Tips for Productive Debugging with GDBの抄訳。
Tips 1: GDB Dashboardを使おう
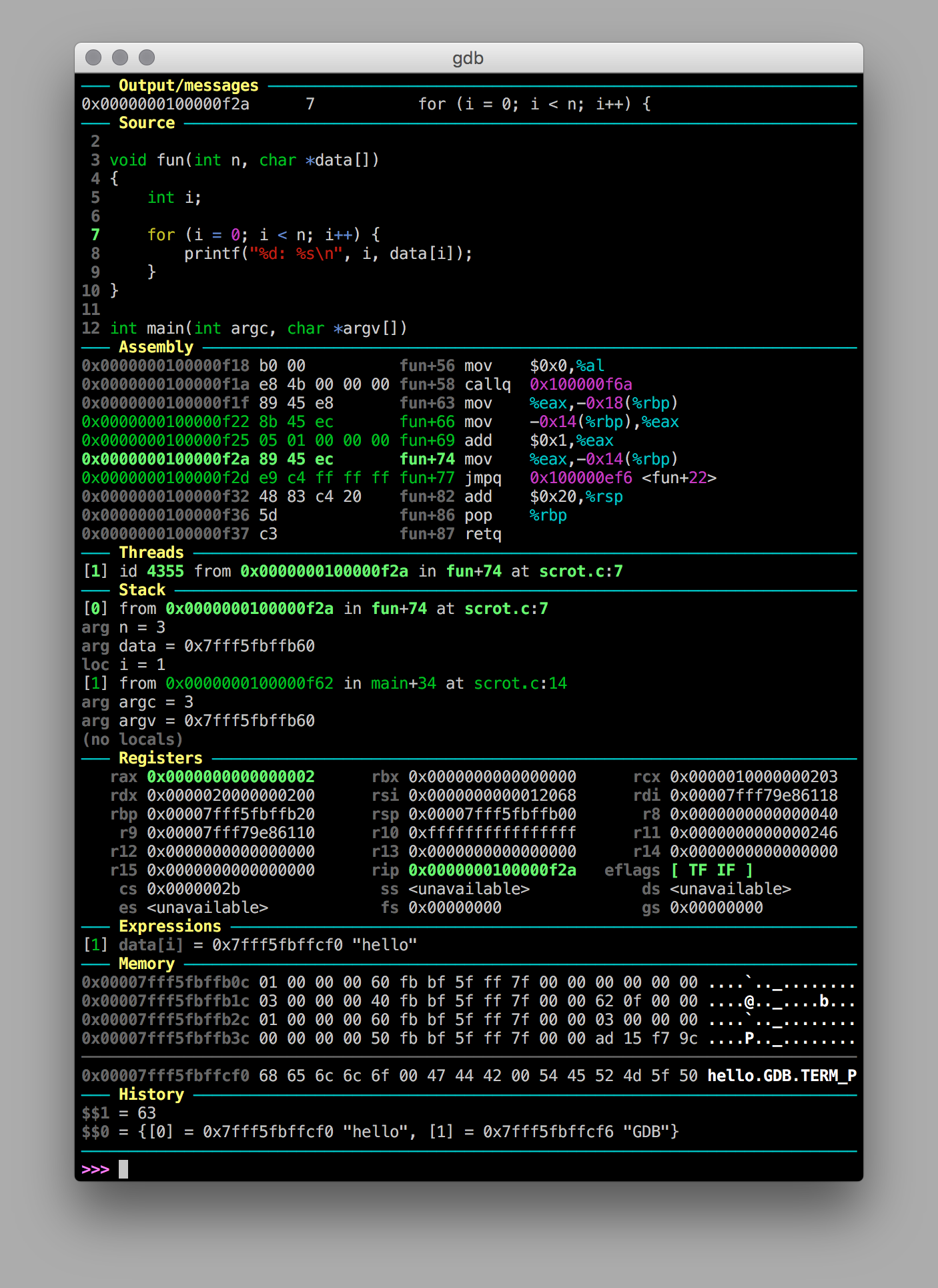
GDB Dashboardは単一の.gdbinitファイルで、ブレークポイントで止まるたびに下図のようなクールな画面を表示してくれる。
https://github.com/cyrus-and/gdb-dashboard
gdbには標準でTUIモード(cursesベースのUI)が搭載されているが、そちらは画面の乱れが頻繁に起こる。GDB Dashboardはcursesを使っていないので乱れが起きない。
スクショではOutput/messages, Source, Assembly, Threadsなど多数のモジュールを全部入りで表示しているためゴチャゴチャしているが、設定で自分に必要なモジュールだけを表示するようにできる。
訳者もしばらく使っているが、非常に実用的だ。
Tips 2: グローバルな.gdbinitとプロジェクト毎の.gdbinitを使おう
~/.gdbinitはグローバルな設定ファイル。その中で下記の設定をしておくとカレントディレクトリから.gdbinitを読み込んでくれる。
set auto-load local-gdbinit
Tips 3: カスタムフォーマッタで構造体やクラスを見やすく表示しよう
4x4の行列を表示するカスタムフォーマッタの作り方はこんな感じ:
class MPEMatrixPrinter:
"""Print a 4x4 matrix."""
