「努力と根性」
概要
ソースはgithubにあります。
今回の動機、TensorFlowでのモデルの記述
TensorFlowではネットワークモデルをプログラムで構築します。自分の場合は以下のような感じ。公式のチュートリアルでもこういうスタイルで記述されています。そしてこれが若干だるい。
(必要があれば)ユーティリティメソッドを作って、
def image_to_conv_layer(image, kernel_size, num_kernel):
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
channels = image.get_shape()[3]
w = weight_variable([kernel_size,kernel_size, channels,num_kernel], name="weight")
b = bias_variable([num_kernel], name="bias")
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
with tf.name_scope('conv_max'):
h_conv = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(image, w) + b)
h_pool = max_pool_2x2(h_conv)
return h_pool
ネットワークを組み上げる。
def build_full_network(images,
with_conv1_pre_train=False, with_conv2_pre_train=False,
with_conv3_pre_train=False):
result = []
with tf.variable_scope('conv1'):
conv1 = image_to_conv_layer(images, 5, 64)
if with_conv1_pre_train:
with tf.variable_scope('pre_train'):
with tf.name_scope('inference'):
pt_inf = conv_to_conv_transpose_layer(conv1, images)
image_summary = tf.image_summary('inference_image', pt_inf)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
pt_loss = pre_train_loss(images, pt_inf)
tf.scalar_summary('loss/conv1', tf.log(tf.reduce_max(pt_loss)))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
pt_train = pre_train_train(pt_loss, 1e-4)
result = [pt_train] + result
# 以降の層が続く
だるさの原因は以下だと思います
- 開発中に調整すべきパラメータがコード中に散財しがち(開発者によるけれども)
- 記述量が多くなる傾向がある
- 複数のモデルを試すときにデータファイルの入れ替えではなくソースの入れ替えをしなければならない
これらを回避するためにモデルをYAMLで書くとどうなるかを試します。
なぜYAMLか
そこそこ込み入ったデータ構造を人間が書こうとしたらYAMLに落ち着くよね、といういつもの話。
- 人間が書ける(XMLでは不可)
- コメントを記述できる(JSONでは不可)
- PyYAMLによりPython classのシリアライズ・デシリアライズが可能
- anchor/alias により少し楽ができる
文書の構成
- YAMLで書かれたモデルの解説
- YAMLパーサの実装の解説
- モデルとパーサの利用の解説
- やってみた感想
- 今後の課題
YAMLで書かれたモデル
モデルを記述したyamlファイルの例を示します。このあと各要素の解説をします。
---
# user data tree
user_variables:
- op_device: &op_device '/cpu:0'
# graph data tree
root: !root
nodes_required: ['root']
nodes:
- !with
# can define tf.variable_scope, tf.name_scope, tf.device at same time
variable_scope: conv1
nodes:
- !conv2d
# nid is node id, to be used for node connection
{ nid: c1, name: out, source: root, width: 5, height: 5, kernels_num: 64 }
- !with
variable_scope: train
tags: [train]
nodes:
- !conv2d_transpose
{nid: c1_tr, name: conv1tr, source: c1, shape_as: root, width: 5, height: 5}
- !conv2d_ae_loss
{nid: c1_ae_loss, source1: root, source2: c1_tr}
- !adam_optimizer {name: optimizer, source: c1_ae_loss, val: 1e-4}
- !with
device_scope: '/cpu:0'
tags: [train, log]
nodes:
- !reduce_mean
{nid: c1_ae_loss_mean, source: c1_ae_loss, dims: [1]}
- !scalar_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv1/loss', source: c1_ae_loss_mean}
- !image_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv1tr/image', source: c1_tr}
- !with
variable_scope: conv2
nodes:
- !conv2d
{ nid: c2, name: out, source: c1, width: 5, height: 5, kernels_num: 64 }
- !with
variable_scope: train
tags: [train]
nodes:
- !conv2d_transpose
{nid: c2_tr, name: conv2tr, source: c2, shape_as: c1, width: 5, height: 5}
- !conv2d_ae_loss
{nid: c2_ae_loss, source1: c1, source2: c2_tr}
- !adam_optimizer {name: optimizer, source: c2_ae_loss, val: 1e-4}
- !with
device_scope: '/cpu:0'
tags: [train, log]
nodes:
- !reduce_mean
{nid: c2_ae_loss_mean, source: c2_ae_loss, dims: [1]}
