java 1.8.0_131
- Spring Boot 1.5.3
参考
- [SpringのAbstractRoutingDataSourceを使ってシャーディングっぽいことをしてみる!] (http://qiita.com/kazuki43zoo/items/9d8aec0ecab117a4d5c1)
- [Spring Boot multiple databases configuration] (http://roufid.com/spring-boot-multiple-databases-configuration/)
- [Multiple databases with Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA] (https://scattercode.co.uk/2016/01/05/multiple-databases-with-spring-boot-and-spring-data-jpa/)
- [Dynamic DataSource Routing with Spring @Transactional] (http://fedulov.website/2015/10/14/dynamic-datasource-routing-with-spring/)
- [[spring]10.5 Declarative transaction management] (http://d.hatena.ne.jp/minokuba/20110501/1304265347)
データベース
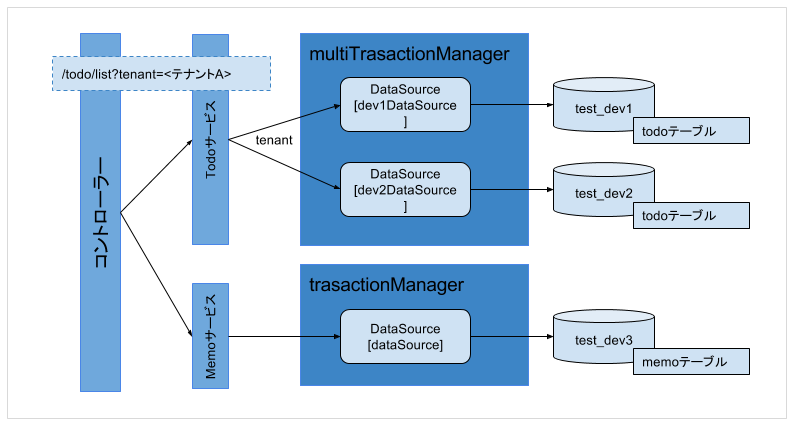
アプリケーションが扱うデータベースが下図のように3つあり、1つ(test_dev3)はアプリケーション共通のデータベース、残りの2つ(test_dev1,test_dev2)はマルチテナント的な扱いをするという想定です。
test_dev1とtest_dev2のデータベースのスキーマは同一で格納するデータが異なります。
- test_dev1をテナントA用のデータベース
- test_dev2をテナントB用のデータベース
- test_dev3をアプリケーション共通のデータベース
このサンプルアプリケーションでは、リクエストパラメータの値でtest_dev1とtest_dev2のデータベースを切り替えます。
またサンプルアプリケーションなので扱うテーブルに特に意味はありません(適当です)。
なお、JpaTransactionManagerでは複数のデータベース(データソース)をまたがるトランザクションは実行できないようです。
構造図
データソースの設定
データソースはapplication.ymlに下記の通り設定します。
spring:
datasource:
dev1:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/test_dev1
username: user_dev1
password: pass1
driverClassName: org.postgresql.Driver
defaultAutoCommit: false
defaultReadOnly: false
validationQuery: SELECT 'dev1'
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 3600000
dev2:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/test_dev2
username: user_dev2
password: pass2
driverClassName: org.postgresql.Driver
defaultAutoCommit: false
defaultReadOnly: false
validationQuery: SELECT 'dev2'
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 3600000
dev3:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/test_dev3
username: user_dev3
password: pass3
driverClassName: org.postgresql.Driver
defaultAutoCommit: false
defaultReadOnly: false
validationQuery: SELECT 'dev3'
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 3600000
jpa:
showSql: true
formatSql: true
logging:
level:
root: INFO
org.springframework: INFO
# org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager: DEBUG
# org.springframework.transaction: TRACE
org.hibernate: DEBUG
org.hibernate.SQL: DEBUG
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder: TRACE
# org.hibernate.transaction: DEBUG
# org.hibernate.jpa.internal: DEBUG
org.hibernate.event.internal: DEBUG
org.hibernate.engine.transaction.internal: DEBUG
org.hibernate.internal.util: DEBUG
データソースの設定コード
test_dev1
テナントA用データソースの設定です。
プロパティファイルの設定値からデータソースをビルドするだけの実装になります。エンティティマネージャ、トランザクションマネージャは別のクラスで実装します。
package com.example.datasource;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class Dev1DataSourceConfigure {
public static final String DEV1_DATASOURCE = "dev1DataSource";
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.dev1")
@Bean(DEV1_DATASOURCE)
public DataSource dataSource() {
DataSource dev1 = DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return dev1;
}
}
test_dev2
テナントB用データソースの設定です。
テナントAと同様の実装です。
package com.example.datasource;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class Dev2DataSourceConfigure {
public static final String DEV2_DATASOURCE = "dev2DataSource";
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.dev2")
@Bean(DEV2_DATASOURCE)
public DataSource dataSource() {
DataSource dev2 = DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return dev2;
}
}
test_dev1とtest_dev2を束ねるデータソースの設定
上記で実装した各テナント別のデータソースを参照するエンティティマネージャ、トランザクションマネージャを実装します。
実装のポイントは
- (1) : orderを指定します。この値はデータソースの切り替えを行うAOPのorderより大きな値にします。
- (2) : AbstractRoutingDataSourceを継承したクラスのインスタンスを生成し、スイッチするデータソースを設定します。
package com.example.datasource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import static com.example.datasource.Dev1DataSourceConfigure.DEV1_DATASOURCE;
import static com.example.datasource.Dev2DataSourceConfigure.DEV2_DATASOURCE;
import static com.example.datasource.MultiDataSourceConfigure.ENTITY_MANAGER;
import static com.example.datasource.MultiDataSourceConfigure.REPOSITORY_PACKAGE;
import static com.example.datasource.MultiDataSourceConfigure.TRANSACTION_MANAGER;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(order = 100) // (1)
@EnableJpaRepositories(
basePackages = {REPOSITORY_PACKAGE},
entityManagerFactoryRef = ENTITY_MANAGER,
transactionManagerRef = TRANSACTION_MANAGER
)
public class MultiDataSourceConfigure {
public static final String REPOSITORY_PACKAGE = "com.example.repository.tenantds";
