はじめに
詳しいことや他のパターンは**デザインパターンをJavaScriptとJavaでの実装を比較して理解する**に書いていきます。
JavaScriptの例はJavaのを見て書きました。
クラス型・プロトタイプ型、型付の強弱、アクセス修飾子など特徴の違いなどは活かしていません。
ご了承ください。
※JavaScriptの関数は第一級関数で動的な言語なので、Strategyパターンの必要性は低いです。
Strategy
strategyとは「戦略」という意味
問題を解くための戦略、すなわちアルゴリズムを他のアルゴリズムに交換することができる
同じ問題を別の方法で解くのを容易にするパターンがStrategyパターン
Javaでの実装
クラス図
コード
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("Usage: java Main randomseed1 randomseed2");
System.out.println("Example: java Main 314 15");
System.exit(0);
}
int seed1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int seed2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
Player player1 = new Player("Taro", new WinningStrategy(seed1));
Player player2 = new Player("Hana", new ProbStrategy(seed2));
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player1);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player2);
player1.lose();
player2.win();
} else {
System.out.println("Even...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
System.out.println("Total result:");
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println(player2.toString());
}
}
public interface Strategy {
public abstract Hand nextHand();
public abstract void study(boolean win);
}
import java.util.Random;
public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private boolean won = false;
private Hand prevHand;
public WinningStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
if (!won) {
prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return prevHand;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
won = win;
}
}
import java.util.Random;
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private int prevHandValue = 0;
private int currentHandValue = 0;
private int[][] history = {
{1, 1, 1,},
{1, 1, 1,},
{1, 1, 1,},
};
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handvalue = 0;
if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) {
handvalue = 0;
} else if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0] + history[currentHandValue][1]) {
handvalue = 1;
} else {
handvalue = 2;
}
prevHandValue = currentHandValue;
currentHandValue = handvalue;
return Hand.getHand(handvalue);
}
private int getSum(int hv) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum += history[hv][i];
}
return sum;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
if (win) {
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++;
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++;
}
}
}
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losecount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) {
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand() {
return strategy.nextHand();
}
public void win() {
strategy.study(true);
wincount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void lose() {
strategy.study(false);
losecount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even() {
gamecount++;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " + wincount + " wind, " + losecount + "lose" + "]";
}
}
public class Hand {
public static final int HANDVALUE_GUU = 0;
public static final int HANDVALUE_CHO = 1;
public static final int HANDVALUE_PAA = 2;
public static final Hand[] hand = {
new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_CHO),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA),
};
private static final String[] name = {
"グー", "チョキ", "パー",
};
private int handvalue;
private Hand(int handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handvalue) {
return hand[handvalue];
}
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h) {
return fight(h) == 1;
}
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h) {
return fight(h) == -1;
}
private int fight(Hand h) {
if (this == h) {
return 0;
} else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public String toString() {
return name[handvalue];
}
}
JavaScript
コード
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Strategy</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="Main.js"></script>
<script src="WinningStrategy.js"></script>
<script src="ProbStrategy.js"></script>
<script src="Player.js"></script>
<script src="Hand.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
MAIN = {};
MAIN.init = function() {