def __init__(self, val, size):
self.val = val
self.size = int(size)
def to_string(self):
return ("\n\t[ %3g %3g %3g %3g ]"
"\n\t[ %3g %3g %3g %3g ]"
"\n\t[ %3g %3g %3g %3g ]"
"\n\t[ %3g %3g %3g %3g ]") % \
(float(self.val["flat"][0]), float(self.val["flat"][1]), float(self.val["flat"][2]), float(self.val["flat"][3]),
float(self.val["flat"][4]), float(self.val["flat"][5]), float(self.val["flat"][6]), float(self.val["flat"][7]),
float(self.val["flat"][8]), float(self.val["flat"][9]), float(self.val["flat"][10]), float(self.val["flat"][11]),
float(self.val["flat"][12]), float(self.val["flat"][13]), float(self.val["flat"][14]), float(self.val["flat"][15]))
def project_type_lookups(val):
lookup_tag = val.type.tag
if lookup_tag == None:
return None
match = re.match(r"^MPEMatrix(\d)$", lookup_tag)
if match:
return MPEMatrixPrinter(val, match.group(1))
gdb.pretty_printers.append(project_type_lookups)
Tips 4: エイリアスを使おう
シェルのエイリアスと同じようなものだ。
alias -a w = dashboard expression watch
Tips 5: 自動でセットされる変数$1...を使おう
printコマンドを使うと自動的にその値が変数$1...に格納される。
irbの_みたいなものだ。
Tips 6: 配列を表示する
>>> print *Array@10
でポインタArrayから10個の要素を表示する。
訳注:下記設定をしておかないと、最大200個の要素しか表示されない。
set print elements 0
Tips 7: デバッガで実行されていることを検出する。
WindowsならIsDebuggerPresentが使える。Unixでは下記が使える:
#ifndef _WIN32
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
static int IsDebuggerPresent()
{
static int Detected;
static int RunningUnderDebugger;
if (!Detected)
{
Detected = 1;
RunningUnderDebugger = ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, 0, 0, 0) == -1;
}
return RunningUnderDebugger;
}
#endif
訳者による追記
gdbを使いこなすコツは、
- コマンド名を
printのような正式名称でなくpのような最短名称で覚えてそちらを使うこと - それでも長いコマンドは遠慮なくエイリアスを定義すること
だと思う。gdbもシェルやgitなど他のUnixコマンドと同じくデフォルトでは少し使いづらい部分があるので、そういう部分はカスタマイズした方がいい。
startコマンド
gdbのstartコマンドは、main関数の入口に1回だけのブレークポイントを張ってプログラムを開始する。
つまり、何度も
(gdb) b main
(gdb) run
とやるのが面倒な人は、シェルでalias gdb='gdb -ex start'としておくと幸せになれるかも。
~/.gdbinitのサンプル
# コマンド履歴を保存する
set history save on
set history size 10000
set history filename ~/.gdb_history
# listコマンドで表示する行数
set listsize 25
# 配列の要素を全て表示する
set print elements 0
# 構造体のメンバを1行ずつ表示できる
set print pretty on
# quitコマンドで終了するときに確認しない
define hook-quit
set confirm off
end
# エイリアス
# よく使うコマンドはガンガンエイリアスを定義しておくのがよいと思う
alias -a a = advance
alias -a w = disp
alias -a uw = undisp
alias -a ib = info b
alias -a ia = info args
alias -a il = info locals
alias -a bd = clear