public static final String ENTITY_PACKAGES = "com.example.entity.tenantds";
public static final String ENTITY_MANAGER = "multiEntityManagerFactory";
public static final String TRANSACTION_MANAGER = "multiTransactionManager";
public static final String MULTI_DATASOURCE_PU = "multiDataSourcePersistenceUnit";
public static final String MULTI_DATASOURCE = "multiDataSource";
@Autowired
@Qualifier(DEV1_DATASOURCE)
private DataSource dev1;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(DEV2_DATASOURCE)
private DataSource dev2;
@Bean(MULTI_DATASOURCE)
public RoutingDataSourceResolver multiDataSource() { // (2)
RoutingDataSourceResolver resolver = new RoutingDataSourceResolver();
// スイッチするデータソースを設定
Map<Object, Object> dataSources = new HashMap<Object,Object>();
dataSources.put(DEV1_DATASOURCE, dev1);
dataSources.put(DEV2_DATASOURCE, dev2);
resolver.setTargetDataSources(dataSources);
resolver.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dev1);
return resolver;
}
@Bean(ENTITY_MANAGER)
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(
EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean emf = builder
.dataSource(multiDataSource())
.persistenceUnit(MULTI_DATASOURCE_PU)
.packages(ENTITY_PACKAGES)
.build();
return emf;
}
@Bean(TRANSACTION_MANAGER)
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(
@Autowired @Qualifier(ENTITY_MANAGER) EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
JpaTransactionManager jtm = new JpaTransactionManager();
jtm.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory);
//jtm.setDataSource(multiDataSource());
return jtm;
}
}
test_dev1とtest_dev2をスイッチする設定
Spring FrameworkのAbstractRoutingDataSourceを継承してスイッチする処理を実装します。
package com.example.datasource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import static com.example.datasource.Dev1DataSourceConfigure.DEV1_DATASOURCE;
import static com.example.datasource.Dev2DataSourceConfigure.DEV2_DATASOURCE;
public class RoutingDataSourceResolver extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
if (MultiDataSourceContextHolder.getTenantType() == null) {
return DEV1_DATASOURCE;
}
// テナントとデータソースのマッピング
switch (MultiDataSourceContextHolder.getTenantType()) {
case TENANT_A:
return DEV1_DATASOURCE;
case TENANT_B:
return DEV2_DATASOURCE;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unknown tenant");
}
}
}
package com.example.datasource;
public class MultiDataSourceContextHolder {
private static ThreadLocal<TenantType> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setTenantType(TenantType tenantType) {
if (tenantType == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
contextHolder.set(tenantType);
}
public static TenantType getTenantType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearTenantType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}
テナントの種類を管理するEnum。
package com.example.datasource;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Optional;
public enum TenantType {
/* test_dev1 */
TENANT_A("aaa"),
/* test_dev2 */
TENANT_B("bbb")
;
private final String tenantName;
TenantType(String tenantName) {
this.tenantName = tenantName;
}
public String getTenantName() {
return this.tenantName;
}
public static TenantType byName(final String tenantName) {
Optional<TenantType> tenantType = Arrays.stream(TenantType.values())
.filter(t -> t.getTenantName().equals(tenantName))
.findFirst();
if (!tenantType.isPresent()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("unknown tenant name : [" + tenantName + "]");
}
return tenantType.get();
}
}
AOPでデータソースの切り替えを行う
データソースを切り替えるにはいくつか方法がありますが、このサンプルアプリケーションではSpring AOPの機能を使って行います。
下記のアノテーションを付与したクラスの「tenant」という引数があるメソッドに対して設定します。
このtenantという引数の値でデータソースの切り替えを行います。
package com.example.aop;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface SwitchingDataSource {
}
Orderアノテーションでトランザクションより先にデータソースの切り替えが行われるように調整します。
実装のポイントは
- (1) : トランザクションマネージャで設定した値より小さな値にします。
- (2) : データソースを切り替えるポイントカットの指定です。アノテーションと引数名で絞り込みを行います。
- (3) : 同上
package com.example.aop;
import com.example.datasource.MultiDataSourceContextHolder;
import com.example.datasource.TenantType;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Order(99) // (1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class SwitchingDataSourceAop {
@Around("@annotation(swds) && args(tenant,..)") // (2)
public Object switchingForMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, SwitchingDataSource swds, String tenant) throws Throwable {
try {
switching(tenant);
Object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
} finally {
clear();
}
}
@Around("@within(swds) && args(tenant,..)") // (3)
