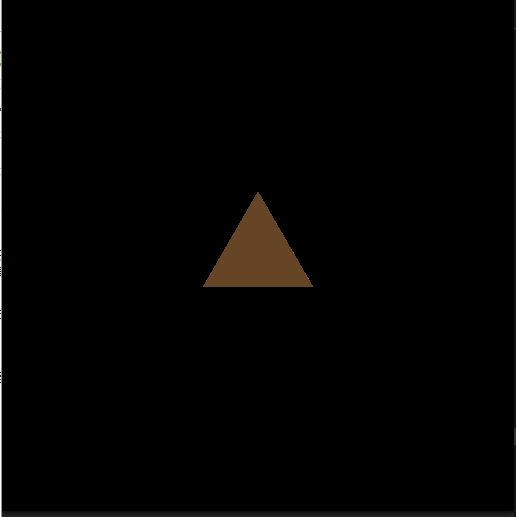
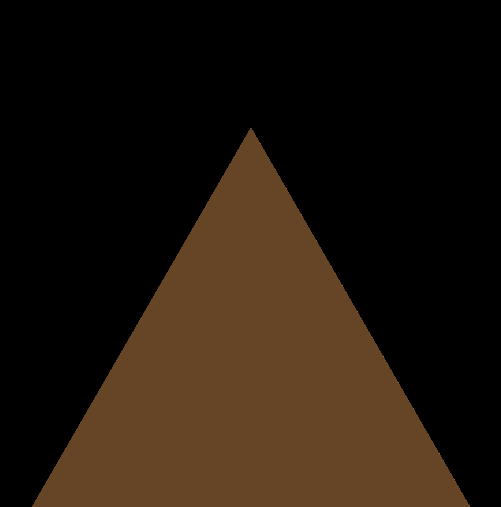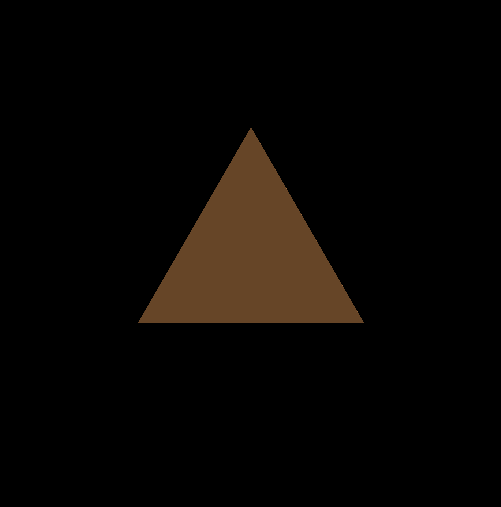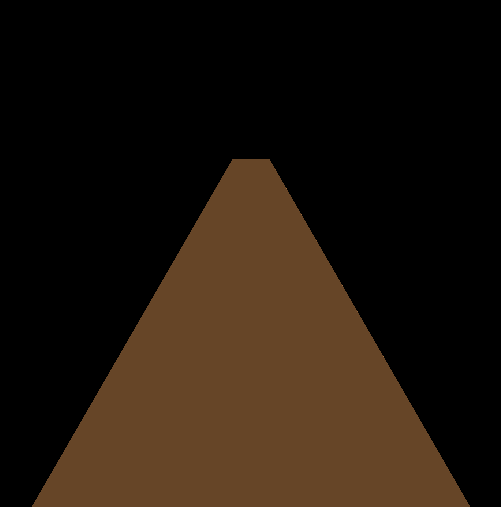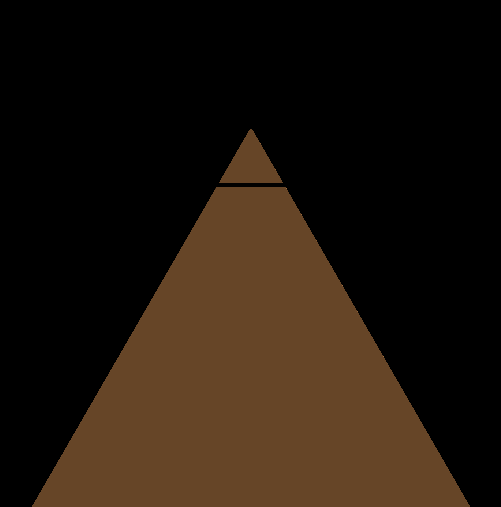
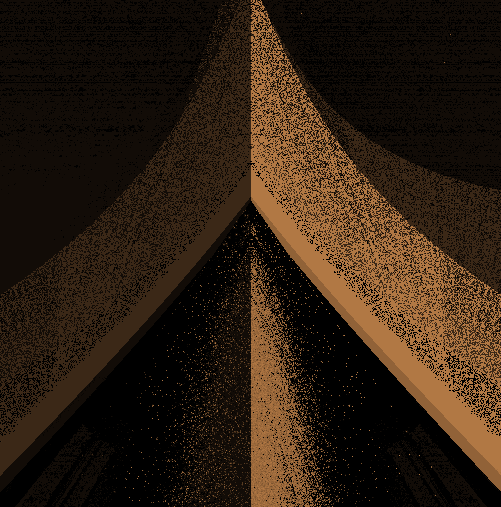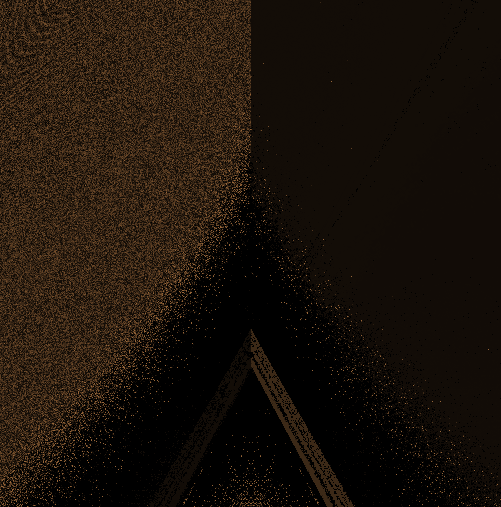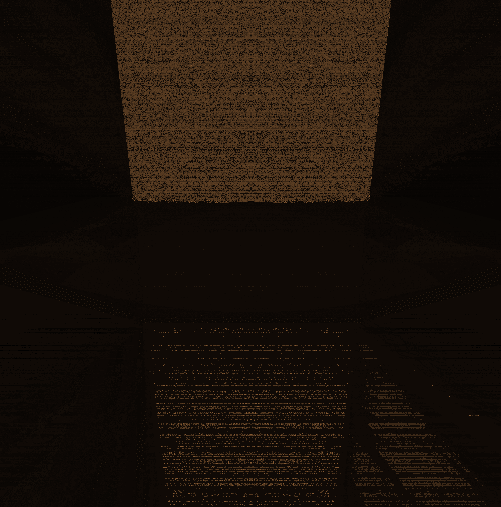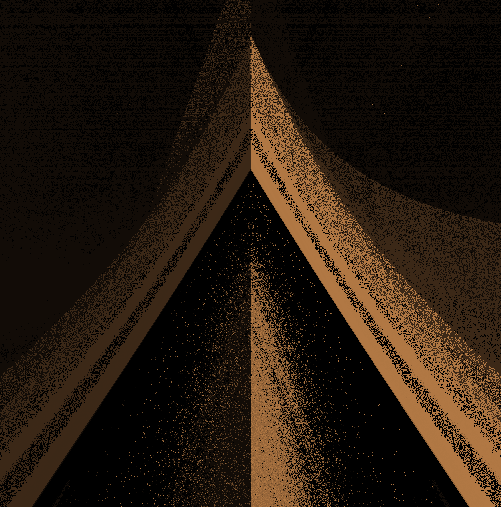
modeling with distance functionsの距離関数の一覧に沿って記事を書いています.
二次元のグラフの描画は、Desmos Graphing Calculator を使っています.
やっていることは、Hexagonalと同じです.
距離関数
// Triangular Prism
vec3 q = abs(p);
