JUnit5 の Alpha 版が公開されてたので、関西DDDに補欠になってしまった悲しみを紛らわすために使い方を調べた。
※Alpha 版なので、今後変更されるかもしれません。
JUnit5 とは
言わずと知れた JUnit の次期バージョン。
Java 8 以上のみをサポートするようになり、 JUnit4 からは大きく変わっている。
でも、テストメソッドとか基本的な考えは変わっていない。
2016/02/06 現在、 Alpha 版が公開されている。
Hello World
Gradle で使う方法(Maven でもいけるらしい)。
ビルドファイル
buildscript {
repositories {
maven { url 'https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots' }
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.junit:junit-gradle:5.0.0-SNAPSHOT'
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.junit.gen5.gradle'
apply plugin: 'java'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testCompile 'org.junit:junit5-api:5.0.0-ALPHA'
}
junit5 {
version '5.0.0-ALPHA'
}
実装
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
assertEquals("hoge", "hoge");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
assertEquals("hoge", "fuga");
}
}
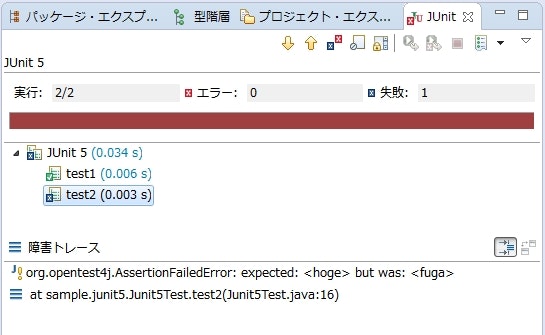
動作確認
> gradle -q junit5Test
2 06, 2016 2:55:35 午後 org.junit.gen5.launcher.main.ServiceLoaderTestEngineRegistry loadTestEngines
情報: Discovered TestEngines with IDs [junit5]
Test failures (1):
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:test2
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test2()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <fuga>
Test run finished after 76 ms
[ 2 tests found ]
[ 0 tests skipped ]
[ 2 tests started ]
[ 0 tests aborted ]
[ 1 tests successful]
[ 1 tests failed ]
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':junit5Test'.
> Process 'command 'C:\Program Files\Java\jdk8\bin\java.exe'' finished with non-zero exit value 1
* Try:
Run with --stacktrace option to get the stack trace. Run with --info or --debug option to get more log output.
- Gradle 用のプラグインが用意されているので、それを利用する。
- とりあえず
junit5.versionを設定したら動いた。 -
junit5Testタスクでテストを実行できる。
テスト結果のファイル
デフォルトでは、 build/test-results/junit5 の下に xml ファイルが出力される。
このファイルは、 JUnit4 までのテスト結果ファイルと同じフォーマットなので、 eclipse などで開いて見ることができる。
テストインスタンスのライフサイクル
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1 : " + this.hashCode());
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2 : " + this.hashCode());
}
}
test1 : 66233253
test2 : 152005629
- テストメソッドが実行されるごとに新しいインスタンスが生成される。
アサーション
標準で、簡単なアサーションがいくつか用意されている。
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void trueであることの検証() {
assertTrue(false);
}
@Test
public void trueであることの検証_ラムダ式も渡せる() {
assertTrue(() -> false);
}
@Test
public void trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをセットできる() {
assertTrue(false, "true を期待したのに false だった");
}
@Test
public void trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをラムダ式でセットできる() {
assertTrue(false, () -> "true を期待したのに false だった");
}
@Test
public void falseであることの検証() {
assertFalse(true);
}
@Test
public void equalsで比較して同じことを検証() {
assertEquals("hoge", "fuga");
}
@Test
public void equalsで比較して異なることを検証() {
assertNotEquals("hoge", "hoge");
}
@Test
public void nullでないことを検証() {
assertNotNull(null);
}
@Test
public void nullであることを検証() {
assertNull("not null");
}
@Test
public void 等号で比較して同じインスタンスであることを検証() {
assertSame(new String("hoge"), new String("hoge"));
}
@Test
public void 指定した例外がスローされることを検証() {
assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {throw new NullPointerException();});
}
@Test
public void スローされた例外を検証したうえで_その例外を取得する() {
IllegalArgumentException e = expectThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("テストです");
});
assertEquals("test です", e.getMessage());
}
@Test
public void 複数のアサーションをまとめて実行() {
assertAll(
() -> assertTrue(false, "true と信じてたら false だった"),
() -> assertEquals("hoge", "fuga", "hoge と信じてる")
);
}
}
Test failures (13):
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:trueであることの検証_ラムダ式も渡せる
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#trueであることの検証_ラムダ式も渡せる()
=> Exception: null
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:指定した例外がスローされることを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#指定した例外がスローされることを検証()
=> Exception: Unexpected exception type thrown ==> expected: <java.lang.IllegalArgumentException> but was: <java.lang.NullPointerException>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをセットできる
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをセットできる()
=> Exception: true を期待したのに false だった
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:equalsで比較して異なることを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#equalsで比較して異なることを検証()
=> Exception: expected: not equal but was: <hoge>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:複数のアサーションをまとめて実行
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#複数のアサーションをまとめて実行()
