状況
すでにある程度作成されたプロジェクトのコードベースをlaravelで作り直す事になった.
しかし, コードは作りなおすが, DBは既存のものを使いたい.
変更する
まずはソースを追ってみる
前回の調査の際に, 最終的にユーザ認証はproviderのretrieveByCredentialsメソッドであることが判明していた.
/**
* Attempt to authenticate a user using the given credentials.
*
* @param array $credentials
* @param bool $remember
* @param bool $login
* @return bool
*/
public function attempt(array $credentials = [], $remember = false, $login = true)
{
$this->fireAttemptEvent($credentials, $remember, $login);
$this->lastAttempted = $user = $this->provider->retrieveByCredentials($credentials);
// If an implementation of UserInterface was returned, we'll ask the provider
// to validate the user against the given credentials, and if they are in
// fact valid we'll log the users into the application and return true.
if ($this->hasValidCredentials($user, $credentials))
{
if ($login) $this->login($user, $remember);
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
では, この$providerが何者かと調べてみると, こいつはIlluminate\Auth\EloquentUserProviderであり,
このインスタンスは, Illuminate\Auth\AuthManagerのcreateEloquentDriverメソッドで生成されており,
AuthManagerはIlluminate\Auth\AuthServiceProviderのregisterAuthenticatorメソッドでDIコンテナにauthという名前で登録されており,
AuthServiceProviderは./config/app.phpにてサービス・プロバイダに指定されていることが分かった.
EloquentUserProvider.phpを読んで見る
ログイン処理の中で, Guardオブジェクトから呼び出されているretrieveByCredentialsの内容は以下のとおり
/**
* Retrieve a user by the given credentials.
*
* @param array $credentials
* @return \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Authenticatable|null
*/
public function retrieveByCredentials(array $credentials)
{
// First we will add each credential element to the query as a where clause.
// Then we can execute the query and, if we found a user, return it in a
// Eloquent User "model" that will be utilized by the Guard instances.
$query = $this->createModel()->newQuery();
foreach ($credentials as $key => $value)
{
if ( ! str_contains($key, 'password'))
{
$query->where($key, $value);
}
}
return $query->first();
}
/**
* Validate a user against the given credentials.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Authenticatable $user
* @param array $credentials
* @return bool
*/
public function validateCredentials(UserContract $user, array $credentials)
{
$plain = $credentials['password'];
return $this->hasher->check($plain, $user->getAuthPassword());
}
見たところ, 単に認証用の情報を元にユーザを検索したり, 平文のパスワードとハッシュ化されたパスワードの比較などを行っているだけの様子.
特に手を入れる余地はなさそうです.
AuthManager.phpを読んで見る
上記プロバイダを生成している, AuthManagerのcreateEloquentProviderの記述は以下のとおり.
/**
* Create an instance of the Eloquent user provider.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Auth\EloquentUserProvider
*/
protected function createEloquentProvider()
{
$model = $this->app['config']['auth.model'];
return new EloquentUserProvider($this->app['hash'], $model);
}
設定から, ユーザmodel名を, コンテナからハッシュ用オブジェクトを取得し, それを元にEloquentUserProviderを生成しています.
この$this->app['config']['auth.model']に対応する設定項目は/config/auth.phpの以下の部分.
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Authentication Model
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| When using the "Eloquent" authentication driver, we need to know which
| Eloquent model should be used to retrieve your users. Of course, it
| is often just the "User" model but you may use whatever you like.
|
*/
'model' => 'App\User',
デフォルトでは, laravel規定のUserモデルを使うようになっています.
ここで, 実際に使いたいモデルを指定するように変更するか, Userモデルを既存ユーザテーブルに合うように変更してやれば良さそうです.
今回は, Userモデルは使い回すことにします.
./app/User.phpを開き, 以下のように変更.
/**
* The database table used by the model.
*
* @var string
*/
# protected $table = 'users';
protected $table = 'my_users';
これで, 既存Userテーブルを使うようになります.
HashServiceの差し替え
ユーザのパスワードについて, Laravelで使われているハッシュ関数と全く同じものを使っていれば問題ないのですが
おそらくそんな都合の良い話はないと思われるので,
ハッシュサービスの差し替えが必要になります.
DIコンテナにハッシュサービスを登録しているプロバイダはIlluminate\Hashing\HashServiceProviderであり, その記述は以下のとおり.
<?php namespace Illuminate\Hashing;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class HashServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider {
/**
* Indicates if loading of the provider is deferred.
