目的
近年、無線通信に対する需要が年々増加している。
一方で、無線通信の活用に関してはQiitaにも取り上げられているが、IEEE802.11についての記事はとても少ない(2017年7月現在、10本程度)。
mac80211についての知識を自分の中で整理することが主な目的であるが、無線通信の下層に興味を持ってくれる人が一人でも増えてくれれば幸いです。
mac80211の背景
無線LANを用いたアプリケーションにはhostapdやwpa_supplicantなどある。
これらを用いることでLinux端末のAP化やSTA化が可能である。
hostapdやwpa_supplicantは、mac80211やcfg80211というカーネルを使用している。
mac80211やcfg80211が、NICやWi-Fiドングル(ハードウェア)とアプリケーション(ユーザ空間)の橋渡しをしている(正確に言えば間にドライバが存在する)。
mac80211は文字通り、IEEE802.11のMAC層部分を担当している。従来のシステムではMAC層の多くの処理はハードウェアが行ってきた。近年はAtherosなどを中心に、IEEE802.11で規格化された多くの処理をソフトウェアで処理をするような流れになっている。
mac80211の構成
下図にLinuxで使われているカーネルの構成を示す[1]。(https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/_media/en/developers/documentation/mac80211.pdf)
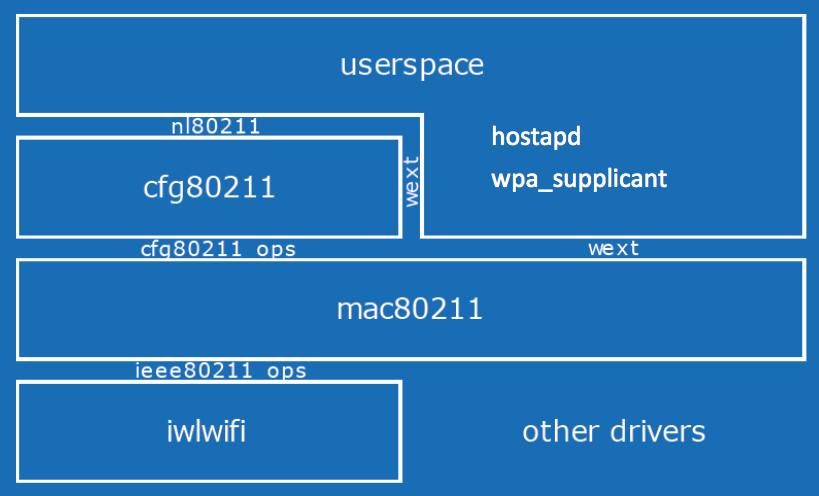
基本的には無線LANに関する情報は一旦mac80211に渡される。
mac80211の例
もしコマンドライン上で、"iw dev wlan0 info"と入力すれば接続しているAPの情報(受信電力やMACアドレスなど)が表示されるはずである。
これらの情報は、net/mac80211.h内で定義されている構造体ieee80211_bss_confに格納されている。この構造体には自分が接続しているBSSの情報が格納されている。格納されている変数はとても多いためここでは一部のみを紹介する。
/**
* struct ieee80211_bss_conf - holds the BSS's changing parameters
*
* This structure keeps information about a BSS (and an association
* to that BSS) that can change during the lifetime of the BSS.
* (省略)
* @sync_tsf: last beacon's/probe response's TSF timestamp (could be old
* as it may have been received during scanning long ago). If the
* HW flag %IEEE80211_HW_TIMING_BEACON_ONLY is set, then this can
* only come from a beacon, but might not become valid until after
* association when a beacon is received (which is notified with the
* %BSS_CHANGED_DTIM flag.). See also sync_dtim_count important notice.