=> Exception: Multiple Failures (2 failures)
true と信じてたら false だった
hoge と信じてる ==> expected: <hoge> but was: <fuga>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:trueであることの検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#trueであることの検証()
=> Exception: null
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:falseであることの検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#falseであることの検証()
=> Exception: null
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:nullでないことを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#nullでないことを検証()
=> Exception: expected: not <null>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:nullであることを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#nullであることを検証()
=> Exception: expected: <null> but was: <not null>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをラムダ式でセットできる
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#trueであることの検証_末尾に任意のメッセージをラムダ式でセットできる()
=> Exception: true を期待したのに false だった
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:equalsで比較して同じことを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#equalsで比較して同じことを検証()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <fuga>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:等号で比較して同じインスタンスであることを検証
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#等号で比較して同じインスタンスであることを検証()
=> Exception: expected: java.lang.String@69d9c55<hoge> but was: java.lang.String@13a57a3b<hoge>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:スローされた例外を検証したうえで_その例外を取得する
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#スローされた例外を検証したうえで_その例外を取得する()
=> Exception: expected: <test です> but was: <テストです>
任意のアサーションライブラリを使う
dependencies {
testCompile 'org.junit:junit5-api:5.0.0-ALPHA'
testCompile 'org.assertj:assertj-core:3.3.0'
testCompile 'org.hamcrest:hamcrest-all:1.3'
}
package sample.junit5;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.*;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void assertj() {
Assertions.assertThat("hoge").isEqualTo("fuga");
}
@Test
public void hamcrest() {
MatcherAssert.assertThat("hoge", is("fuga"));
}
}
Test failures (2):
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:assertj
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#assertj()
=> Exception:
Expecting:
<"hoge">
to be equal to:
<"fuga">
but was not.
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:hamcrest
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#hamcrest()
=> Exception:
Expected: is "fuga"
but: was "hoge"
Test run finished after 109 ms
[ 2 tests found ]
[ 0 tests skipped ]
[ 2 tests started ]
[ 0 tests aborted ]
[ 0 tests successful]
[ 2 tests failed ]
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.
- JUnit5 は特定のアサーションライブラリに依存しておらず、任意のライブラリを使用できる。
- 試しに Hamcrest と AssertJ を試したが、問題なく動いた。
- どちらも JUnit4 に依存してるんじゃないの? って思ってたけど、
gradle dependenciesで確認したら依存してなかった。 - よくできとるわ。
- どちらも JUnit4 に依存してるんじゃないの? って思ってたけど、
アノテーション
@Test
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
public void test0() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test0");
}
@Test
public void test1() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test1");
}
@Test
protected void test2() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test2");
}
@Test
void test3() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test3");
}
@Test
private void test4() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test4");
}
}
Test failures (3):
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:test1
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test1()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <test1>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:test2
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test2()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <test2>
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:test3
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test3()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <test3>
Test run finished after 81 ms
[ 3 tests found ]
[ 0 tests skipped ]
[ 3 tests started ]
[ 0 tests aborted ]
[ 0 tests successful]
[ 3 tests failed ]
-
@Testでアノテートしたメソッドがテストメソッドになる。- JUnit4 の
@Testとはパッケージが異なる。
- JUnit4 の
- テストメソッドは
public,protected, デフォルトのいずれか。-
privateを@Testでアノテートしてもエラーにはならずに無視される。
-
@DisplayName
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
@DisplayName("JUnit5 のテスト")
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
@DisplayName("1つ目のテストやで!")
public void test1() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
assertEquals("hoge", "test2");
}
}
Test failures (2):
JUnit 5:JUnit5 のテスト:1つ目のテストやで!