'use strict';
var player1 = new Player("Taro", new WinningStrategy());
var player2 = new Player("Hana", new ProbStrategy());
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
var nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
var nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
console.log(Hand.jankenName[nextHand1.handvalue], Hand.jankenName[nextHand2.handvalue]);
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
console.log("Winner:" + player1.name);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
console.log("Winner:" + player2.name);
player2.win();
player1.lose();
} else {
console.log("Even...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
console.log("Total result:");
console.log(player1.toString());
console.log(player2.toString());
}
window.addEventListener("load", MAIN.init);
var Player = function(name, strategy) {
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
this.wincount = 0;
this.losecount = 0;
this.gamecount = 0;
}
Player.prototype = {
constructor: "Player",
nextHand: function() {
return this.strategy.nextHand();
},
win: function() {
this.strategy.study(true);
this.wincount++;
this.gamecount++;
},
lose: function() {
this.strategy.study(false);
this.losecount++;
this.gamecount++;
},
even: function() {
this.gamecount++;
},
toString: function() {
return "[" + this.name + ":" + this.gamecount + " games, " + this.wincount + " wind, " + this.losecount + " lose" + "]";
}
}
var WinningStrategy = function() {
this.random = Math.floor(Math.random() * 3);
this.won = false;
this. prevHand;
}
WinningStrategy.prototype = {
constructor: "WinningStrategy",
nextHand: function() {
return Hand.getHand(this.random);
},
study: function(win) {
if (win) {
won = win;
}
}
};
var ProbStrategy = function() {
this.random = Math.floor(Math.random() * 3);
this.prevHandValue = 0;
this.currentHandValue = 0;
this.history = [
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1]
];
};
ProbStrategy.prototype = {
constructor: "ProbStrategy",
nextHand: function() {
let bet = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.getSum(this.currentHandValue));
let handvalue = 0;
if (bet < this.history[this.currentHandValue][0]) {
handvalue = 0;
} else if (bet < this.history[this.currentHandValue][0] + this.history[this.currentHandValue][1]) {
handvalue = 1;
} else {
handvalue = 2;
}
this.prevHandValue = this.currentHandValue;
this.currentHandValue = handvalue;
return Hand.getHand(handvalue);
},
getSum: function(hv) {
let sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum += this.history[hv][i];
}
return sum;
},
study: function(win) {
if (win) {
this.history[this.prevHandValue][(this.currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++;
this.history[this.prevHandValue][(this.currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++;
}
}
}
var Hand = function(handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
};
Hand.prototype = {
constructor: "Hand",
isStrongerThan: function(h) {
return this.fight(h) == 1;
},
fight(h) {
if (this == h) {
return 0;
} else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
};
Hand.HANDVALUE_GUU = 0;
Hand.HANDVALUE_CHO = 1;
Hand.HANDVALUE_PAA = 2;
Hand.hand = [
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_GUU),
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_CHO),
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_PAA),
];
Hand.jankenName = ["グー", "チョキ", "パー"];
Hand.getHand = function(handvalue) {
return Hand.hand[handvalue];
}
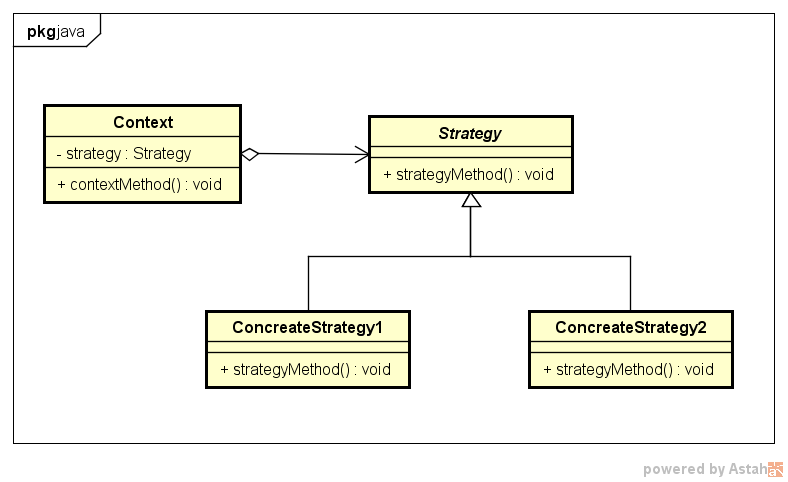
Decoratorパターンの登場人物
Strategy(戦略)の役
インタフェース(API)だけを定める
サンプルプログラム→Strategy(interface)
ConcreateStrategy(具体的戦略)の役
Strategy役のインタフェースを実装する役
具体的な戦略をプログラムする
サンプルプログラム→WinningStrategy(class)
ProbStrategy(class)
Context(文脈)の役
Strategy役を利用する役
ConcreateStrategy役を持っている
サンプルプログラム→player(class)
Decoratorパターンのクラス図
Decoratorパターンの必要性
基本的にはアルゴリズムをメソッドの中に書いてしまう
だが、Strategyパターンではアルゴリズムの部分を意識的に分離する
委譲によりアルゴリズムを利用することにより、
アルゴリズムの修正を行いたい場合はConcreateStrategyを修正
アルゴリズムの変更を行いたい場合はContextを修正すれば良い
アルゴリズムを分離することで動的に変更することも可能になる
Decoratorパターンの使い時
今日スマホで見たり、パソコンで見たりする状況があると思う
スマホのような非力なCPUとパソコンのような強力なCPUでアルゴリズムを使い分けたいときなど
Strategyパターンを利用することで可能にする
関連しているパターン
- Flyweightパターン
- Abstract Factoryパターン
- Stateパターン