mocha で始めるnode のテスト自動化
前回nodeunit を使ってテストの自動化を行いましたが、今回はMocha を使ってやってみます。
テストするプログラムは前回と同様、与えられた数値を2 で割って小数点以下を切り捨てた値を計算するプログラムをBDD・テストファーストで作成していくプロセスを例に解説していきます。
- 前回記事: nodeunit で始めるNodejs の単体テスト自動化
環境構築
実施環境
今回は以下の環境で手順を実施しました。
- システム構成
| OS | Ubuntu 15.10 |
|---|---|
| Node | v0.10.25 |
| mocha | 2.4.5 |
| mocha-sinon | 1.1.5 |
| chai | 3.5.0 |
ディレクトリ構成は以下のようにします。
nodeprj/ // <- ワークディレクトリ
+--lib/
| +--divided.js // <- テスト対象のプログラム
+--test/
+--test-divided.js // <- divided.js をテストするプログラム
予めディレクトリを作成しておきます。
$ mkdir -p nodeprj
$ cd nodeprj
$ mkdir {lib,test}
パッケージのインストール
mocha 及びそれに関するパッケージをインストールします。
$ sudo npm install -g mocha
$ sudo npm install -g chai
$ sudo npm install -g mocha-sinon
インストール後、バージョンを確認します。
$ mocha --version
2.4.5
NODE_PATH の設定
アサーションライブラリchai を使用するためにNODE_PATH 環境変数を予め設定しておくようにします。
$ export NODE_PATH=/usr/local/lib/node_modules
上記のコマンドを~/.bashrc ファイルなどに予め記載しておいてください。
代替方法として、~/.node_libraries シンボリックリンクを作成し、/usr/local/lib/node_modules ディレクトリにリンクさせることでも対応可能です。
テストの実施
テストの概要
本セクションでは、次のようなテスト方法について、実際の簡単なプログラムをテストすることで説明していきます。
- 同期的な処理のテスト(基本的なテスト)
- 例外がスローされるかどうかの処理のテスト
- 非同期な処理のテスト
- hook を使ったテストコードのリファクタリング
同期的な処理のテスト(基本的な計算処理のテスト)
test/test-divided.js ファイルを新規に作成し、以下のプログラムを作成します。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
});
});
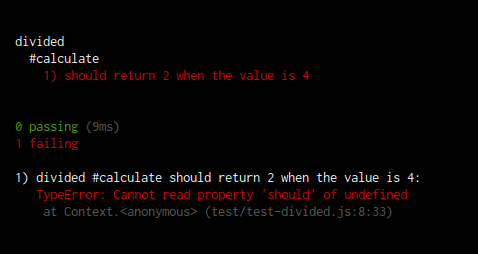
テストプログラムを作成したらmocha コマンドを実行してテストをしてみましょう。
$ mocha
module.js:340
throw err;
^
Error: Cannot find module '../lib/divided'
at Function.Module._resolveFilename (module.js:338:15)
......
at node.js:902:3
すると上記のように../lib/divided モジュールが見つからないため、テストがエラーとなって終了しました。
それではlib/divided.js ファイルを作成し、calculate メソッドを実装してみましょう。
/** 与えられた値を2 で割って小数点以下を切り捨てた結果を返す関数 */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
};
上記のようにファイルにコードを記載したら、もう一度mocha コマンドを実行してみます。
$ mocha
すると、想定した結果が2 であるのに対し、undefined が返ってきているためエラーとなっています。 もう一度divided.js ファイルを開き処理を追加してみましょう。
/** 与えられた値を2 で割って小数点以下を切り捨てた結果を返す関数 */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
return num / 2;
};
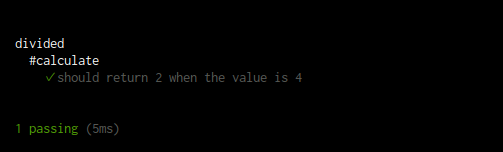
上記のコードを作成したらmocha コマンドを再度実行してみます。
$ mocha
テストに成功しました。
それでは次のテストとして、計算結果が割り切れなかった場合に小数点以下を切り捨てられうかどうかのテストを追加してみます。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
var divided = require('../lib/divided');
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
it('should return 1 when the value is 3', function() {
divided.calculate(3).should.equal(1);
});
});
});
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
1) should return 1 when the value is 3
1 passing (9ms)
1 failing
1) divided #calculate should return 1 when the value is 3:
AssertionError: expected 1.5 to equal 1
+ expected - actual
-1.5
+1
at Context.<anonymous> (test/test-divided.js:11:41)
すると上記のように、1 が返ることを想定していたところ、1.5 が返ってきたためエラーとなっています。
上記結果を参考に、プログラムに小数点以下を切り捨てる処理を追加します。
/** This is a function return a half of parameter, and round it to zero decimal places. */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
return Math.floor(num / 2);
};
mocha を実行します。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
2 passing (6ms)
これで小数点以下を切り捨てる処理の実装は完了です。
should 記法とexpect 記法
chai ライブラリを使用することで、アサーション処理をshould で記載する方法とexpect で記載する方法があります。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should()
, expect = chai.expect;
// ......