- !scalar_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv2/loss', source: c2_ae_loss_mean}
- !with
variable_scope: conv3
nodes:
- !conv2d
{ nid: c3, name: out, source: c2, width: 5, height: 5, kernels_num: 64 }
- !with
variable_scope: train
tags: [train]
nodes:
- !conv2d_transpose
{nid: c3_tr, name: conv2tr, source: c3, shape_as: c2, width: 5, height: 5}
- !conv2d_ae_loss
{nid: c3_ae_loss, source1: c2, source2: c3_tr}
- !adam_optimizer {name: optimizer, source: c3_ae_loss, val: 1e-4}
- !with
device_scope: '/cpu:0'
tags: [train, log]
nodes:
- !reduce_mean
{nid: c3_ae_loss_mean, source: c3_ae_loss, dims: [1]}
- !scalar_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv3/loss', source: c3_ae_loss_mean}
- !with
variable_scope: maxpool
nodes:
- !max_pool_2x2
{nid: mp1, source: c3}
冒頭から。ドキュメント区切りとユーザーデータです。ドキュメント自体をひとつのオブジェクトにはしていないためアプリケーションやYAML内で利用する任意のデータを記述することができます。今回は試しにデバイスの名前を入れていますが利用していません。
---
# user data tree
user_variables:
- op_device: &op_device '/cpu:0'
キーrootに!rootタグを指定してグラフのルートとしています。nodes_requiredはこのグラフの入力に指定すべき名前です。このYAMLを読み込んでグラフを構築する際に利用します。nodes以下の配列にTensorFlowのノードが並びます。
# graph data tree
root: !root
nodes_required: ['root']
nodes:
TensorFlowで頻繁に利用するwith tf.variable_scope('some_scope'):と等価です。variable_scopeの他にname_scope、deviceの各キーを同時に指定できます。nodes以下の配列にwith内のノードが並びます。
- !with
# can define tf.variable_scope, tf.name_scope, tf.device at same time
variable_scope: conv1
nodes:
conv層のノードです。nidはnode idの略で主にYAML内で他のノードから参照されるための名前です。nameはTensorFlowのノードのname、sourceはこのノードへの入力でnidを指定します。width、height、kernels_numはconv層のパラメータです。
nid、nameは省略可能です。scalar_summaryのような終端ノードでは省略してよいでしょう。
- !conv2d
# nid is node id, to be used for node connection
{ nid: c1, name: out, source: root, width: 5, height: 5, kernels_num: 64 }
!withや!conv2dなど!root以外のノードにはtagsを指定できます。現在は特定のタグについてTensorFlowのノード生成を行わない指定をするために利用しています。
- !with
variable_scope: train
tags: [train]
nodes:
nodesは配列を想定しているため当然に複数のノードを並べられます。
- !conv2d_transpose
{nid: c1_tr, name: conv1tr, source: c1, shape_as: root, width: 5, height: 5}
- !conv2d_ae_loss
{nid: c1_ae_loss, source1: root, source2: c1_tr}
- !adam_optimizer {name: optimizer, source: c1_ae_loss, val: 1e-4}
TensorBoard向けのサマリーのためのノード群です。サマリーはCPUで行う必要があるためdeviceを指定します。また!scalar_summary、!image_summaryはそのあと参照する必要が無いためnidを記述していません。
- !with
device_scope: '/cpu:0'
tags: [train, log]
nodes:
- !reduce_mean
{nid: c1_ae_loss_mean, source: c1_ae_loss, dims: [1]}
- !scalar_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv1/loss', source: c1_ae_loss_mean}
- !image_summary
{summary_tag: 'conv1tr/image', source: c1_tr}
以下、同様に続きます。
YAMLの読み込み
パースには PyYAML を利用しています。yaml.YAMLObjectを利用してYAMLの各タグをタグ種ごとに対応するクラスのオブジェクトに変換します。個々のオブジェクトがTensorFlowのノードを生成します。以下、パースコードです。個別に解説します。
冒頭、雑多なメソッド群です。with文に何もしないオブジェクトを入れ込むためにclass WithNoneを定義しています。
import yaml
import tensorflow as tf
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# utilities
# ------------------------------------------------------------
def weight_variable(shape, dev=0.35, name=None):
"""create weight variable for conv2d(weight sharing)"""
return tf.get_variable(name, shape,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=dev))
def bias_variable(shape, val=0.1, name=None):
"""create bias variable for conv2d(weight sharing)"""
return tf.get_variable(
name, shape, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(val))
class WithNone:
def __enter__(self): pass
def __exit__(self,t,v,tb): pass
アサーションのためのメソッド群です。YAMLデータのチェックをテーブル化するのに利用します。nop()は別で型変換をしないためのメソッドです。
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# assert
# ------------------------------------------------------------
def nop(val):
return val
def is_exist(key, val):
return (val, '{} required'.format(key))
def not_empty(key, val):
return (len(val) > 0, '{} must not be empty'.format(key))
class is_greater_than:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
def __call__(self, key, val):
return (val > self.val, '{} must be > {}'.format(key, self.val))
class is_typeof:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
def __call__(self, key, val):
return (type(val) is self.val, '{} must be {}'.format(key, self.val))
YAMLのパースの際にnidのユニークチェックのための辞書を引き回したいのでyaml.Loaderをカスタムしています。
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# YAML Graph Nodes
# ------------------------------------------------------------
class Loader(yaml.Loader):
def __init__(self, stream):
self.nids = {}
super(Loader, self).__init__(stream)
ノードに共通する抽象クラスです。YAMLのパースとTensorFlowノード生成の際の冗長な処理をまとめています。parse()ではYAMLのkey, valueをオブジェクトのkey, valueに変換します。デフォルト値の挿入、簡単な型チェック、アサーションも行います。これら処理の具象は各派生クラスから辞書で渡されます。
build()では除外タグのスキップとユニークチェックのための辞書の追加を行っています。
class Node:
def __init__():
pass
def parse(self,loader,node,params):
yaml_dict = loader.construct_mapping(node, deep=True)
self.__dict__['nid'] = None
for key, value in params.items():
got = yaml_dict.get(key, value[1])
self.__dict__[key] = value[0](got) if got is not None else got
assert self.nid not in loader.nids, \
'line {}: nid "{}" is already exists at line {}'.format(
node.end_mark.line+1, self.nid, loader.nids[self.nid].line+1)
for key, val in params.items():
for cond in val[2]:
ret, mess = cond(key, self.__dict__[key])
assert ret, 'line {}: {}'.format(node.end_mark.line+1, mess)
if self.nid: loader.nids[self.nid] = node.end_mark
def build(self, nids, exclude_tags):
for exclude_tag in exclude_tags:
if exclude_tag in self.tags:
return nids
nids, nid, node = self.create_node(nids, exclude_tags)
if nid and node is not None: nids[nid] = node
return nids
グラフルートです。他のノードとは異なるbuild()を提供しています。
class Root(yaml.YAMLObject):
yaml_tag = u'!root'
def __init__(self, nodes, nodes_required):
self.nodes = nodes
self.nodes_required = nodes_required
def __repr__(self):
return 'Root'
@classmethod
def from_yaml(cls, loader, node):
yaml_dict = loader.construct_mapping(node)
args = {
'nodes': yaml_dict.get('nodes', None),
'nodes_required': yaml_dict.get('nodes_required', None),
}
assert type(args['nodes']) is list, \
'line {}: nodes must be list'.format(node.end_mark.line+1)
assert type(args['nodes_required']) is list, \
'line {}: nodes_required must be list'.format(node.end_mark.line+1)
for required_node in args['nodes_required']:
assert required_node not in loader.nids, \
'line {}: nid "{}" is already exists'.format(node.end_mark.line+1, required_node)
print(required_node)
loader.nids[required_node] = node.end_mark
return cls(**args)
def build(self, feed_dict={}, exclude_tags=[]):
self.__nids = {}
for key, val in feed_dict.items():
self.__nids[key] = val
for required_node in self.nodes_required:
if required_node not in self.__nids:
raise ValueError('feed_dict requires {}.'.format(self.nodes_required))
for node in self.nodes:
self.__nids = node.build(self.__nids, exclude_tags)
!withタグに対応するクラスです。
__init__()は他のノードクラスでも共通ですがparams辞書を作ってNodeクラスのparse()に渡すというのがルーチンです。
params辞書の'tags': (nop, [], [is_typeof(list)])は「YAMLの'tags'要素について、型変換を行わず、デフォルト値は[]で、型がlistであることをチェックする」という意味になります。'kernels_num': (int, 0, [is_greater_than(0)])だと「'kernels_num'要素について、intに変換して、初期値は0で、0より大きいことをチェックする」という意味になります。初期値ではチェックが失敗するので必須要素ということになります。
(型変換を入れている理由はPyYAMLがパースの際に浮動小数点数の指数表記を正しくパースしてくれないからです)
create_node()が実際のTensorFlowのノードを生成する箇所になります。!withはノードを持たないのでTensorFlowのwith ...を作ってその中でnodes以下の要素のbuild()を再帰的に呼び出すだけです。
class With(yaml.YAMLObject, Node):
yaml_tag = u'!with'
def __init__(self, loader, node):
params = {
'tags': (nop, [], [is_typeof(list)]),
'nodes': (nop, [], [is_typeof(list), not_empty]),
'variable_scope': (str, '', []),
'name_scope': (str, '', []),
'device_scope': (str, '', [])
}
self.parse(loader, node, params)
assert self.variable_scope or self.name_scope or self.device_scope, \
'at leaset each of variable, name, device should not be None'
def __repr__(self):
return 'With'
@classmethod
def from_yaml(cls, loader, node):
return cls(loader, node)
def create_node(self, nids, exclude_tags):
vs = lambda x: ( tf.variable_scope(x) if x else WithNone() )
ns = lambda x: ( tf.name_scope(x) if x else WithNone() )
dv = lambda x: ( tf.device(x) if x else WithNone() )
with vs(self.variable_scope), ns(self.name_scope), dv(self.device_scope):
for node in self.nodes:
nids = node.build(nids, exclude_tags)
return nids, None, None
!conv2dのノードクラスです。__init__()はWithと同様でYAMLのキーとそれに対応する変換型、初期値、アサーションを並べるだけです。
create_node()で実際にTensorFlowのノードを生成します。入力のノードはYAMLで指定したnidの辞書が引数として引き回されてくるのでそこから参照します。
class Conv2d(yaml.YAMLObject, Node):
yaml_tag = u'!conv2d'
def __init__(self, loader, node):
params = {
'nid': (str, None, []),
'tags': (nop, [], [is_typeof(list)]),
'source': (nop, None, [is_exist]),
'width': (int, 0, [is_greater_than(0)]),
'height': (int, 0, [is_greater_than(0)]),
'kernels_num': (int, 0, [is_greater_than(0)]),
'strides': (nop, [1,1,1,1], [is_typeof(list)]),
'b_init': (float, 0.1, []),
'padding': (str, 'SAME', []),
'name': (str, None, []),
'variable_scope': (str, None, [])
}
self.parse(loader, node, params)
def __repr__(self):
return 'Conv2d'
@classmethod
def from_yaml(cls, loader, node):
return cls(loader, node)
def create_node(self, nids, exclude_tags):
source_node = nids[self.source]
channels = source_node.get_shape()[3]
with tf.variable_scope(self.variable_scope) if self.variable_scope else WithNone():
w = weight_variable(
[self.height, self.width, channels,self.kernels_num], name="weight")
b = bias_variable([self.kernels_num], val=self.b_init, name="bias")
return nids, self.nid, tf.add( tf.nn.conv2d(
source_node, w, strides=self.strides, padding=self.padding), b, name=self.name)
以下、TensorFlowのノードクラスが続き、最後にロードメソッドですが大したことはしていません。
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Loader function
# ------------------------------------------------------------
def load(path):
graph= yaml.load(open(str(path)).read(), Loader=Loader)
if type(graph['root']) is not Root:
raise IOError("no Root in yaml file")
return graph['root']
こうしてYAMLをロードする準備が整ったのでパーサを使い始めます。
モデルの利用
基本はload()してbuild()するだけです。build()のfeed_dictにはYAMLで記述したnodes_requiredを指定する必要があります。これがこのモデルへの入力になります。
import yaml_loader as yl
MODEL_YAML_PATH='abies_model.yaml'