vec2 h = vec2(1.0, 1.0);
return max(q.z-h.y,max(q.x*0.866025+p.y*0.5,-p.y)-h.x*0.5);
導出方法
前回の
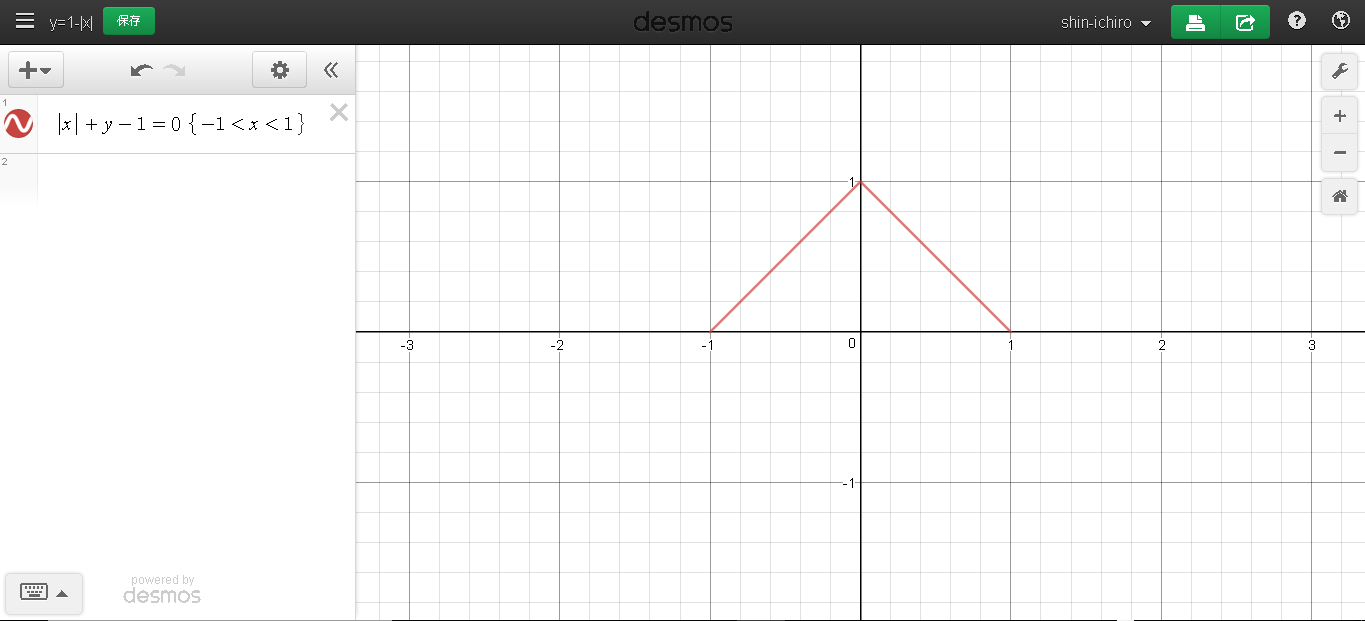
|x| + |y| = 1 (-1<x<1)
から y の絶対値をぬいた.
|x| + y = 1(−1<x<1)
を使う.
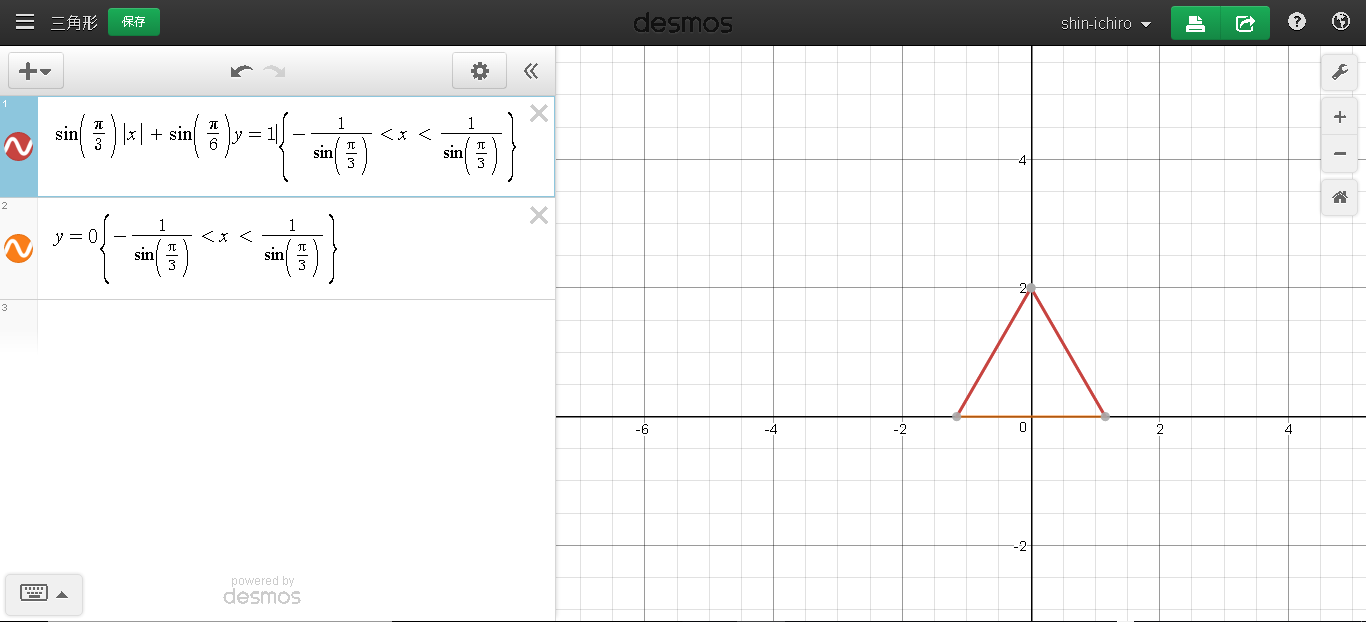
係数を合わせて,
\sin(\frac{\pi}{3})|x|+\sin(\frac{\pi}{6})y = 1 (-1<x<1)
で、距離関数はこれ、
// Triangular Prism1
float radio = 1.0; // 一辺の長さ
float hight = 1.0; // 厚さ(高さ)
return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
もとに、記事の通りだとこれ
// Triangular Prism2
vec3 q = abs(p);
float radio = 1.0; // 一辺の長さ
float hight = 1.0; // 厚さ(高さ)
return max(q.z-hight,max(q.x*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
三角柱の距離関数をいじる
アニメーション1
// motion01
return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y*sin(time))-radio);
アニメーション2
- x軸回転を入れる
- z成分を
abs(sin(time))倍する
// 回転
mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time));
p = m_x * p;
return max(abs(p.z*abs(sin(time)))-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
アニメーション3
けいれんぽい感じ
p.x に max(abs(p.x)*0.866025, abs(p.x)*abs(sin(exp(10.0*abs(sin(time))))) を入れる.