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test1()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <test1>
JUnit 5:JUnit5 のテスト:test2
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test2()
=> Exception: expected: <hoge> but was: <test2>
- テスト名を指定できる。
- 先頭が数字でもいいし、スペースが入っていてもいい。
- クラスもアノテートできる。
@BeforeEach - @AfterEach
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeEach
public void before1() {
System.out.println("before1");
}
@BeforeEach
protected void before2() {
System.out.println("before2");
}
@BeforeEach
void before3() {
System.out.println("before3");
}
@BeforeEach
private void before4() {
System.out.println("before4");
}
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println(" test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println(" test2");
}
@AfterEach
public void after1() {
System.out.println("after1");
}
@AfterEach
protected void after2() {
System.out.println("after2");
}
@AfterEach
void after3() {
System.out.println("after3");
}
@AfterEach
private void after4() {
System.out.println("after4");
}
}
before1
before2
before3
before4
test1
after4
after3
after2
after1
before1
before2
before3
before4
test2
after4
after3
after2
after1
- テストメソッド単位で前処理と後処理を挟める。
-
@BeforeEachが前処理で、@AfterEachが後処理。 - メソッドの可視性はなんでもいい。
@BeforeAll - @AfterAll
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll1() {
System.out.println("beforeAll1");
}
@BeforeAll
protected static void beforeAll2() {
System.out.println("beforeAll2");
}
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll3() {
System.out.println("beforeAll3");
}
@BeforeAll
private static void beforeAll4() {
System.out.println("beforeAll4");
}
@BeforeEach
public void before() {
System.out.println(" before");
}
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println(" test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println(" test2");
}
@AfterEach
public void after() {
System.out.println(" after");
}
@AfterAll
public static void afterAll1() {
System.out.println("afterAll1");
}
@AfterAll
protected static void afterAll2() {
System.out.println("afterAll2");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll3() {
System.out.println("afterAll3");
}
@AfterAll
private static void afterAll4() {
System.out.println("afterAll4");
}
}
beforeAll1
beforeAll2
beforeAll3
beforeAll4
before
test1
after
before
test2
after
afterAll4
afterAll3
afterAll2
afterAll1
- テストクラス単位で前処理と後処理を挟める。
-
@BeforeAllが前処理で、@AfterAllが後処理。 - メソッドの可視性はなんでもいい。
- メソッドは
staticにしておく必要がある。
@Nested
基本
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Nested;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Nested
public class NestedTest {
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
}
test2
test1
-
@Nestedでインナークラスをアノテートすることで、テストクラスの入れ子ができるようになる。 - インナークラスは非
staticにする。
@DisplayName との組み合わせ
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Nested;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
@DisplayName("JUnit5 のテスト")
public class Junit5Test {
@Nested
@DisplayName("◯◯の場合")
public class NestedTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("テスト1")
public void test1() {
assertEquals("foo", "bar");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("テスト2")
public void test2() {
assertEquals("foo", "bar");
}
}
}
Test failures (2):
JUnit 5:JUnit5 のテスト:◯◯の場合:テスト1
sample.junit5.Junit5Test$NestedTest#test1()
=> Exception: expected: <foo> but was: <bar>
JUnit 5:JUnit5 のテスト:◯◯の場合:テスト2
sample.junit5.Junit5Test$NestedTest#test2()
=> Exception: expected: <foo> but was: <bar>
-
@DisplayNameでインナークラスをアノテートできる。 - 結果の表示にインナークラスの分も反映される。
@BeforeEach とかとの組み合わせ
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Nested;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("beforeAll");
}
@BeforeEach
public void before1() {
System.out.println(" before1");
}
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println(" test1");
}
@AfterEach
public void after1() {
System.out.println(" after1");
}
@AfterAll
public static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("afterAll");
}
@Nested
public class NestedClass {
@BeforeEach
public void before2() {
System.out.println(" before2");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println(" test2");
}
@AfterEach
public void after2() {
System.out.println(" after2");
}
}
}
beforeAll
beforeAll
before1
before2
test2
after2
after1
afterAll
before1
test1
after1
afterAll
-
@BeforeAllはネストされたクラスも含めて、それぞれのクラスの最初と最後で実行される。- ↑の実行結果では、最初と最後の
beforeAll,afterAllがJUnit5Testの分で、 - 2つ目の
beforeAllとafterAllがNestedClassの分になっている。
- ↑の実行結果では、最初と最後の
- ネストされたクラスの外にある
@BeforeEach,@AfterEachは、ネストされたクラス内のテストメソッドに対しても有効になる。
クラスを継承している場合
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Nested;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll1() {
System.out.println("beforeAll1");
}
@AfterAll
public static void afterAll1() {