# ...
with tf.variable_scope(ROOT_VARIABLE_SCOPE):
print('build network')
graph_root = yl.load(MODEL_YAML_PATH)
graph_root.build(feed_dict={'root': batch_images})
build時にexclude_tagsを指定するとそのタグが付いている要素はTensorFlowのノードの生成を行いません。TensorBoardでネットワークの確認をするときに事前学習のための余計なノードを表示したくない時に使っています。
with tf.variable_scope(ROOT_VARIABLE_SCOPE):
graph_root = yl.load(MODEL_YAML_PATH)
tags = graph_root.build(feed_dict={'root': batch_images},
exclude_tags=['train'])
| trainタグのノード入り | trainタグのノードを除外したもの |
|---|---|
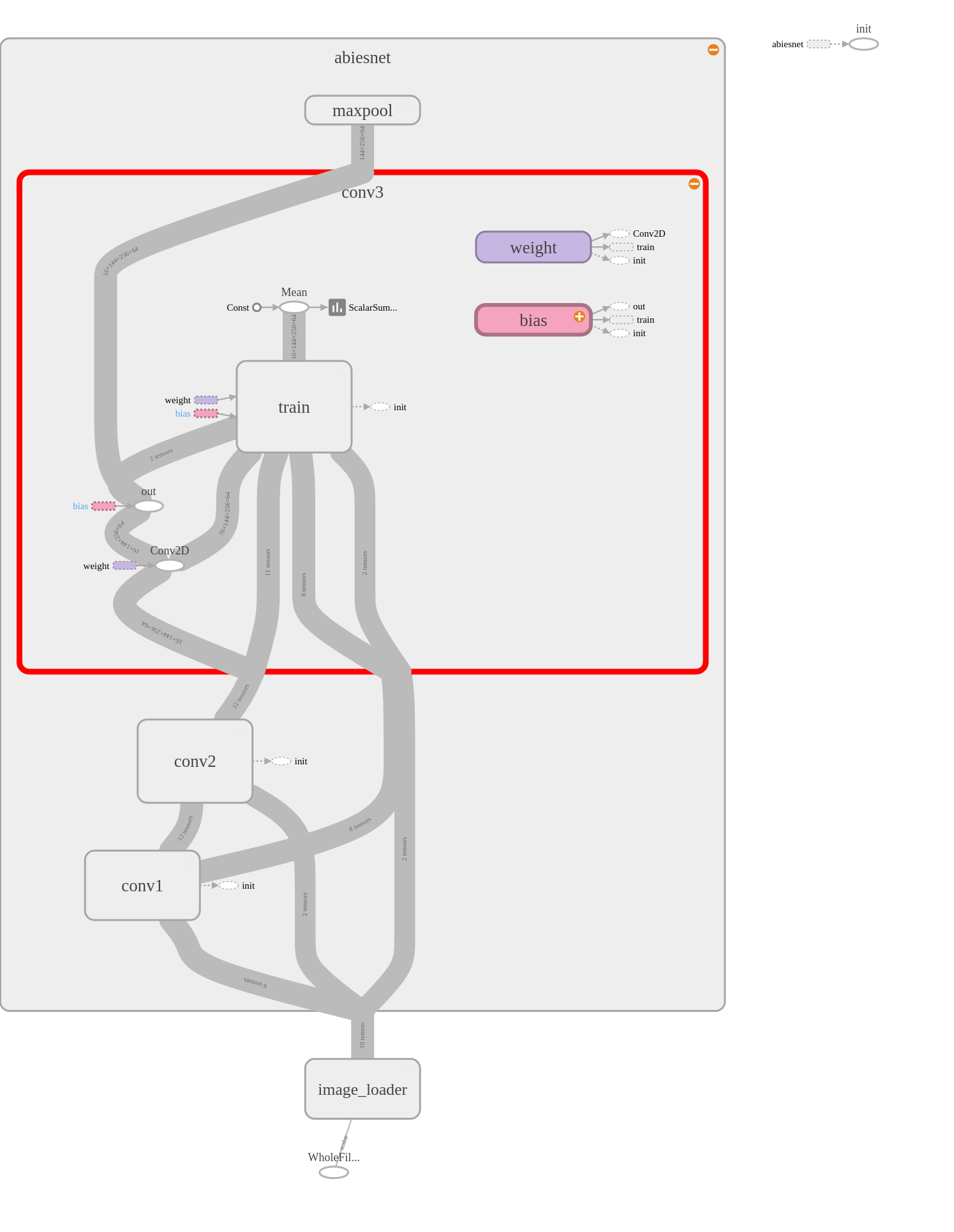 |
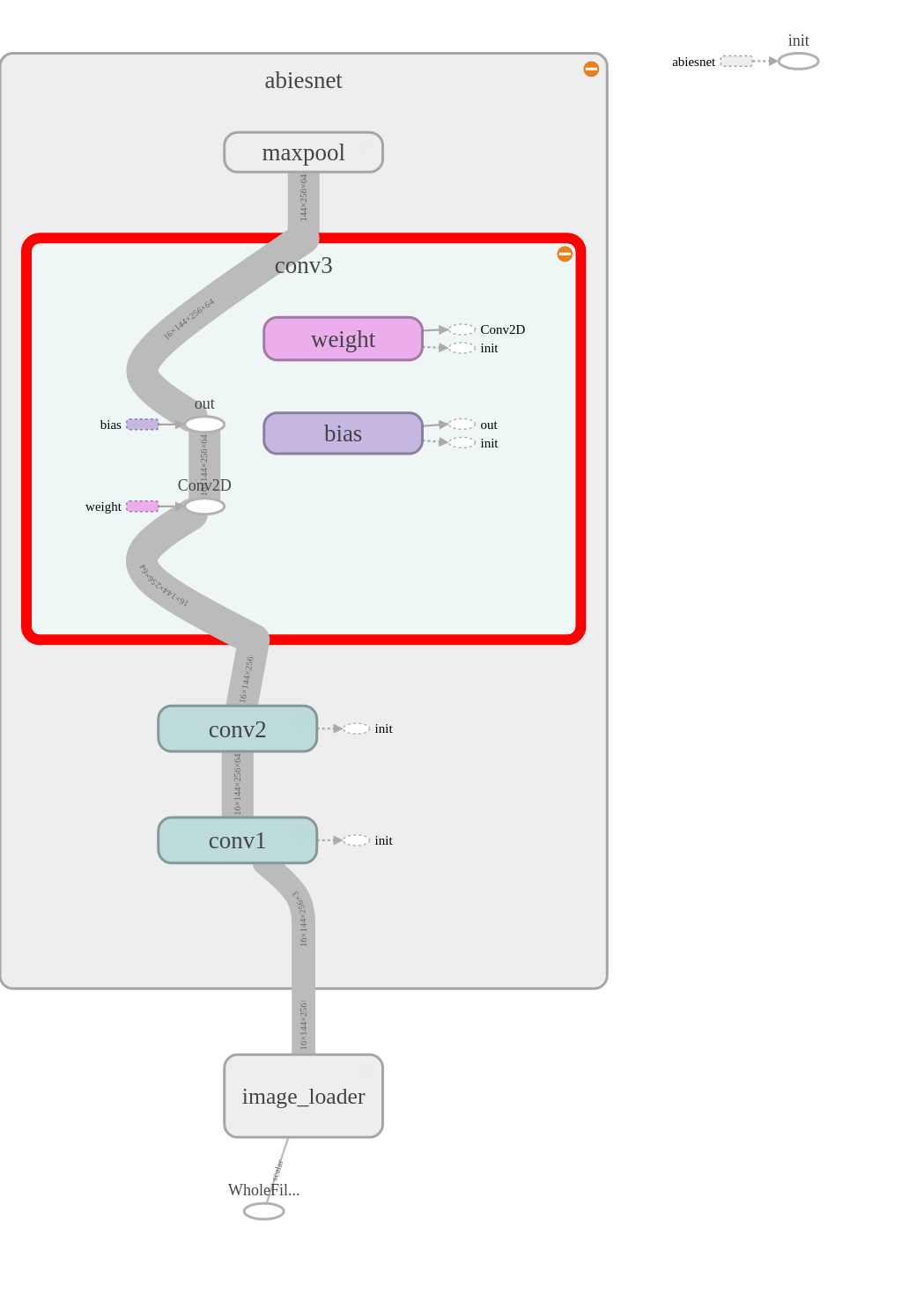 |
やってみた感想
以下感想
- 記述量は元のTensorFlowコードとあんまり変わってなくね?
- パラメータの見通しはよくなったかも
- ひとつのプロジェクトについて似たモデル、パラメータ違いの同一構造のモデルを複数のファイルにわけてバージョン管理できるのは良いかもしれない。pythonモジュールとしてコードで書いてしまうと差し替えやバージョン管理がグダグダになりがちなので。
- TensorFlowはすべての計算要素がグラフのノードになっているのでこういうユーティリティをシンプルな設計で書きやすいなと思った。
今後の課題
自分用に便利に育てていきます。
- TensorFlowの基本的なオペレーションについて自分が使用するものからどんどん追加していきたい
-
sourceに直接ノードを記述できるようにしたい。サマリー用の変換なんかはノードとして独立に書く必要が薄いので。 - yaml_loader.py の各クラスの記述をもうちょっと楽にできないものか。