はじめに
chainerでLSTMを実装する際に、備え付けのlinks/connection/lstm.pyなどを使わずに書いた場合、convLSTMへの変更が楽だと気づいた。そこでLSTMをconvLSTMへ改良してみる。
環境
GPU GTX1070
ubuntu 14.04
chainer 1.14.0
など
convLSTMについて
convLSTMはX. Shiらが提案しているconvolutionとLSTMを組み合わせた手法である。
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.04214.pdf
通常のLSTMはlinearな状態で処理されるので、画像などは位置的な情報が死んでしまう。convLSTMは画像の状態を維持したまま入力するので位置情報が保持される。linearの場合の行列演算はconvolutionに置き換えれられる。これによりLSTMの時間情報、convolutionの位置情報が同時にいかされる。
peepholeがないヴァージョンのLSTMにおける順伝播計算は以下の図のようになるだろう。
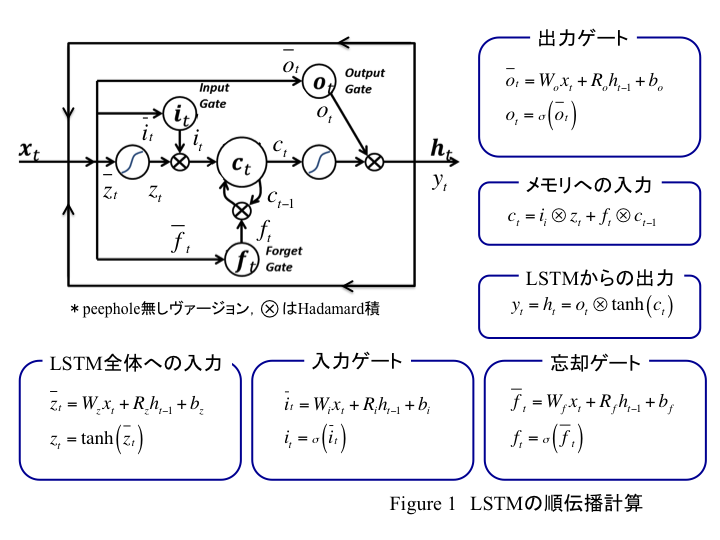
入力や各ゲート等で行列積が使われる。これに対してconvLSTMは以下のようになる。
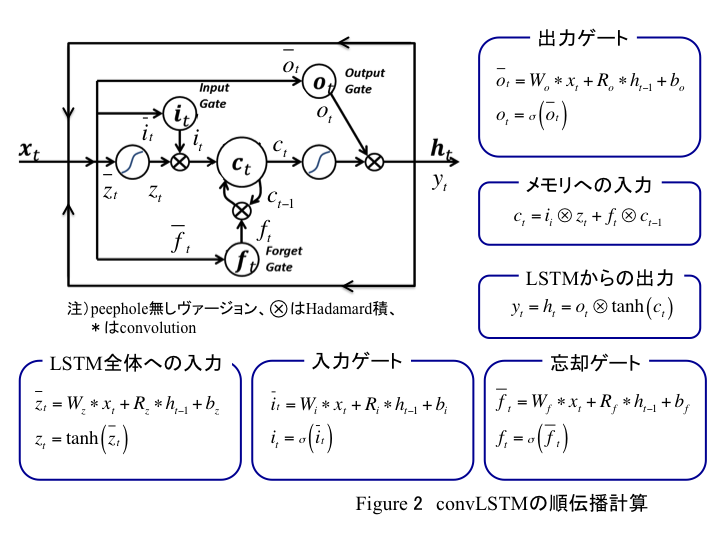
行列積がconvlutionになっただけ。これをコード上で変更する。
基本とするLSTMコード
LSTMを最小単位で作成する。ただし、後にconvLSTMへの変更を考えて、処理するデータは画像とする。具体的にはKitti datasetの時系列画像を入力していく。
あるtの画像を入力して、目標値をt+1の画像とする。つまり、次の瞬間の画像を予測するように学習させる。
# !/usr/bin/env python
import six
import cupy
# import numpy
import chainer
from chainer import computational_graph, Chain, Variable, utils, gradient_check, Function
from chainer import cuda
import chainer.links as L
import chainer.functions as F
from chainer import optimizers
from chainer import serializers
from PIL import Image
# read Kitti datas
str_dir1 = '65x65data/'
str_png = '.png'
str_03 = '500'
str_02 = '50'
str_01 = '5'
imgArrayTrain = cupy.zeros((126, 65, 65), dtype=cupy.float32)
# imgArrayTest = cupy.zeros((26, 65, 65), dtype=cupy.float32)
imgArrayOut = cupy.zeros(4225, dtype=cupy.float32)
# load to train array
for i in range(126):
str_sum = str_dir1
if i < 10:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_03 + str(i) + str_png
elif i < 100:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_02 + str(i) + str_png
else:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_01 + str(i) + str_png
img_read = Image.open(str_sum)
imgArrayPart = cupy.asarray(img_read).astype(dtype=cupy.float32)
imgArrayTrain[i] = imgArrayPart
imgArrayTrain = imgArrayTrain / 255
print 'imgArrayTrain.shape =', imgArrayTrain.shape
print 'imgArrayTrain.max()', imgArrayTrain.max()
print 'imgArrayTrain.min()', imgArrayTrain.min()
# load to Test array
for i in range(26):
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_01 + str(i + 126) + str_png
img_read = Image.open(str_sum)
imgArrayPart = cupy.asarray(img_read).astype(dtype=cupy.float32)
imgArrayTest[i] = imgArrayPart
imgArrayTest = imgArrayTest / 255
# Array reshape
imgArrayTrain2 = imgArrayTrain.reshape((len(imgArrayTrain), -1)).astype(dtype=imgArrayTrain.dtype)
imgArrayTest2 = imgArrayTest.reshape((len(imgArrayTest), -1)).astype(dtype=imgArrayTest.dtype)
print 'imgArrayTrain2.shape =', imgArrayTrain2.shape
print 'imgArrayTest2.shape =', imgArrayTest2.shape
len_1data = 25
count_j = 0
count_epoch = 0
# model class
class MyLSTM(chainer.Chain):