System.out.println("afterAll1");
}
@BeforeEach
public void before1() {
System.out.println(" before1");
}
@AfterEach
public void after1() {
System.out.println(" after1");
}
public static class Base {
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll2() {
System.out.println(" beforeAll2");
}
@AfterAll
public static void afterAll2() {
System.out.println(" afterAll2");
}
@BeforeEach
public void before2() {
System.out.println(" before2");
}
@AfterEach
public void after2() {
System.out.println(" after2");
}
}
@Nested
public class NestedTest extends Base {
@BeforeEach
public void before3() {
System.out.println(" before3");
}
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println(" test");
}
@AfterEach
public void after3() {
System.out.println(" after3");
}
}
}
beforeAll1
beforeAll1
beforeAll2
before1
before2
before3
test
after3
after2
after1
afterAll2
afterAll1
afterAll1
- ネストしたクラスの親が
@BeforeEachや@BeforeAllを持つ場合、それらも有効になる。
@Tag
基本
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Tag;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
@Tag("hoge")
public void test1() {
System.out.println("[hoge] test1");
}
@Test
@Tag("fuga")
public void test2() {
System.out.println("[fuga] test2");
}
@Test
@Tag("hoge") @Tag("fuga")
public void test3() {
System.out.println("[hoge, fuga] test3");
}
@Test
@Tag("hoge") @Tag("piyo")
public void test4() {
System.out.println("[hoge, piyo] test4");
}
}
junit5 {
version '5.0.0-ALPHA'
requireTag 'hoge'
excludeTag 'piyo'
}
[hoge] test1
[hoge, fuga] test3
- テストメソッドを任意の名前でタグ付けできる。
- 1つのメソッドに複数のタグを設定することもできる。
- クラスにタグを付けることも可能。
- オプションの
requireTagまたはexcludeTagで、実行するタグを絞り込める。-
requireTagで実行するタグを絞り込む。 -
excludeTagで実行しないタグを絞り込む。 - 両方の条件に一致する場合は、
excludeTagが優先される(test4())。
-
requireTag, excludeTag で複数のタグを指定したい場合は、以下のように記述する。
junit5 {
version '5.0.0-ALPHA'
requireTag 'hoge'
requireTag 'fuga'
}
メタアノテーション
package sample.junit5;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Tag;
@Tag("hoge")
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Hoge {
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
@Hoge
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
junit5 {
version '5.0.0-ALPHA'
requireTag 'hoge'
}
test1
-
@Tagなどでアノテートした独自のアノテーションを作ることができる。 - 複数のアノテーションをまとめることもできる。
@Disabled
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
@Disabled
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
test1
-
@Disabledでアノテートされたメソッド(クラス)はテスト対象外になる。
Assumptions(特定の条件が満たされているときだけテストを続行する)
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assumptions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
assumeTrue(true);
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
assumeTrue(false);
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
test1
Test run finished after 76 ms
[ 2 tests found ]
[ 0 tests skipped ]
[ 2 tests started ]
[ 1 tests aborted ]
[ 1 tests successful]
[ 0 tests failed ]
-
Assumptionsに定義されているstaticメソッドを使う。 - 条件が満たされたときだけ、テストが続行される。
- 条件が満たされなかったテストは
abortedにカウントされている。
- 条件が満たされなかったテストは
- ユーザーガイドにあった利用例では、環境変数の値を見て環境によって実行するテストを動的に切り替えたりするのに使うらしい。
メソッド引数
テスト名を受け取る
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.TestInfo;
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeEach
public void before(TestInfo info) {
System.out.println(
"[before]\n" +
"displayName=" + info.getDisplayName() + "\n" +
"name=" + info.getName()
);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("テスト")
public void test(TestInfo info) {
System.out.println(
"[test]\n" +
"displayName=" + info.getDisplayName() + "\n" +
"name=" + info.getName()
);
}
}
[before]
displayName=テスト
name=sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test(org.junit.gen5.api.TestInfo)
[test]
displayName=テスト
name=sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test(org.junit.gen5.api.TestInfo)
-
TestInfoを引数として受け取るようにすると、自動的にインスタンスが渡される。 -
@BeforeEachなどでも受け取れる。
JUnit4 を使って JUnit5 を動かす
JUnit4 を使って JUnit5 を動かすことができる。
この仕組を利用すれば、既存の JUnit4 をサポートしている IDE やビルドツール上から JUnit5 のテストを動かすことができる。
apply plugin: 'java'
sourceCompatibility = '1.8'
targetCompatibility = '1.8'
[compileJava, compileTestJava]*.options*.encoding = 'UTF-8'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
testCompile 'org.junit:junit5-api:5.0.0-ALPHA'
testCompile 'org.junit:junit4-runner:5.0.0-ALPHA'
testCompile 'org.junit:junit5-engine:5.0.0-ALPHA'
}
- JUnit4 に加えて、以下を設定する。
junit5-apijunit4-runnerjunit5-engine
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.junit4.runner.JUnit5;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(JUnit5.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
@DisplayName("テストです")
public void test() {
assertEquals("hoge", "fuga");
}
}
-
@RunWithでJUnit5.classを指定することで、 JUnit4 上で JUnit5 を実行できるようになる。
> gradle -q test
1 test completed, 1 failed
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.
