こんにちは。
二次元平面で、与えられた点が、多角形領域の内部に含まれるかどうかを判定しました(内外判定、被覆判定)。下記ソース内の pointInPolygon() 関数です。
アルゴリズム
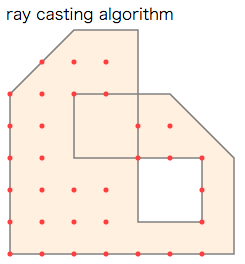
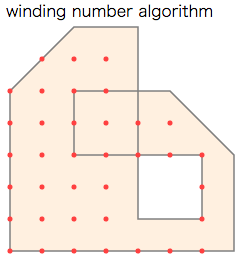
判定アルゴリズムの基本は、その点から正の方向へ伸ばしたx軸(半直線)が多角形境界線と交差する回数を符号付きで数えます1 2 3 4 5。下記の二種類を扱いました。
- "ray casting algorithm" では奇数回被覆された領域を内部と判定。
- "winding number algorithm" では一回以上被覆された領域を内部と判定。
実行例
実行例では、内部と判定された点をプロットしました(下図内の赤い点)。
ソース
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>pointInPolygon</title>
<script src="http://d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
ray casting algorithm
<div id="result"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function pointInPolygon(point, poly) {
const x=point[0], y=point[1];
let windingNumber=0, i=poly.length-1; // indexLast(poly)
for (let j=0, xi, xj, yi, yj, crossDirectionY, crossPositionX; i>=0; j=i--) {
yi=poly[i][1]-y; yj=poly[j][1]-y;
if ((yi>0)==(yj>0)) continue;
xi=poly[i][0]-x; xj=poly[j][0]-x;
crossDirectionY=(yj>yi)?1:-1;
crossPositionX = crossDirectionY*(xi*yj-xj*yi); // crossPositionX_true = (xi*yj-xj*yi)/(yj-yi)
if (crossPositionX>0) windingNumber+=crossDirectionY;
}
return windingNumber%2==1; // ray casting algorithm
}
// return windingNumber!==0; // winding number algorithm
const points = [], max = 7, poly = [[0,0], [7,0], [7,2], [7,3], [5,5], [2,5], [2,3], [6,3], [6,1], [4,1], [4,7], [2,7], [0,5]];
for (let j=0; j<=max; j++) {
for (let i=0; i<=max; i++) {
const p = [i, j];
if (pointInPolygon(p, poly)) {points.push(p)}
}
}
function mytransform(p) {
const scale = 32;
return [(p[0]+1)*scale, (max-p[1]+1)*scale]
}
const svg = d3.select("#result")
.append("svg")
.attr("width",300)
.attr("height",300);
svg.append("polygon")
.data([poly.map(mytransform)])
.attr("points", function(d){return d.join(" ")})
.attr("stroke", "gray")
.attr("fill", "#fff0e0")
.attr("stroke-width", 1.5);
svg.selectAll("points")
.data(points.map(mytransform))
.enter().append("circle")
.attr("fill", "#ff4040")
.attr("r", 2.5)
.attr("transform", function(d){return `translate(${d})`});
</script>
</body>
</html>
補足
なお ray casting algorithm の方ならば、下記のように偶奇を判定する Boolean 型変数 inside の利用へ置き換え可能です。
// let inside = false; // initialization
if ((yi>0)!=(yj>0) && (yj>yi)==(yj*(poly[i][0]-x)>yi*(poly[j][0]-x)))
inside = !inside;
// return inside; // ray casting algorithm
また今回の用途には、sign(a, b)は下記の定義を使わず、上記のように (a > b) の値を使えば十分です。
function sign(a, b) {
return (a > b) ? 1 : (a < b) ? -1 : 0;
}
また、indexLast(poly)は下記の定義を使わず、上記のように poly.length-1 の値を使えば十分です。
function indexLast(arr) {
let last = arr.length - 1;
if (arr[0][0]==arr[last][0]&&arr[0][1]==arr[last][1]) last -= 1;
return last;
}
-
反時計回りを正とします。 ↩
-
参考記事として、"Inclusion of a point in a polygon" (Dan Sunday)、"point-in-polygon" (GitHub)。 ↩
-
ただし多角形の全辺を走査することになります。辺数が多い多角形に対して、多数の与点を判定したい場合は、計算量低減(毎回全辺を走査しない)を考える必要があります。例えば、"Expedicious and Exact Extracts with Osmium" (Jochen Topf's Blog)。 ↩
-
左側の辺、および下側の水平な辺上も内部と判定されます。 ↩
-
ソースコードから分かるように、winding number を求める計算も、ray casting algorithm とほぼ同じアルゴリズムに帰着できます。角度計算不要なので計算効率が良いです。 ↩