前回記事ニューラルネットワークについてメモの続き
二層のニューラルネットワークを作り,MNISTを学習してみた.
ゼロから作るDeepLearningの第4章を参考
TwoLayerNet.py
import numpy as np
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size,output_size,weight_init_std=0.01):
#重みの初期化
self.params = {}
#784 * 50の重み行列
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size,hidden_size)
#50 * 10の重み行列
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size,output_size)
#バイアス,隠れ層の数だけ
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
#バイアス,出力層の数だけ
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def softmax(self,a):
c = np.max(a)
exp_a = np.exp(a - c)#オーバーフロー対策
sum_exp_a = np.sum(exp_a)
y = exp_a / sum_exp_a
return y
def _numerical_gradient_1d(self,f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
for idx in range(x.size):
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2*h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 値を元に戻す
return grad
def numerical_gradient(self,f, X):
if X.ndim == 1:
return self._numerical_gradient_1d(f, X)
else:
grad = np.zeros_like(X)
for idx, x in enumerate(X):
grad[idx] = self._numerical_gradient_1d(f, x)
return grad
def cross_entropy_error(self,y,t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1,t.size)
y = y.reshape(1,y.size)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(t * np.log(y)) / batch_size
def predict(self,x):
W1,W2 = self.params['W1'],self.params['W2']
b1,b2 = self.params['b1'],self.params['b2']
a1 = np.dot(x,W1) + b1 #a = Wx + b
z1 = self.sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(z1,W2) + b2
z2 = self.softmax(a2)
return z2
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return self.cross_entropy_error(y,t)
def gradient(self,x,t):
loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(x,t)
grads = {}
grads['W1'] = self.numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['W1'])
grads['W2'] = self.numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['W2'])
grads['b1'] = self.numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['b1'])
grads['b2'] = self.numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['b2'])
return grads
これに対して,MNISTのデータからミニバッチ学習(大きさ50)を500回行った.
LearningMNIST.py
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_mldata
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
mnist = fetch_mldata('MNIST original', data_home=".")
x_train = mnist['data'][:60000]
t_train = mnist['target'][:60000]
train_loss_list = []
# データの正規化(0<=x<=1)を行う
x_train = x_train.astype(np.float64)
x_train /= x_train.max()
# one-hotベクトルに変換
t_train = t_train.reshape(1, -1).transpose()
encoder = OneHotEncoder(n_values=max(t_train)+1)
t_train = encoder.fit_transform(t_train).toarray()
# hyper parameter
iters_num = 500
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
# 画像データが28x28のデータのため入力層が784,隠れ層が50,出力層がラベル数に合わせ10
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784,hidden_size=50,output_size=10)
for i in range(iters_num):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size,batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
grad = network.gradient(x_batch,t_batch)
for key in ('W1','W2','b1','b2'):
network.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
loss = network.loss(x_batch,t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
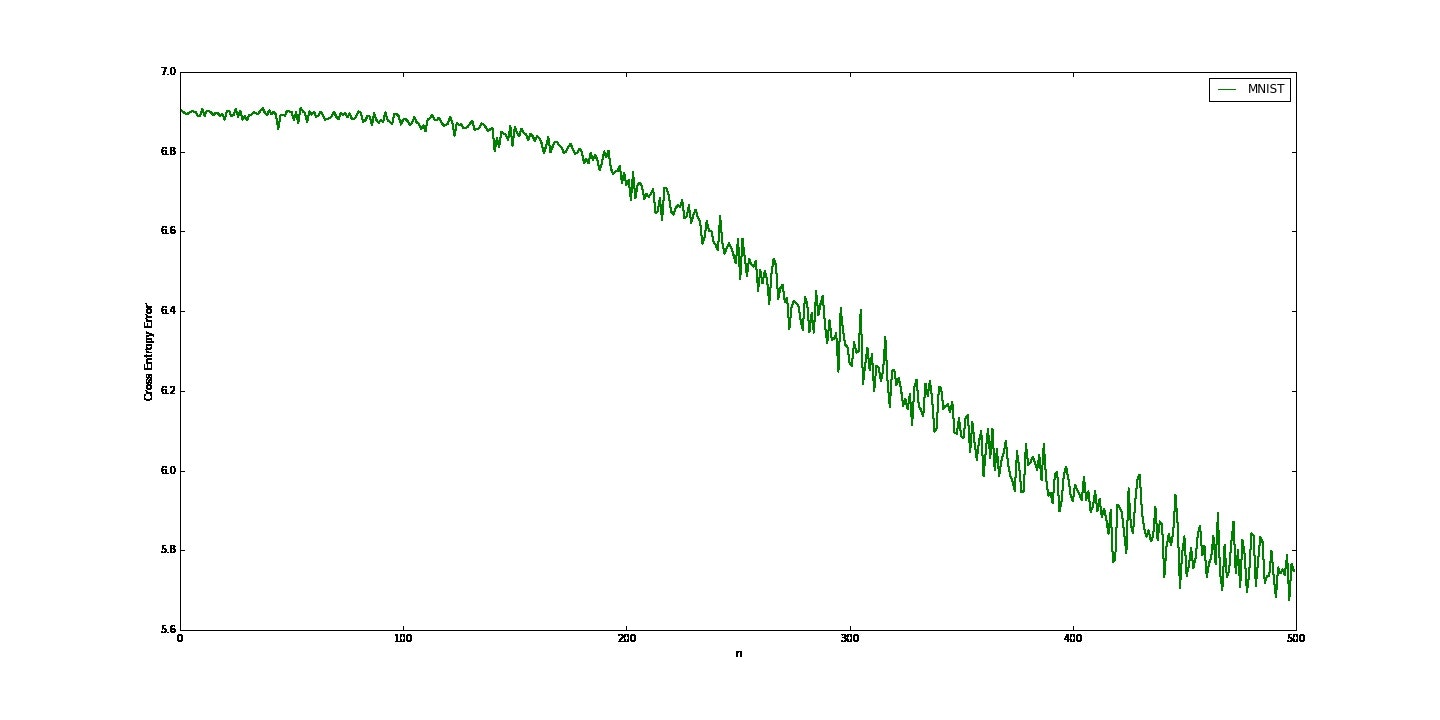
この結果が下のグラフ,縦軸が交差エントロピー誤差で横軸が学習の反復回数.
交差エントロピー誤差が減っている.
次回は,このニューラルネットワークの予測精度を確認する.