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2); // should による記法
expect(divided.calculate(4)).to.equal(2); // expect による記法
-
should 記法
-
expect 記法
例外を判定するテストを作成する(数値じゃないものが渡された時に例外を投げる処理のテスト)
数値以外の値がメソッドの引数に渡されたら例外を投げるメソッドのテストケースを作成します。
例外がスローされるかどうかのテストケースを実装する場合はアサーションライブラリChai の構文should.Throw を使用します。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
var divided = require('../lib/divided');
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
it('should return 1 when the value is 3', function() {
divided.calculate(3).should.equal(1);
});
it('should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers', function() {
(divided.calculate).should.throw(Error);
(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).should.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).should.throw(Error, / numeric /);
(function() {divided.calculate([])}).should.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
//// expect-style sentences are below.
// var expect = chai.expect;
// expect(divided.calculate).to.throw(Error);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).to.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
// expect(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).to.throw(Error, / numeric /);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate([])}).to.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
});
});
});
ここで注意したいのは、should.throw 内部ではtru/catch を使って例外の判定を行っているので、実行可能なメソッドを渡すようにしてください。
divided.calculate().should.throw(Error); と書いても想定したとおりにテストが行われないので注意してください。
それでは準備ができたらテストを実行します。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
1) should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
2 passing (9ms)
1 failing
1) divided #calculate should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers:
AssertionError: expected [Function] to throw Error
at Context.<anonymous> (test/test-divided.js:14:45)
想定した例外がスローされていないためテストが失敗しています。
lib/divided.js に数値以外の値が指定されたら例外をスローする処理を追加します。
/** This is a function return a half of parameter, and round it to zero decimal places. */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
if (typeof num !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Type of numeric is expected.');
}
return Math.floor(num / 2);
};
テストを再実行します。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
3 passing (7ms)
成功しました。
非同期処理のテストをする(標準入力から値を受け取ってコンソールに出力すること)
非同期で標準入力から値を読み込むプログラムをテストします。
今回は標準入力から値を受け取り、計算結果をconsole.log で結果をコンソールに出力するプログラムのテストケースを追記します。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
var divided = require('../lib/divided');
var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter;
require('mocha-sinon');
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
it('should return 1 when the value is 3', function() {
divided.calculate(3).should.equal(1);
});
it('should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers', function() {
(divided.calculate).should.throw(Error);
(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).should.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).should.throw(Error, / numeric /);
(function() {divided.calculate([])}).should.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
//// expect-style sentences are below.
// var expect = chai.expect;
// expect(divided.calculate).to.throw(Error);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).to.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
// expect(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).to.throw(Error, / numeric /);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate([])}).to.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
});
});
describe('#read', function() {
it('should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin', function(done) {
var ev = new EventEmitter();
var _console_log = console.log;
this.sinon.stub(console, 'log');
process.openStdin = this.sinon.stub().returns(ev);
divided.read();
ev.emit('data', '8');
console.log.calledOnce.should.be.true;
console.log.calledWith('result: 4').should.be.true;
//// expect-style sentences are below.