// motion03
return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(max(abs(p.x)*0.866025, abs(p.x)*abs(sin(exp(10.0*abs(sin(time))))))+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
アニメーション4
砂嵐ぽいもの
そとの max を mod に変えました。
// motion04
mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time));
p = m_x * p;
return mod(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
// ============================================================================
// Triangular Prism function
// ============================================================================
precision mediump float;
uniform vec2 resolution; // resolution (512.0, 512.0)
uniform vec2 mouse; // mouse (-1.0 ~ 1.0)
uniform float time; // time (1second == 1.0)
uniform sampler2D prevScene; // previous scene texture
// Triangular Prismの距離関数
float sdTriPrism(vec3 p)
{
float radio = 1.0; // 一辺の長さ
float hight = 1.0; // 厚さ(高さ)
// 回転
// mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time));
// p = m_x * p;
// mat3 m_y = mat3(cos(time),0,-sin(time),0,1,0,sin(time),0,cos(time));
// p = m_y * p;
// mat3 m_z = mat3(cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time),0,0,0,1);
// p = m_z * p;
// mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(1.57),-sin(1.57),0,sin(1.57),cos(1.57));
// p = m_x * p;
// Triangular Prism1
return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
// Triangular Prism2
// vec3 q = abs(p);
// return max(q.z-hight,max(q.x*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
// motion01
// return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y*sin(time))-radio);
// motion02
// mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time));
// p = m_x * p;
// return max(abs(p.z*abs(sin(time)))-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
// motion03
// return max(abs(p.z)-hight,max(max(abs(p.x)*0.866025, abs(p.x)*abs(sin(exp(10.0*abs(sin(time))))))+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
// motion04
// mat3 m_x = mat3(1,0,0,0,cos(time),-sin(time),0,sin(time),cos(time));
// p = m_x * p;
// return mod(abs(p.z)-hight,max(abs(p.x)*0.866025+p.y*0.5, -p.y)-radio);
}
// 距離関数を呼び出すハブ関数
float distanceHub(vec3 p){
return sdTriPrism(p);
}
// 法線を生成する
vec3 genNormal(vec3 p){
float d = 0.001;
return normalize(vec3(
distanceHub(p + vec3( d, 0.0, 0.0)) - distanceHub(p + vec3( -d, 0.0, 0.0)),
distanceHub(p + vec3(0.0, d, 0.0)) - distanceHub(p + vec3(0.0, -d, 0.0)),
distanceHub(p + vec3(0.0, 0.0, d)) - distanceHub(p + vec3(0.0, 0.0, -d))
));
}
void main(){
// スクリーンスペースを考慮して座標を正規化する
vec2 p = (gl_FragCoord.xy * 2.0 - resolution) / min(resolution.x, resolution.y);
// カメラを定義する
vec3 cPos = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 5.0); // カメラの位置
vec3 cDir = vec3(0.0, 0.0, -1.0); // カメラの向き(視線)
vec3 cUp = vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // カメラの上方向
vec3 cSide = cross(cDir, cUp); // 外積を使って横方向を算出
float targetDepth = 1.0; // フォーカスする深度
// カメラの情報からレイを定義する
vec3 ray = normalize(cSide * p.x + cUp * p.y + cDir * targetDepth);
// マーチングループを組む
float dist = 0.0; // レイとオブジェクト間の最短距離
float rLen = 0.0; // レイに継ぎ足す長さ
vec3 rPos = cPos; // レイの先端位置(初期位置)
for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i){
dist = distanceHub(rPos);
rLen += dist;
rPos = cPos + ray * rLen;
}
// レイとオブジェクトの距離を確認
if(abs(dist) < 0.001){
// 法線を算出
vec3 normal = genNormal(rPos);
// ライトベクトルの定義
vec3 light = normalize(vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0));
// ライトベクトルとの内積を取る
float diff = max(dot(normal, light), 0.1);
// gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(diff, diff, diff), 1.0);
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(diff*177.0/255.0, diff*120.0/255.0, diff*68.0/255.0), 1.0);
}else{
// 衝突しなかった場合はそのまま黒
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
}
}