* (省略)
* @bssid: The BSSID for this BSS
sync_tsfにはAPが送信するBeaconフレームに含まれているtimestampの情報が含まれている。
bssidには文字通りBSSIDに関する情報が含まれている。
ieee80211_bss_confには他にもAPの送信電力やBeaconフレームの送信間隔などの情報も含まれている。以下に構造体の構成を示す。
struct ieee80211_bss_conf {
const u8 *bssid;
/* association related data */
bool assoc, ibss_joined;
bool ibss_creator;
u16 aid;
/* erp related data */
bool use_cts_prot;
bool use_short_preamble;
bool use_short_slot;
bool enable_beacon;
u8 dtim_period;
u16 beacon_int;
u16 assoc_capability;
u64 sync_tsf;
u32 sync_device_ts;
u8 sync_dtim_count;
u32 basic_rates;
struct ieee80211_rate *beacon_rate;
int mcast_rate[NUM_NL80211_BANDS];
u16 ht_operation_mode;
s32 cqm_rssi_thold;
u32 cqm_rssi_hyst;
s32 cqm_rssi_low;
s32 cqm_rssi_high;
struct cfg80211_chan_def chandef;
struct ieee80211_mu_group_data mu_group;
__be32 arp_addr_list[IEEE80211_BSS_ARP_ADDR_LIST_LEN];
int arp_addr_cnt;
bool qos;
bool idle;
bool ps;
u8 ssid[IEEE80211_MAX_SSID_LEN];
size_t ssid_len;
bool hidden_ssid;
int txpower;
enum nl80211_tx_power_setting txpower_type;
struct ieee80211_p2p_noa_attr p2p_noa_attr;
bool allow_p2p_go_ps;
u16 max_idle_period;
bool protected_keep_alive;
};
ここではBSSの情報のみに触れたが、他にもMCS番号や帯域幅などの情報を持った構造体も定義されている。
受信側でのmac80211の簡単な流れ
上では主にmac80211.hに触れたが、mac80211には他にも多くのソースが含まれている。
フレームの送信受信に関しては、/net/mac80211/tx.cやrx.c。
他のAPの情報を調べるスキャンに関しては、/net/mac80211/scan.c。
MLME部分の処理を行う/net/mac80211/mlme.c。
本記事で全てを説明することはできないが、受信側での簡単な流れを説明する。
1. ドライバーがフレームを取得
2. 受信フレームをieee80211_rx()に渡す。mac80211に送る。このときドライバから受け取った情報をieee80211_rx_statusに格納する。
3. ieee80211_rx_dataをieee80211_prepare_and_rx_handle()に渡す。この中で受信したフレームの宛先のアドレスなどを確認し、受け入れるかどうかを判断する(ieee80211_accept_frame())。
4. その後、ieee80211_rx_handlers()に渡され、STA側で行なわれる様々な処理を行なう(ieee80211_rx_h_sta_process, ieee80211_rx_h_ctrlなど)。
以下に上で紹介した構造体ieee80211_rx_statusとieee80211_rx_dataを示す。
/**
* struct ieee80211_rx_status - receive status
*
* The low-level driver should provide this information (the subset
* supported by hardware) to the 802.11 code with each received
* frame, in the skb's control buffer (cb).
*
* @mactime: value in microseconds of the 64-bit Time Synchronization Function
* (TSF) timer when the first data symbol (MPDU) arrived at the hardware.
* @boottime_ns: CLOCK_BOOTTIME timestamp the frame was received at, this is
* needed only for beacons and probe responses that update the scan cache.
* @device_timestamp: arbitrary timestamp for the device, mac80211 doesn't use
* it but can store it and pass it back to the driver for synchronisation
* @band: the active band when this frame was received
* @freq: frequency the radio was tuned to when receiving this frame, in MHz
* This field must be set for management frames, but isn't strictly needed
* for data (other) frames - for those it only affects radiotap reporting.
* @signal: signal strength when receiving this frame, either in dBm, in dB or
* unspecified depending on the hardware capabilities flags
* @IEEE80211_HW_SIGNAL_*
* @chains: bitmask of receive chains for which separate signal strength
* values were filled.
* @chain_signal: per-chain signal strength, in dBm (unlike @signal, doesn't
* support dB or unspecified units)
* @antenna: antenna used
* @rate_idx: index of data rate into band's supported rates or MCS index if
* HT or VHT is used (%RX_FLAG_HT/%RX_FLAG_VHT)
* @nss: number of streams (VHT and HE only)
* @flag: %RX_FLAG_\*
* @encoding: &enum mac80211_rx_encoding
* @bw: &enum rate_info_bw
* @enc_flags: uses bits from &enum mac80211_rx_encoding_flags
* @rx_flags: internal RX flags for mac80211
* @ampdu_reference: A-MPDU reference number, must be a different value for
* each A-MPDU but the same for each subframe within one A-MPDU
* @ampdu_delimiter_crc: A-MPDU delimiter CRC
*/
struct ieee80211_rx_status {
u64 mactime;
u64 boottime_ns;
u32 device_timestamp;
u32 ampdu_reference;
u32 flag;
u16 freq;
u8 enc_flags;
u8 encoding:2, bw:3;
u8 rate_idx;
u8 nss;
u8 rx_flags;
u8 band;
u8 antenna;
s8 signal;
u8 chains;
s8 chain_signal[IEEE80211_MAX_CHAINS];
u8 ampdu_delimiter_crc;
};
struct ieee80211_rx_data {
struct napi_struct *napi;
struct sk_buff *skb;
struct ieee80211_local *local;
struct ieee80211_sub_if_data *sdata;
struct sta_info *sta;
struct ieee80211_key *key;
unsigned int flags;
/*
* Index into sequence numbers array, 0..16
* since the last (16) is used for non-QoS,
* will be 16 on non-QoS frames.
*/
int seqno_idx;
/*
* Index into the security IV/PN arrays, 0..16
* since the last (16) is used for CCMP-encrypted
* management frames, will be set to 16 on mgmt
* frames and 0 on non-QoS frames.
*/
int security_idx;
u32 tkip_iv32;
u16 tkip_iv16;
};
まとめ
今回はmac80211がどのようなことを行っているのかを簡単にまとめた。
本文では受信側についてしか触れていないが、今後送信側に関する内容も追記する予定である。
参考文献
[1] https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/_media/en/developers/documentation/mac80211.pdf
[2] mac80211のソースコード