def __init__(self, k):
super(MyLSTM, self).__init__(
Wz = L.Linear(k, k),
Wi = L.Linear(k, k),
Wf = L.Linear(k, k),
Wo = L.Linear(k, k),
Rz = L.Linear(k, k),
Ri = L.Linear(k, k),
Rf = L.Linear(k, k),
Ro = L.Linear(k, k),
W = L.Linear(k, k),
)
def __call__(self, s):
accum_loss = None
k = len(imgArrayTrain2[0])
#v, k = self.embed.W.data.shape
h = Variable(cupy.zeros((1,k), dtype=cupy.float32))
c = Variable(cupy.zeros((1,k), dtype=cupy.float32))
for i in range(len(s) - 1): #len(s) is expected to 26
tx = Variable(cupy.array(s[i + 1], dtype=cupy.float32).reshape(1,-1))
x_k = Variable(cupy.array([s[i]], dtype=cupy.float32).reshape(1,-1))
z0 = self.Wz(x_k) + self.Rz(h)
z1 = F.tanh(z0)
i0 = self.Wi(x_k) + self.Ri(h)
i1 = F.sigmoid(i0)
f0 = self.Wf(x_k) + self.Rf(h)
f1 = F.sigmoid(f0)
c = z1 * i1 + f1 * c
o0 = self.Wo(x_k) + self.Ro(h)
o1 = F.sigmoid(o0)
h = o1 * F.tanh(c)
loss = F.mean_squared_error(self.W(h), tx)
accum_loss = loss if accum_loss is None else accum_loss + loss
return accum_loss
# optimize
model = MyLSTM(len(imgArrayTrain2[0]))
cuda.get_device(0).use() #for GPU
model.to_gpu() #for GPU
optimizer = optimizers.Adam()
optimizer.setup(model)
# learning phase
for epoch in range(10):
print "epoch =", epoch
for j in range(5):
s = imgArrayTrain2[j*25:(j+1)*25 + 1,:]
model.zerograds()
loss = model(s)
loss.backward()
optimizer.update()
count_epoch += 1
print 'learning is finished'
LSTMの行列演算は、MyLSTMクラス内のcall関数におけるループ内。ここで上図のFigure1の演算を行っている。つまり、ここを中心に変更する。
convLSTMへの変更
まずMyLSTMクラスの初期化をL.LinearからL.Convolution2Dへ変更する。
def __init__(self):
super(MyLSTM, self).__init__(
Wz = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wi = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wf = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wo = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Rz = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Ri = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Rf = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Ro = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
)
そうすると、call関数のループはそのままでよい。また、convolutionの場合、Variableへ入力するnumpy(cupy)データは(batchsize, channel, heith, width)になるので要注意。このあたりも若干変更する。最終的なコードは以下。
# !/usr/bin/env python
import six
import cupy
# import numpy
import chainer
from chainer import computational_graph, Chain, Variable, utils, gradient_check, Function
from chainer import cuda
import chainer.links as L
import chainer.functions as F
from chainer import optimizers
from chainer import serializers
from PIL import Image
# read Kitti datas
str_dir1 = '65x65data/'
str_png = '.png'
str_03 = '500'
str_02 = '50'
str_01 = '5'
epochNum = 10 # the number of epoch
len_1data = 25
channelIn = 1 #channel number of input image