//var expect = chai.expect;
//expect(console.log.calledOnce).to.be.true;
//expect(console.log.calledWith('result: 4')).to.be.true;
console.log = _console_log;
done();
});
});
});
上記のサンプルコードでは、EventEmitter を使用してdata イベントを発生させることにより、標準入力をエミュレートしています。
divided は、この後記載しますが、標準入力から与えられた8 を2 で割って標準出力にresult: 4 と出力されることを想定しています。
また、mocha-sinon を使用し、stub を定義し、console.log メソッドが呼ばれたかどうかをチェックするようにしています。
stub (console.log) が呼ばれたかどうかをチェックするにはcalledOnce の値を確認し、どのような引数を使って呼ばれたかを確認するにはcalledWith('string') を使用することで確認することができます。
それではテストを実行してみましょう。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
#read
3 passing (14ms)
1 failing
1) divided #read should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin:
TypeError: Object #<Object> has no method 'read'
at Context.<anonymous> (test/test-divided.js:37:21)
lib/divided.js のread メソッドが定義されていないためテストに失敗しました。lib/divided.js にread メソッドを追加していきましょう。
/** 与えられた値を2 で割って小数点以下を切り捨てた結果を返す関数 */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
if (typeof num !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Type of numeric is expected.');
}
return Math.floor(num / 2);
};
/** 標準入力から値を受け取り、計算結果を返すメソッド */
exports.read = function() {
var stdin = process.openStdin();
stdin.on('data', function(chunk) {
var param = parseFloat(chunk);
var result = exports.calculate(param);
console.log('result: ' + result);
});
};
再度テストを実行してみます。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
#read
✓ should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin
4 passing (13ms)
テストに成功しました。
非同期処理に例外をスローする処理を追加する
標準入力から値を受け取り、数値以外のものが渡された場合に例外をキャッチし、エラーメッセージが表示されるという要件を追加します。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
var divided = require('../lib/divided');
var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter;
require('mocha-sinon');
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
it('should return 1 when the value is 3', function() {
divided.calculate(3).should.equal(1);
});
it('should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers', function() {
(divided.calculate).should.throw(Error);
(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).should.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).should.throw(Error, / numeric /);
(function() {divided.calculate([])}).should.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
//// expect-style sentences are below.
// var expect = chai.expect;
// expect(divided.calculate).to.throw(Error);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).to.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
// expect(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).to.throw(Error, / numeric /);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate([])}).to.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
});
});
describe('#read', function() {
it('should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin', function(done) {
var ev = new EventEmitter();
var _console_log = console.log;
this.sinon.stub(console, 'log');
process.openStdin = this.sinon.stub().returns(ev);
divided.read();
ev.emit('data', '8');
console.log.calledOnce.should.be.true;
console.log.calledWith('result: 4').should.be.true;
//// expect-style sentences are below.
//var expect = chai.expect;
//expect(console.log.calledOnce).to.be.true;
//expect(console.log.calledWith('result: 4')).to.be.true;
console.log = _console_log;
done();
});
it('should print "Type of numeric is expected." when the value is not a numeric', function(done) {
var ev = new EventEmitter();
var _console_log = console.log;
this.sinon.stub(console, 'log');
process.openStdin = this.sinon.stub().returns(ev);
divided.read();
ev.emit('data', 'abc');
console.log.calledOnce.should.be.true;
console.log.calledWithMatch('Type of numeric is expected.').should.be.true;
console.log = _console_log;
done();
});
});
});
内部で例外をスローして'Type of numeric is expected.' が表示されることを想定しています。
ではテストを実行して見ましょう。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
#read
✓ should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin
4 passing (17ms)
1 failing
1) divided #read should print "Type of numeric is expected." when the value is not a numeric:
AssertionError: expected false to be true
at Context.<anonymous> (test/test-divided.js:62:82)
例外をハンドリングする処理がまだ追加されていないためエラーとなりました。
例外をスローする処理を追加していきます。
/** 与えられた値を2 で割って小数点以下を切り捨てた結果を返す関数 */
exports.calculate = function(num) {
if (typeof num !== 'number' || num !== num) { // <- NaN を判定する条件をこっそり追加しています…(^^;)
throw new Error('Type of numeric is expected.');
}
return Math.floor(num / 2);
};
/** 標準入力から値を受け取り、計算結果を返すメソッド */
exports.read = function() {
var stdin = process.openStdin();
stdin.on('data', function(chunk) {
var param = parseFloat(chunk);
try {
var result = exports.calculate(param);
console.log('result: ' + result);
} catch(e) {
console.log(e.toString());
}
});
};
それでは再度テストを実行してみましょう。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
#read
✓ should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin
✓ should print "Type of numeric is expected." when the value is not a numeric
5 passing (16ms)
上記のようになればテストは成功です。
フック(hook)を使ったテストケース前後に処理を定義する(before(), after(), beforeEach(), afterEach())
hook 機能を利用することでテストの開始、終了時及び各テストケースの開始、終了時に処理を呼び出すことができるようになります。
mocha で使用できるhook としては以下のようなものがあります。
- mocha で使用できるhook 一覧
| beforeEach() | 各テストケースが実行される直前に呼ばれる |
|---|---|
| afterEach() | 各テストケースが実行された直後に呼ばれる |
| before() | テスト全体が実行される前に呼ばれる |
| after() | テスト全体が実行された後に呼ばれる |
実装例は次のようになります。
describe('divided', function() {
before(function() {
// ......
