はじめに
細線化処理(骨格検出,Thinning,Skeletonization)は最も基本的な画像処理の1つですが,いくつかある方法の1つとしてHilditchの方法をC++で実装したのでメモ
Hilditchの細線化
注目画素 P0 の8近傍の画素 P1〜P8 を以下のように定義する.
| P(4) | P(3) | P(2) |
| P(5) | P(0) | P(1) |
| P(6) | P(7) | P(8) |
以下を定義
N_8 = \left\{ P_1, P_2, P_3, P_4, P_5, P_6, P_7, P_8 \right\}
N_{odd} = \left\{P_1, P_3, P_5, P_7 \right\}
また,画素 Pi (i=0...8) の階調値を B(Pi) (i=0...8) と表記する.ただし,ここで背景がその階調値を0, 前景画素の階調値を1とする.
原画像をラスタ走査し,ある注目画素 P0 (前景画素)が次の6つの条件を全て満たしたとき,画素 P0 の階調値を-1,すなわち B(P0)=-1 とする.
条件1:前景画素である
B(P_0) = 1
条件2:境界点である
\sum_{k \ni N_{odd}} \left\{ 1-|B(P_k)| \right\} \geq 1
条件3:端点を削除しない
\sum_{k \ni N_8} |B(P_k)| \geq 2
条件4:孤立点を削除しない
\sum_{k \ni N_8} C_k \geq 1, C_k = \left\{ \begin{array}{} 1 & for & B(P_k) = 1 \\ 0 & for & B(P_k) \neq 1 \end{array} \right\}
条件5:連結性を保存する
N^{8}_{C} (P_0) = 1, WHERE, N^{8}_C (P_0) = \sum_{k \ni N_{odd}} \left\{D(P_k)-D(P_k) D(P_{k+1}) D(P_{k+2}) \right\}
条件6:線幅2の線分の片側だけを削除する
全ての n (n = 0...8) に対して,次のいずれかが成り立つ.
(i) \hspace{10pt} B(P_n) \neq -1 \\
(ii) \hspace{10pt} B(P_n) = 0, THAN, N^{8}_{C} = 1
この処理を原画像中の全ての前景画素について行った後,階調値が-1の全ての画素の階調値を0(背景画素)にした後,前景がその条件を調べる段階に戻って処理を繰り返す.階調値が-1に変更される画素がなくなった時点で処理を終了する.
実装
/**
* @brief Thinning (Hilditxh method)
*
* @param src Source image pixels pointer (depth: 8UC)
* @param dst Output image pixels pointer (dspth: 8UC)
* @param w Source image width
* @param h Source image height
*/
void hilditchThinning(const unsigned char* src, unsigned char* dst, int w, int h)
{
int offset[9][2] = {{0,0}, {1,0}, {1,-1}, {0,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,0}, {-1,1}, {0,1}, {1,1}};
int nOdd[4] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int b[9];
int px, py;
bitset<6> condition;
memcpy(dst, src, w * h);
int path = 1;
int counter;
auto funcNc8 = [&nOdd](int *b)
{
array<int, 10> d;
int j;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; ++i)
{
j = i;
if (i == 9) j = 1;
if (abs( *(b + j)) == 1)
d[i] = 1;
else
d[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
j = nOdd[i];
sum = sum + d[j] - d[j] * d[j+1] * d[j+2];
}
return sum;
};
cout << "start thinning " << endl;
clock_t beginTime = clock();
do {
cout << ".";
counter = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < h; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < w; ++x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
{
b[i] = 0;
px = x + offset[i][0];
py = y + offset[i][1];
if (px >= 0 && px < w && py >= 0 && py < h)
{
int idx = w * py + px;
if (dst[idx] == 255)
{
b[i] = 1;
}
else if (dst[idx] == 127)
{
b[i] = -1;
}
}
}
condition.reset();
// Condition 1
if (b[0] == 1) condition.set(0, true);
// Condition 2
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
sum = sum + 1 - abs(b[nOdd[i]]);
}
if (sum >= 1) condition.set(1, true);
// Condition 3
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i)
{
sum = sum + abs(b[i]);
}
if (sum >= 2) condition.set(2, true);
// Condition 4
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i)
{
if (b[i] == 1) ++sum;
}
if (sum >= 1) condition.set(3, true);
// Condition 5
if (funcNc8(b) == 1) condition.set(4, true);
// Condition 6
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i)
{
if (b[i] != -1)
{
++sum;
}
else {
int copy = b[i];
b[i] = 0;
if (funcNc8(b) == 1) ++sum;
b[i] = copy;
}
}
if (sum == 8) condition.set(5, true);
// Final judgement
if (condition.all())
{
int idx = y * w + x;
dst[idx] = 127;
++counter;
}
}
}
if (counter != 0)
{
for (int y = 0; y < h; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < w; ++x)
{
int idx = y * w + x;
if (dst[idx] == 127)
{
dst[idx] = 0;
}
}
}
}
++path;
}
while (counter != 0);
clock_t endTime = clock() - beginTime;
cout << " Done! Time: " << (double)(endTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << " sec, Num Path: " << path << endl;
}
使い方
第一引数に予め読み込んだ画像のピクセル(unsigned char, 8bit, single channel),第二引数は同じ型の出力画像ピクセル,第三,第四引数に入力画像の横幅,縦幅を入れます.