public Object switchingForClass(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, SwitchingDataSource swds, String tenant) throws Throwable {
try {
switching(tenant);
Object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
} finally {
clear();
}
}
private void switching(String tenant) {
TenantType tenantType = TenantType.byName(tenant);
MultiDataSourceContextHolder.setTenantType(tenantType);
}
private void clear() {
MultiDataSourceContextHolder.clearTenantType();
}
}
test_dev3用のデータソース
アプリケーション共通のデータソースは切り替えを行う必要がないので、このクラスでエンティティマネージャ、トランザクションマネージャの実装まで行います。
ちなみにこの設定がデフォルトとなるようにPrimaryアノテーションを付けています。
package com.example.datasource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Properties;
import static com.example.datasource.SingleDataSourceConfigure.ENTITY_MANAGER;
import static com.example.datasource.SingleDataSourceConfigure.REPOSITORY_PACKAGES;
import static com.example.datasource.SingleDataSourceConfigure.TRANSACTION_MANAGER;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(order = 101)
@EnableJpaRepositories(
basePackages = {REPOSITORY_PACKAGES},
entityManagerFactoryRef = ENTITY_MANAGER,
transactionManagerRef = TRANSACTION_MANAGER
)
public class SingleDataSourceConfigure {
public static final String REPOSITORY_PACKAGES = "com.example.repository.appds";
public static final String ENTITY_PACKAGES = "com.example.entity.appds";
public static final String ENTITY_MANAGER = "entityManagerFactory";
public static final String TRANSACTION_MANAGER = "transactionManager";
public static final String SINGLE_DATASOURCE_PU = "singleDataSourcePersistenceUnit";
public static final String SINGLE_DATASOURCE = "singleDataSource";
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.dev3")
@Bean(SINGLE_DATASOURCE)
public DataSource singleDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return dataSource;
}
@Primary
@Bean(ENTITY_MANAGER)
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(
EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean emf = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
emf.setDataSource(singleDataSource());
emf.setPersistenceUnitName(SINGLE_DATASOURCE_PU);
emf.setPackagesToScan(ENTITY_PACKAGES);
JpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
emf.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
emf.setJpaProperties(additionalProperties());
return emf;
}
@Primary
@Bean(TRANSACTION_MANAGER)
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(
@Autowired @Qualifier(ENTITY_MANAGER) EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
JpaTransactionManager jtm = new JpaTransactionManager();
jtm.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory);
//jtm.setDataSource(singleDataSource());
return jtm;
}
@Bean
public PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor exceptionTranslation(){
return new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor();
}
private Properties additionalProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.use_sql_comments", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.generate_statistics", "false");
return properties;
}
}
エンティティとリポジトリ
下記のようにテナント用とアプリケーション共通用をパッケージを分けて管理します。
なお、エンティティ、リポジトリより上位のサービスクラスはパッケージを分ける必要が無いので分けていません。
com.example
|
+--- entity
| |
| +--- tenantds //tenant datasource
| | |
| | +--- Todo
| |
| +--- appds //application datasource
| |
| +--- Memo
|
+--- repository
| |
| +--- tenantds
| | |
| | +--- TodoRepository
| |
| +--- appds
| |
| +--- MemoRepository
|
+--- service
|
+--- impl
| |
| +--- TodoService
| +--- MemoService
|
+--- TodoServiceImpl
+--- MemoServiceImpl
エンティティ
パッケージを分けるだけで実装に特別なところはありません。
package com.example.entity.tenantds;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.SequenceGenerator;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
@Table(name="todo")
@SequenceGenerator(name = "todo_id_gen", sequenceName = "todo_id_seq", allocationSize = 1)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Todo {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@Column(name="done")
private Boolean done;
@Column(name="updated")
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date updated;
}
package com.example.entity.appds;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.SequenceGenerator;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
@Table(name="memo")
@SequenceGenerator(name = "memo_id_gen", sequenceName = "memo_id_seq", allocationSize = 1)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Memo {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@Column(name="description")
private String description;
@Column(name="done")
private Boolean done;
@Column(name="updated")