- Gradle から実行できた。
- Eclipse プラグインを使って Eclipse プロジェクト化してインポートすれば、普通に Eclipse 上でも実行できる。
Extension Model
JUnit5 では、テストを拡張するための仕組みとして Extension Model というのが用意されている。
基本
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ConditionEvaluationResult;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExecutionCondition;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements TestExecutionCondition {
@Override
public ConditionEvaluationResult evaluate(TestExtensionContext context) {
String name = context.getDisplayName();
if (name.startsWith("hoge")) {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.enabled("hoge で始まってるので");
} else {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.disabled("hoge で始まってないので");
}
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void hoge() {
System.out.println("hoge");
}
@Test
public void fuga() {
System.out.println("fuga");
}
}
hoge
- 拡張用のクラスは、
ExtensionPointというインターフェースを実装することで作成する。- ただし、
ExtensionPoint自体はただのマーカーインターフェースで、実際はそれを継承したインターフェースを実装する。 - ここでは
TestExecutionConditionというインターフェースを実装している。
- ただし、
- 作成したクラスは、
@ExtendWithアノテーションの引数に、そのClassオブジェクトを渡すことで利用できる。
ContainerExecutionCondition
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ConditionEvaluationResult;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ContainerExecutionCondition;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ContainerExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements ContainerExecutionCondition {
@Override
public ConditionEvaluationResult evaluate(ContainerExtensionContext context) {
String displayName = context.getDisplayName();
if (displayName.contains("Hoge")) {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.enabled("Hoge なので");
} else {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.disabled("Hoge でないので");
}
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Nested;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
public class Junit5Test {
@Nested
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Hoge {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("Hoge.test");
}
}
@Nested
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Fuga {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("Fuga.test");
}
}
}
Hoge.test
- テストクラス単位でテストを実行するかどうかを制御できる。
-
ConditionEvaluationResult.enabled()で生成したインスタンスを返せばテストが実行され、ConditionEvaluationResult.disabled()で生成したインスタンスを返せばテストをスキップする。
TestExecutionCondition
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ConditionEvaluationResult;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExecutionCondition;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements TestExecutionCondition {
@Override
public ConditionEvaluationResult evaluate(TestExtensionContext context) {
String displayName = context.getDisplayName();
if ("hoge".equals(displayName)) {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.enabled("hoge なので");
} else {
return ConditionEvaluationResult.disabled("hoge じゃないので");
}
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void hoge() {
System.out.println("hoge");
}
@Test
public void fuga() {
System.out.println("fuga");
}
}
hoge
- メソッド単位でテストを実行するかどうかを制御できる。
InstancePostProcessor
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.InstancePostProcessor;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements InstancePostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessTestInstance(TestExtensionContext context) throws Exception {
Object testInstance = context.getTestInstance();
System.out.println(testInstance.getClass());
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.gen5.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("beforeAll");
}
@BeforeEach
public void before() {
System.out.println("before");
}
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
beforeAll
class sample.junit5.Junit5Test
before
test1
class sample.junit5.Junit5Test
before
test2
- テストクラスのインスタンスが生成されるたびに実行する処理を定義できる。
- テストインスタンスに依存する他のインスタンスをインジェクションしたいときなどに利用する。
MethodParameterResolver
基本
package sample.junit5;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtensionContext;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.MethodInvocationContext;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.MethodParameterResolver;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ParameterResolutionException;