計算結果
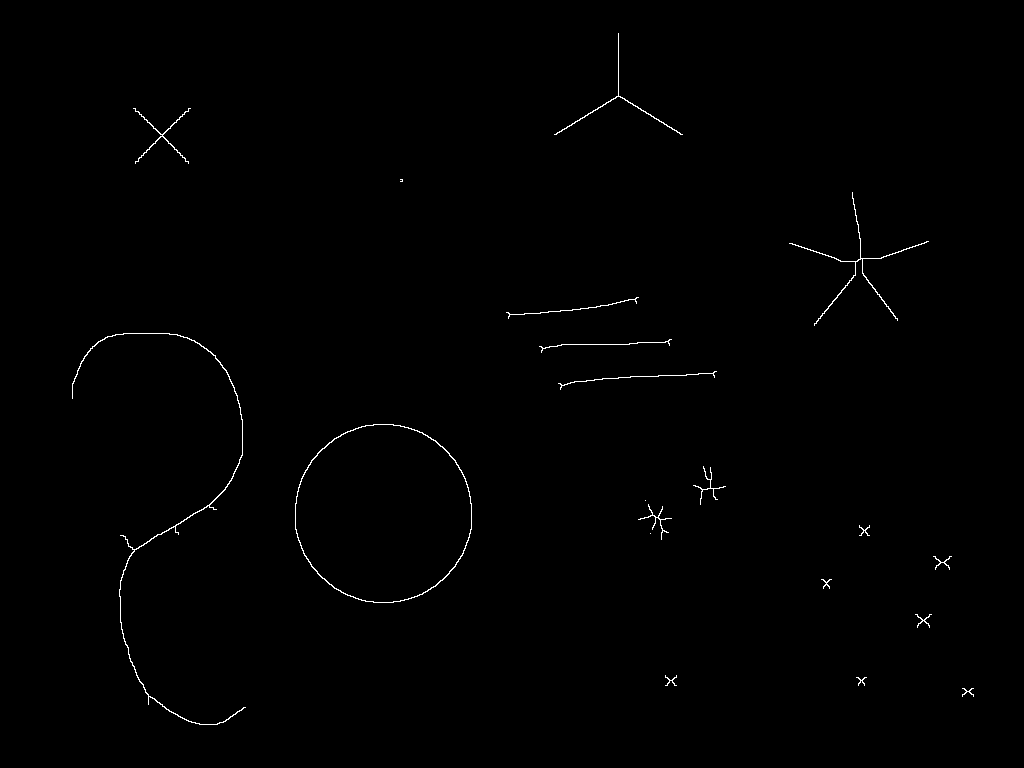
入力画像
出力画像
既知の問題としては真円がX状になったり,「ひげ」が残ったりすることがあり,目的によってはこれらをどうするか悩みどころだったりはします.
あと,上記のコードですが,計算そのものの問題でもありますが結構時間かかります.上の画像でも10秒ぐらいかかりました.なのでリアルタイムな実用は難しいですね.
細線化は他にもいろんな方法がありますが,時間があれば書きます.