});
after(function() {
// ......
});
beforeEach(function() {
// ......
});
afterEach(function() {
// ......
});
// ......
});
それでは今までのテストをこれらの機能を使って各テストケースが開始されるタイミングでstub を初期化する処理を実行させてみましょう。
before(), after(), beforeEach(), afterEach() を追加し、整理したものが以下のようになります。
var chai = require('chai')
, should = chai.should();
var divided = require('../lib/divided');
var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter;
require('mocha-sinon');
describe('divided', function() {
describe('#calculate', function() {
it('should return 2 when the value is 4', function() {
divided.calculate(4).should.equal(2);
});
it('should return 1 when the value is 3', function() {
divided.calculate(3).should.equal(1);
});
it('should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers', function() {
(divided.calculate).should.throw(Error);
(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).should.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).should.throw(Error, / numeric /);
(function() {divided.calculate([])}).should.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
//// expect-style sentences are below.
// var expect = chai.expect;
// expect(divided.calculate).to.throw(Error);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate(null)}).to.throw(Error, 'Type of numeric is expected.');
// expect(function() {divided.calculate("abc")}).to.throw(Error, / numeric /);
// expect(function() {divided.calculate([])}).to.throw(Error, /^Type of numeric /);
});
});
describe('#read', function() {
var _console_log;
var _process_openStdin;
var ev;
before(function() {
_console_log = console.log;
_process_openStdin = process.openStdin;
});
after(function() {
console.log = _console_log;
process.openStdin = _process_openStdin;
});
beforeEach(function() {
ev = new EventEmitter();
this.sinon.stub(console, 'log');
process.openStdin = this.sinon.stub().returns(ev);
});
afterEach(function() {
});
it('should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin', function(done) {
divided.read();
ev.emit('data', '8');
console.log.calledOnce.should.be.true;
console.log.calledWith('result: 4').should.be.true;
//// expect-style sentences are below.
//var expect = chai.expect;
//expect(console.log.calledOnce).to.be.true;
//expect(console.log.calledWith('result: 4')).to.be.true;
console.log = _console_log;
done();
});
it('should print "Type of numeric is expected." when the value is not a numeric', function(done) {
process.openStdin = this.sinon.stub().returns(ev);
divided.read();
ev.emit('data', 'abc');
console.log.calledOnce.should.be.true;
console.log.calledWithMatch('Type of numeric is expected.').should.be.true;
console.log = _console_log;
done();
});
});
});
テストを実行します。
divided
#calculate
✓ should return 2 when the value is 4
✓ should return 1 when the value is 3
✓ should throw exceptions when the value are other than numbers
#read
✓ should print "result: 4" when the value is 8 that given from the stdin
✓ should print "Type of numeric is expected." when the value is not a numeric
5 passing (15ms)
上記のように結果が出力されれば、成功です。
以上で基本的なmocha の使い方の説明は完了です。
おまけ:Reporter 機能について
-R オプションを使用してレポーター機能を使用することができます。
レポーター機能はテストの結果をレポーターがレポートしてくれるという機能です。
例えば、mocha -R nyan と実行すると有名なあれがテスト結果をレポートをしてくれるようになります…。何が出現するかは実際に使ってみてのお楽しみです。
参考
-
mocha
-
How To Use Mocha With Node.js For Test-Driven Development to Avoid Pain and Ship Products Faster
-
Chai Assertion Livrary
-
How Should I Throw
-
How to test event emitters in node
-
THE GREAT CHEATSHEET FOR Chai.js
-
how to unit test console output with mocha on nodejs