channelOut = 1 #channel number of output image
width = 65 #width of input image
height = 65 #height of imput image
ksize = 5
padsize = (ksize - 1) / 2
imgArrayTrain = cupy.zeros((126, height, width), dtype=cupy.float32)
imgArrayTest = cupy.zeros((26, height, width), dtype=cupy.float32)
# load to train array
for i in range(126):
str_sum = str_dir1
if i < 10:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_03 + str(i) + str_png
elif i < 100:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_02 + str(i) + str_png
else:
str_sum = str_dir1 + str_01 + str(i) + str_png
img_read = Image.open(str_sum)
imgArrayPart = cupy.asarray(img_read).astype(dtype=cupy.float32)
imgArrayTrain[i] = imgArrayPart
imgArrayTrain = imgArrayTrain / 255
imgArrayTrain2 = imgArrayTrain.reshape(len(imgArrayTrain), height, width).astype(dtype=cupy.float32)
# model class
class MyLSTM(chainer.Chain):
def __init__(self):
super(MyLSTM, self).__init__(
Wz = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wi = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wf = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Wo = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Rz = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Ri = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Rf = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
Ro = L.Convolution2D(channelIn, channelOut, ksize, stride=1, pad=padsize),
)
def __call__(self, s): #s is expected to cupyArray(num, height, width)
accum_loss = None
chan = channelIn
hei = len(s[0])
wid = len(s[0][0])
h = Variable(cupy.zeros((1, chan, hei, wid), dtype=cupy.float32))
c = Variable(cupy.zeros((1, chan, hei, wid), dtype=cupy.float32))
for i in range(len(s) - 1): #len(s) is expected to 26
tx = Variable(cupy.array(s[i + 1], dtype=cupy.float32).reshape(1, chan, hei, wid))
x_k = Variable(cupy.array(s[i], dtype=cupy.float32).reshape(1, chan, hei, wid))
z0 = self.Wz(x_k) + self.Rz(h)
z1 = F.tanh(z0)
i0 = self.Wi(x_k) + self.Ri(h)
i1 = F.sigmoid(i0)
f0 = self.Wf(x_k) + self.Rf(h)
f1 = F.sigmoid(f0)
c = z1 * i1 + f1 * c
o0 = self.Wo(x_k) + self.Ro(h)
o1 = F.sigmoid(o0)
h = o1 * F.tanh(c)
loss = F.mean_squared_error(h, tx)
accum_loss = loss if accum_loss is None else accum_loss + loss
return accum_loss
# optimize
model = MyLSTM()
cuda.get_device(0).use() #for GPU
model.to_gpu() #for GPU
optimizer = optimizers.Adam()
optimizer.setup(model)
# learning phase
for epoch in range(epochNum):
print "epoch =", epoch
for j in range(5):
print "now j is", j
s = imgArrayTrain[j*25:(j+1)*25 + 1,:]
model.zerograds()
loss = model(s)
loss.backward()
optimizer.update()
print 'learning is finished'
コードの保存場所
このコードはこちらへあげました。
https://github.com/masataka46/convLSTM_minimum