*
* @var bool
*/
protected $defer = true;
/**
* Register the service provider.
*
* @return void
*/
public function register()
{
$this->app->singleton('hash', function() { return new BcryptHasher; });
}
/**
* Get the services provided by the provider.
*
* @return array
*/
public function provides()
{
return array('hash');
}
}
どうやら, LaravelではBcyptHasherというサービスが規定のHashServiceとして使われているようです.
そこで, 同じようなHashServiceを自前で用意し...
<?php namespace App\Services;
use RuntimeException;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Hashing\Hasher as HasherContract;
class PlainHasher implements HasherContract {
/**
* Hash the given value.
*
* @param string $value
* @param array $options
* @return string
*
* @throws \RuntimeException
*/
public function make($value, array $options = array())
{
return $value;
}
/**
* Check the given plain value against a hash.
*
* @param string $value
* @param string $hashedValue
* @param array $options
* @return bool
*/
public function check($value, $hashedValue, array $options = array())
{
return $this->make($value, $options) === $hashedValue;
}
/**
* Check if the given hash has been hashed using the given options.
*
* @param string $hashedValue
* @param array $options
* @return bool
*/
public function needsRehash($hashedValue, array $options = array())
{
return false;
}
}
/config/app.phpでHashServiceを登録しないように変更し
'providers' => [
...
// 'Illuminate\Hashing\HashServiceProvider', # <- コメントアウト
...
/*
` * Application Service Providers...
*/
'App\Providers\AppServiceProvider',
...
適当にApp\Providers\AppServiceProviderあたりに, 先ほど作成したサービスをDIに登録する記述を追加します.
/**
* Register any application services.
*
* This service provider is a great spot to register your various container
* bindings with the application. As you can see, we are registering our
* "Registrar" implementation here. You can add your own bindings too!
*
* @return void
*/
public function register()
{
$this->app->bind(
'Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Registrar',
'Atls\Services\Registrar'
);
$this->app->singleton('hash', function() { return new PlainHasher(); });
}
ここまでやれば, 既存のユーザデータでログインができるようになるはずです.
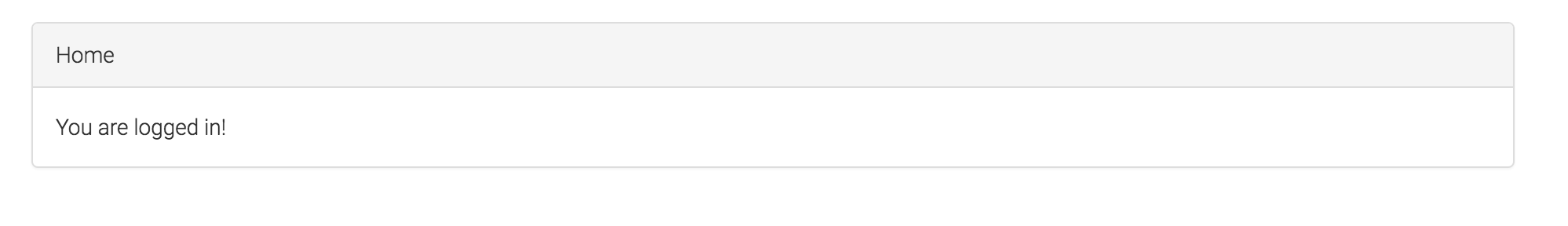
∩ ́・ω・ ∩バンジャーイ
と喜んだのもつかの間...
ログアウトしてみると

ログアウトできないじゃないですかヤダー!
メッセージを見ると, remember_tokenをセットしようとしてエラーになっているようす.
たしかにそんなカラムはない.
ログアウト時, どこでこのremember_tokenのセットを行っているか調べたところ, Guardクラスのlogoutメソッドの中と判明.
流石にこいつまで差し替えるのは大変そうなので, Userモデルに以下のようなメソッドを追加してみる.
/**
* RememerTokenをセットする
*
* 当システムでは使っていないので, 何もしない
*
* @var array
*/
public function setRememberToken($value) {
return $this;
}
改めてログアウトしてみると...
∩ ́・ω・ ∩バンジャーイ
まとめ
ソースいろいろ追ってみた結果, 規定のサービスは/config/app.phpのなかでだいたいDIコンテナに登録されているようなので
providerの設定をコメントアウトして, 自前のproviderを設定してやれば, サービスの差し替えは行えるようです.