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date updated;
}
リポジトリ
package com.example.repository.tenantds;
import com.example.entity.multids.Todo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Lock;
import javax.persistence.LockModeType;
public interface TodoRepository extends JpaRepository<Todo, Long> {
@Lock(LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
Todo findById(Long id);
}
package com.example.repository.appds;
import com.example.entity.singleds.Memo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Lock;
import javax.persistence.LockModeType;
public interface MemoRepository extends JpaRepository<Memo, Long> {
@Lock(LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
Memo findById(Long id);
}
コントローラーとサービス
コントローラー
リクエストパラメータ「tenant」の値でデータソースを切り替えます。
/todo/list?tenant=<テナントコード>
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.entity.tenantds.Todo;
import com.example.service.TodoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@RequestMapping(path = "todo")
@RestController
public class TodoController {
@Autowired
private TodoService service;
@GetMapping(path = "list", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public List<Todo> list(
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = true) String tenant) throws Exception {
List<Todo> lists = service.list(tenant);
return lists;
}
@GetMapping(path = "update", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public Todo update(
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = true) String tenant,
@RequestParam(value = "id", required = true) Long id,
@RequestParam(value = "title") String title,
@RequestParam(value = "done", defaultValue = "FALSE") Boolean done,
@RequestParam(value = "wt", defaultValue = "30") Long waittime) throws Exception {
Todo todo = service.lockAndUpdate(tenant, id, title, done, new Date(), waittime);
return todo;
}
@GetMapping(path = "insert", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public Todo insert(
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = true) String tenant,
@RequestParam(name = "title", required = true) String title) throws Exception {
Todo todo = service.insert(tenant, title, Boolean.FALSE, new Date());
return todo;
}
}
サービス
package com.example.service;
import com.example.entity.tenantds.Todo;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public interface TodoService {
List<Todo> list(String tenant);
Todo lockAndUpdate(String tenant, Long id, String title, Boolean done, Date updated, Long waittime) throws Exception;
Todo insert(String tenant, String title, Boolean done, Date updated) throws Exception;
}
実装にいくつかポイントがあります。
- (1) : データソースの切り替えを行うクラスに、このアノテーションを付与します。
- (2) : トランザクションマネージャを明記します。
- (3) : 1番目にtenantという名前の引数を取ります。
(1)と(3)はAOPでデータソースを切り替えるために必要な実装になります。
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.aop.SwitchingDataSource;
import com.example.entity.tenantds.Todo;
import com.example.repository.tenantds.TodoRepository;
import com.example.service.TodoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static com.example.datasource.MultiDataSourceConfigure.TRANSACTION_MANAGER;
@Service
@SwitchingDataSource // (1)
@Transactional(readOnly = true, timeout = 10, transactionManager = TRANSACTION_MANAGER) // (2)
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
@Autowired
private TodoRepository repository;
@Override
public List<Todo> list(String tenant) { // (3)
Sort sort = new Sort(new Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "updated"), new Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id"));
List<Todo> lists = repository.findAll(sort);
return lists;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = false, timeout = 120, rollbackFor = Exception.class, transactionManager = TRANSACTION_MANAGER)
@Override
public Todo lockAndUpdate(String tenant, Long id, String title, Boolean done, Date updated, Long waittime) throws Exception {
Todo todo = repository.findById(id);
todo.setTitle(title);
todo.setDone(done);
todo.setUpdated(updated);
// タイムアウトテスト用コード
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(waittime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("timeout:" + e.getMessage());
throw new Exception("timeout");
}
repository.save(todo);
return todo;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = false, rollbackFor = Exception.class, transactionManager = TRANSACTION_MANAGER)
@Override
public Todo insert(String tenant, String title, Boolean done, Date updated) throws Exception {
Todo todo = Todo.builder().title(title).done(done).updated(updated).build();
repository.save(todo);
return todo;
}
}