デートコースを決めよう
彼女と遊園地に行くことになりました。彼女の満足度を最大化するには、どのように遊園地の施設を回ったらよいでしょうか?ただし、彼女の門限があるので、遊園地には200分しかいられません。
このような問題を組合せ最適化で解くことができます。
ナップサック問題と巡回セールスマン問題に似ていますが、さっそく定式化してみましょう。
定式化
| 変数 | $x_{fr, to} \in \{0, 1\} ~ ~ \forall fr, to \in 施設$ | 施設$fr$から施設$to$に移動するかどうか(1) |
| $y_i ~ ~ \forall i \in 施設$ | 施設$i$の利用終了時刻(2) | |
| 目的関数 | $\sum_{fr, to \in 施設}~~~{満足度_{fr} ~ x_{fr,to}}$ → 最大化 | 総満足度(3) |
| 制約条件 | $\sum_{fr,to \in 施設 | fr=i}~~~{x_{fr,to}} = 1 ~~~ i = S$ | 入り口は必ず通る(4) |
| $\sum_{fr,to \in 施設 | fr=i}~~~{x_{fr,to}} \le 1 ~~~ \forall i \in 施設 \setminus S$ | 利用回数は1回まで(4) | |
| $\sum_{fr,to \in 施設 | fr=i}~~~{x_{fr,to}} = \sum_{fr,to \in 施設 | to=i}~~~{x_{fr,to}} ~~~ \forall i \in 施設$ | 施設への入りと出が同じ(5) | |
| $y_{to} \ge TM_{fr,to}+TU_{to} ~~~ \forall fr,to \in 施設, fr=S$ | 施設利用終了時刻の設定(6) | |
| $y_{to} \ge TM_{fr,to}+TU_{to}+y_{fr} ~~~ \forall fr,to \in 施設, fr \ne S$ | 施設利用終了時刻の設定(6) | |
| $y_i ~~~ \le 200 ~~~ i=S$ | 滞在時間上限(7) |
ただし、$TM_{fr,to}$は、施設$fr$から$to$への移動時間、$TU_{to}$は、施設$to$での利用時間とします。また、制約条件(6)は、$x_{fr,to}$が1の場合のみ有効とします。
最初の施設Sは、遊園地の入り口とし、最後に入り口に戻ります。また、同じ施設は1度までとします。
Pythonで解く
JupyterのPython3.5で試してみましょう。
dockerが使えるなら、tsutomu7/jupyter または、tsutomu7/alpine-python:jupyter で実行できます。
準備
利用ライブラリをインポートし、描画の設定をします。
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np, pandas as pd, matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import OrderedDict
from pulp import *
from pulp.constants import LpConstraintEQ as EQ, LpConstraintLE as LE
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'IPAexGothic'
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 16
施設と移動時間の設定
n = 6
np.random.seed(2)
a = pd.DataFrame(OrderedDict([
('施設', ['S'] + [chr(65+i) for i in range(n-1)]),
('満足度', np.random.randint(50, 100, n)),
('利用時間', np.random.randint(3, 6, n) * 10),
]))
a.loc[0, a.columns[1:]] = 0
移動時間 = np.random.randint(1, 7, (n, n))
移動時間 += 移動時間.T # 対称行列にする
a
|施設|満足度|利用時間
:--|:--|--:|--:
0|S|0|0
1|A|65|30
2|B|95|50
3|C|58|40
4|D|72|40
5|E|93|50
OrderedDictを使うと、列の順番を固定できます。
定式化して解く
def solve_route(a, limit):
n = a.shape[0]
m = LpProblem(sense=LpMaximize)
b = pd.DataFrame([(i, j, LpVariable('x%s%s'%(i,j), cat=LpBinary))
for i in a.施設 for j in a.施設], columns=['fr','to','x']) # (1)
b['移動時間'] = 移動時間.flatten()
b = b.query('fr!=to')
y = {i:LpVariable('y%s'%i) for i in a.施設} # その施設の利用終了時刻(2)
m += lpDot(*pd.merge(b, a, left_on='fr', right_on='施設')
[['x', '満足度']].values.T) # 目的関数(3)
for i in a.施設:
m += LpConstraint(lpSum(b[b.fr==i].x), EQ if i=='S' else LE, rhs=1) # (4)
m += lpSum(b[b.fr==i].x) == lpSum(b[b.to==i].x) # (5)
M = b.移動時間.sum() + a.利用時間.sum() # 十分大きな値
for _, r in b.iterrows():
m += y[r.to] >= r.移動時間 + a[a.施設==r.to].利用時間.sum() \
+ (0 if r.fr=='S' else y[r.fr]) - (1-r.x)*M # (6)
m += y['S'] <= limit # (7)
m.solve()
return value(m.objective), b[b.x.apply(value)>0]
objv, rs = solve_route(a, 200)
print('総満足度 = %g'%objv)
rs
>>>
総満足度 = 311
|fr|to|x|移動時間
:--|:--|:--|:--|--:
1|S|A|xSA|8
11|A|E|xAE|5
12|B|S|xBS|10
20|C|B|xCB|2
33|E|C|xEC|4
入り口(S)から A -> E -> C -> B と回ると、総満足度を最大の311にできることが分かります。
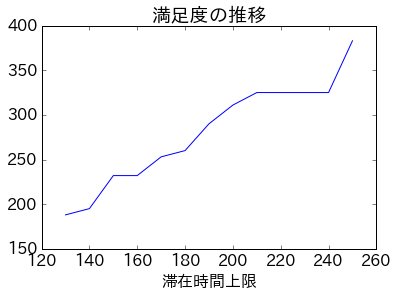
滞在時間と満足度の推移を見てみる
%%time
rng = np.linspace(250, 130, 13)
rsl = [solve_route(a, i)[0] for i in rng]
plt.title('満足度の推移')
plt.xlabel('滞在時間上限')
plt.plot(rng, rsl);
>>>
CPU times: user 1.11 s, sys: 128 ms, total: 1.24 s
Wall time: 6.47 s
一緒にいる時間が長いほど満足できるようです。
この問題は、混合整数最適化問題とよばれる難しい問題になります。施設数が増えると急に解けなくなりますので、その場合は、近似解法を使うなどの工夫が必要になります。
以上