public class MyExtend implements MethodParameterResolver {
@Override
public boolean supports(Parameter parameter, MethodInvocationContext methodInvocationContext, ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws ParameterResolutionException {
System.out.println("supports()");
return String.class.equals(parameter.getType());
}
@Override
public Object resolve(Parameter parameter, MethodInvocationContext methodInvocationContext, ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws ParameterResolutionException {
System.out.println("resolve()");
return "hoge";
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
public void test2(String string) {
System.out.println("test2 string=" + string);
}
}
test1
supports()
resolve()
test2 string=hoge
- メソッドの引数を解決することができる。
-
supports()とresolve()を実装する。- どちらも、次の3つの引数を受け取る。
-
Parameter:対象の引数のメタ情報 -
MethodInvocationContext:対象のテストメソッドのメタ情報 -
ExtensionContext:対象テストのメタ情報
-
-
supports()は、対象の引数が処理対象となるかどうかを判定してbooleanで返す。 -
resolve()は、引数に渡す値を返す。
- どちらも、次の3つの引数を受け取る。
- テストメソッドが引数を持つ場合に、
supports()メソッドが呼ばれる。
サポートしない引数を持つ場合
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test(int number) {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
supports()
Test failures (1):
JUnit 5:sample.junit5.Junit5Test:test
sample.junit5.Junit5Test#test(int)
=> Exception: No MethodParameterResolver registered for parameter [int arg0] in method [public void sample.junit5.Junit5Test.test(int)].
- エラーになる。
引数が複数存在する場合
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test(String str1, String str2) {
System.out.println("test str1=" + str1 + ", str2=" + str2);
}
}
supports()
resolve()
supports()
resolve()
test str1=hoge, str2=hoge
- それぞれの引数に対して
supports()-resolve()が呼ばれる。
ライフサイクル・コールバック
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.BeforeEachExtensionPoint;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements BeforeEachExtensionPoint {
@Override
public void beforeEach(TestExtensionContext context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyExtend.beforeEach()");
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
}
MyExtend.beforeEach()
test1
MyExtend.beforeEach()
test2
-
BeforeEachExtensionPointを実装することで、テストメソッドの前処理を実装できる。 - これ以外には、以下のインターフェースが用意されている。
AfterEachExtensionPointBeforeAllExtensionPointAfterAllExtensionPoint
- それぞれ、名前から予想されるとおりに動くと思う。
ExceptionHandlerExtensionPoint
package sample.junit5;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExceptionHandlerExtensionPoint;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.TestExtensionContext;
public class MyExtend implements ExceptionHandlerExtensionPoint {
@Override
public void handleException(TestExtensionContext context, Throwable throwable) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("handleException() class=" + throwable.getClass() + ", message=" + throwable.getMessage());
}
}
package sample.junit5;
import static org.junit.gen5.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.gen5.api.Test;
import org.junit.gen5.api.extension.ExtendWith;
@ExtendWith(MyExtend.class)
public class Junit5Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
assertEquals("hoge", "fuga");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
throw new NullPointerException("test");
}
}
handleException() class=class org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError, message=expected: <hoge> but was: <fuga>
handleException() class=class java.lang.NullPointerException, message=test
Test run finished after 70 ms
[ 2 tests found ]
[ 0 tests skipped ]
[ 2 tests started ]
[ 0 tests aborted ]
[ 2 tests successful]
[ 0 tests failed ]
- スローされた例外をハンドリングできる。
- アサーションで失敗になったときの例外もハンドリングされてしまう。
- ハンドリングした例外をスローし直さないと、テストが成功扱いになる!(これはこわい)。
所感
- 良いなと思ったところ
- テスト名が任意の文字列で定義できるようになったこと。
- だからと言って、テストメソッドを適当な名前にすると、今まで Eclipse の「クイック・アウトライン」とかでテストメソッドの俯瞰をしていた人(俺)は辛くなりそう。
- しかし、
@DisplayNameと重複する名前つけるのはなんだかなぁ。
- ネストされたテストが標準で、自然な形でサポートされるようになった。
- 拡張方法が
@Ruleに比べれば単純な気がする。 - 拡張ポイントも色々あって夢が広がる。
- テスト名が任意の文字列で定義できるようになったこと。
- といっても、既に JUnit4 で動いているテストをあえて JUnit5 にする必要はないかなぁと思う。
- 4.12 ならネストしたテストもできるので。
- IDE やビルドツールが標準で JUnit5 をサポートし始めたら、新規に作るテストは JUnit5 にしていく感じでいいと思う。